- 快召唤伙伴们来围观吧
- 微博 QQ QQ空间 贴吧
- 文档嵌入链接
- 复制
- 微信扫一扫分享
- 已成功复制到剪贴板
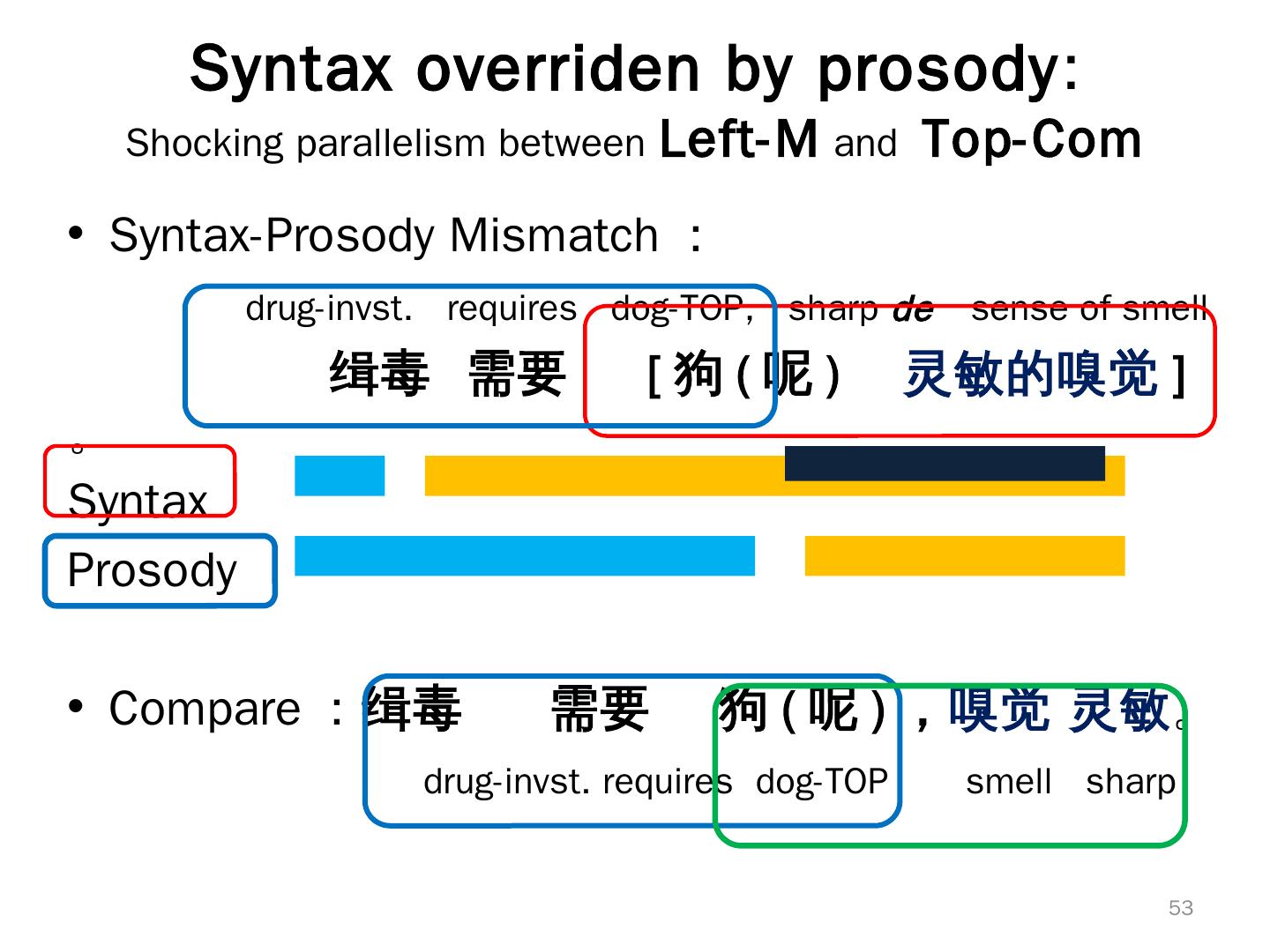
(呢),嗅觉灵敏
展开查看详情
1 .10 Dec 2013, Research Institute of Linguistics, HAS, Budapest, Hungary Topicalization as a prominent device in Chinese: With reference to relativization and complementation TANG Zhengda Associate Professor of Institute of Linguistics, Chinese Academy of Social Sciences Beijing, China
2 . Outlines • Iconicity • Topicalization & Complimentation as Subject • Topicality & Relativization Accessibility in Chinese • Topic within Nominal Phrases • Conclusion 2
3 . Iconicity : differing from similarity 3
4 . Iconicity: Model & Icon Amilyen az anya, olyan a lánya 有其父,必有其子 4
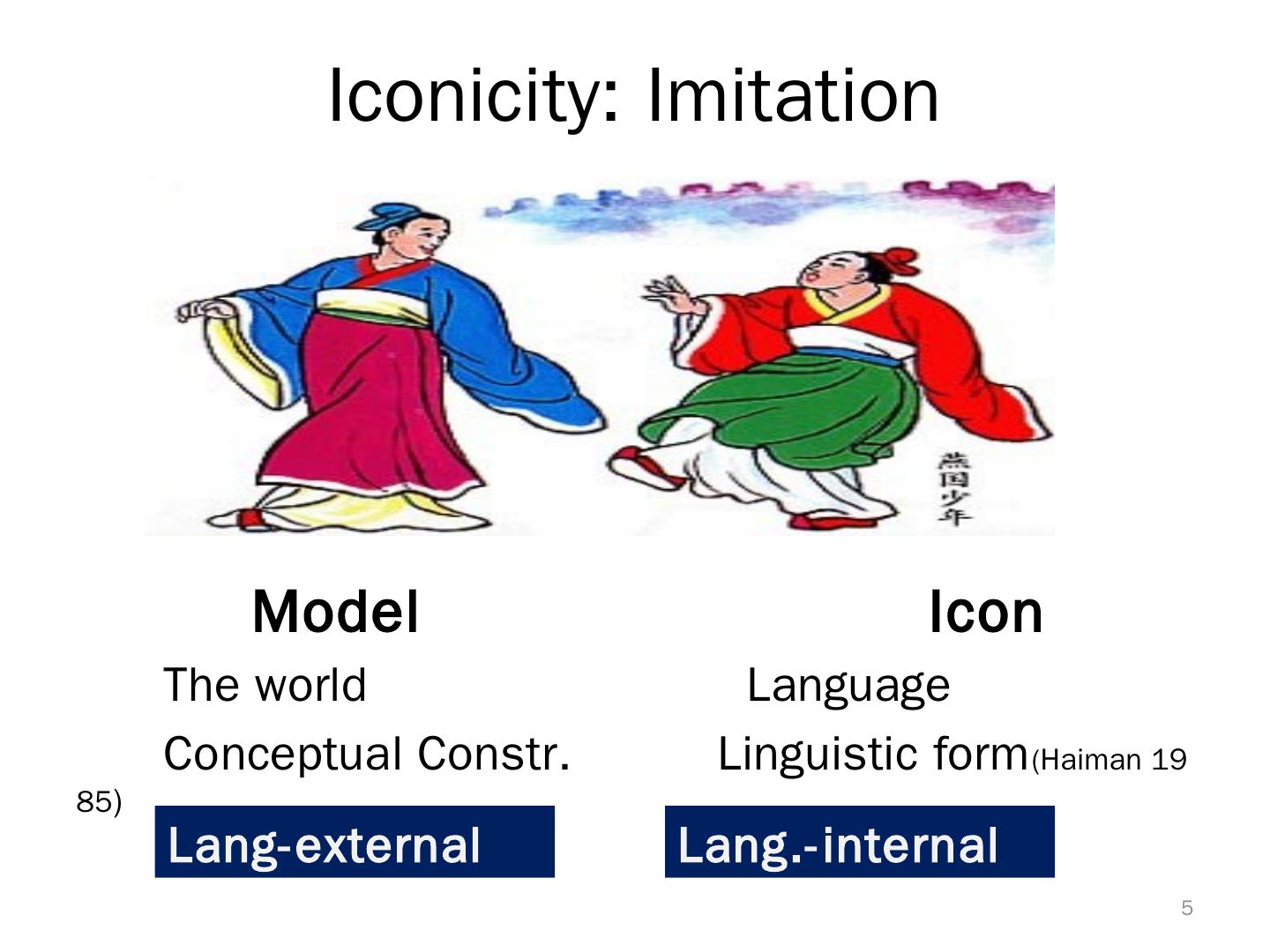
5 . Iconicity: Imitation Model Icon The world Language Conceptual Constr. Linguistic form (Haiman 19 85) Lang-external Lang.-internal 5
6 . Iconicity in simplest ways • Onomatopoeia, Interjections, etc. Cat meowing – In Arabic, miao – In Chinese, Mandarin, miāo miāo – In Hungarian miaú, nyau – In English, meow [miˈaʊ], miaow (UK), or mew [mjuː] – In Estonian, mjäu , njäu – In Filipino, ngyaw – In Greek, niau , (νιάου) • Source of Noun: ya (duck), e (google), wuya (crow) • Source of Verbs: flap, flip, chirp, cuckoo, roar, zip, zig-zag • Implosives for collecting flocks, Qu (go) for shouting away • Negation ( nasal/labial )—— close to deny • Demonstratives and person prons (Sonority, length, height, backness) 6
7 . Iconicity and order (narrative sequence) • Veni, vidi, vici (Julius Caesar) Jakobson1965 • Subj – Obj. : SVO, SOV, VSO : Majority • Obj – Subj : OVS, OSV, VOS : Minority • Conditionals : Protasis-apodosis : Majority • Info. Str. : Given – New • Temporal Sequential Principle (Tai 1985) : • 在马背 - 上 跳 - 跳 在 马背 - 上 • Prep. horse.back-up jump Jump prep. Horse.back-up Keep Jumping on the horse back Jump onto the horse back 7
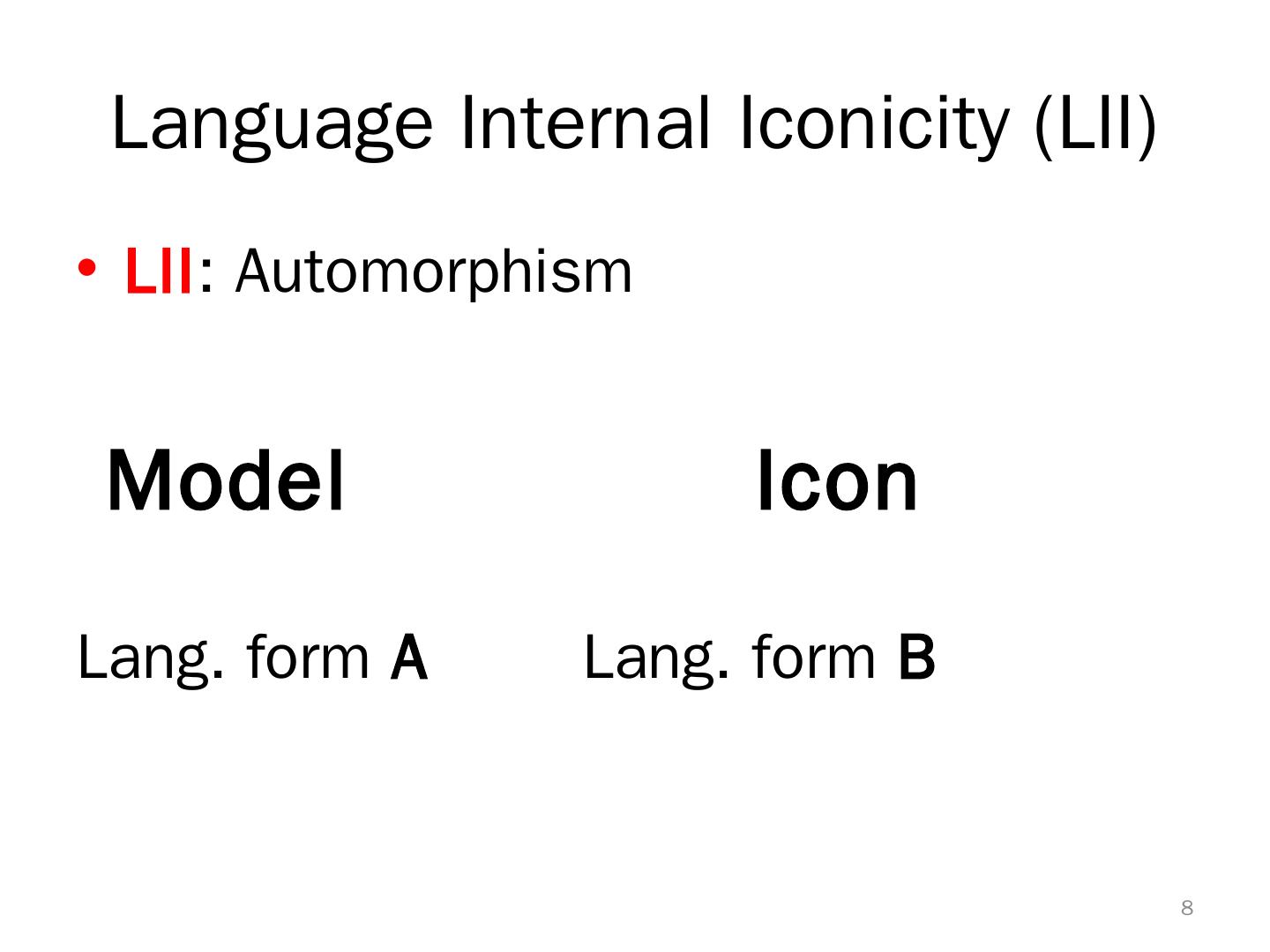
8 . Language Internal Iconicity (LII) • LII: Automorphism Model Icon Lang. form A Lang. form B 8
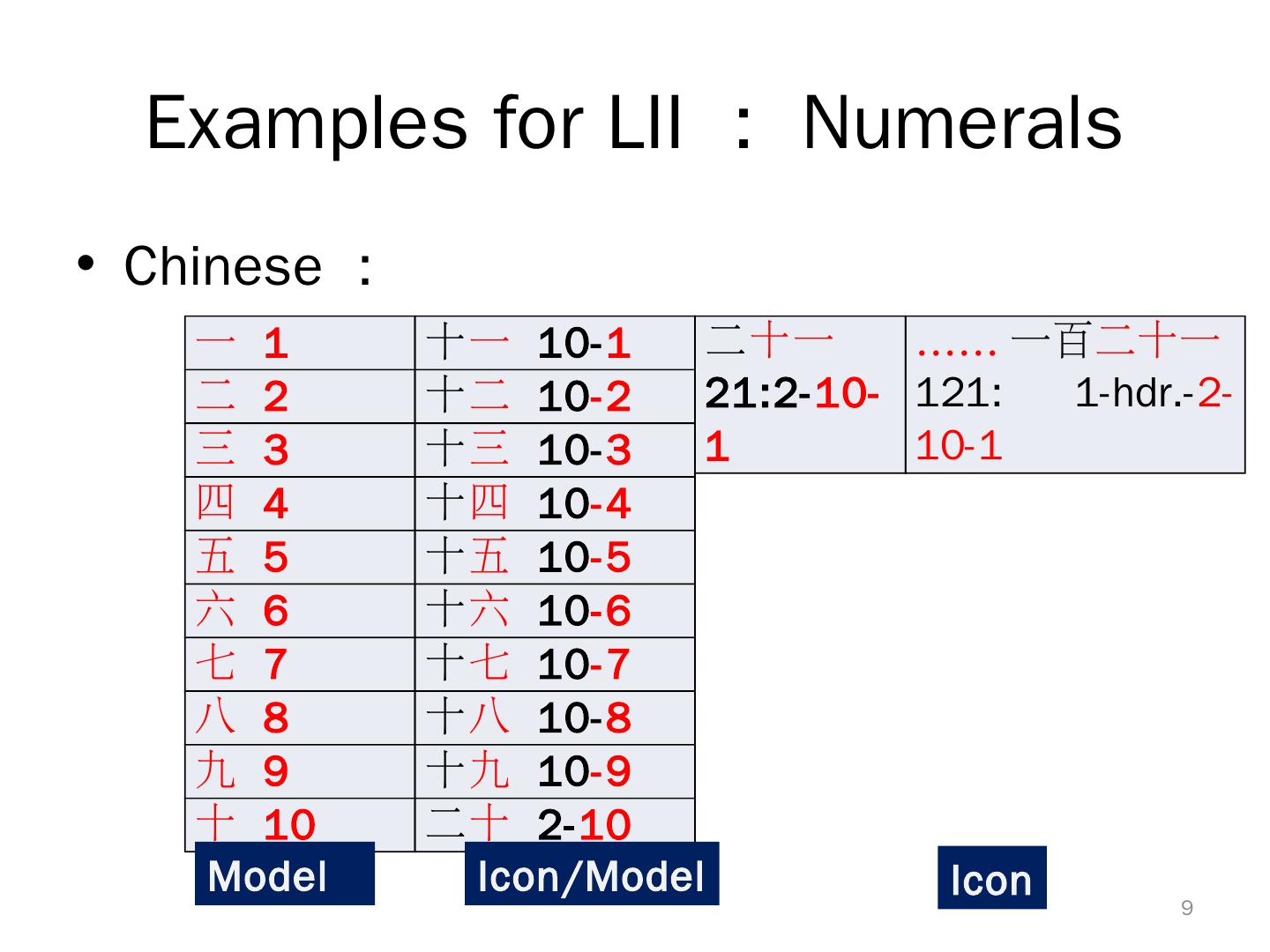
9 . Examples for LII : Numerals • Chinese : 一 1 十 一 10-1 二十一 …… 一百二十一 二 2 十 二 10-2 21:2-10- 121: 1-hdr.-2- 三 3 十 三 10-3 1 10-1 四 4 十 四 10-4 五 5 十 五 10-5 六 6 十 六 10-6 七 7 十 七 10-7 八 8 十 八 10-8 九 9 十 九 10-9 十 10 二 十 2-10 Model Icon/Model Icon 9
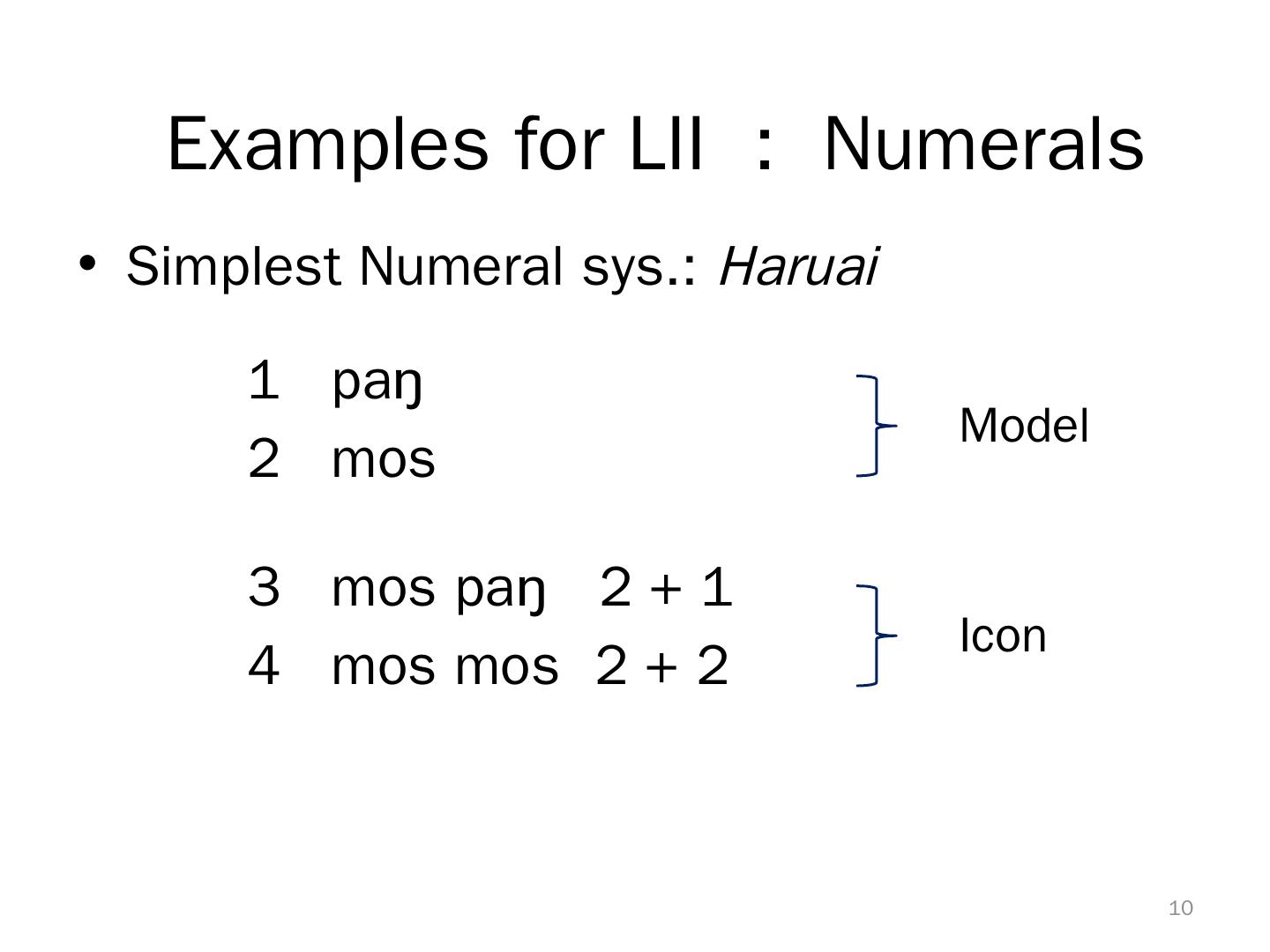
10 . Examples for LII : Numerals • Simplest Numeral sys.: Haruai 1 paŋ Model 2 mos 3 mos paŋ 2 + 1 Icon 4 mos mos 2 + 2 10
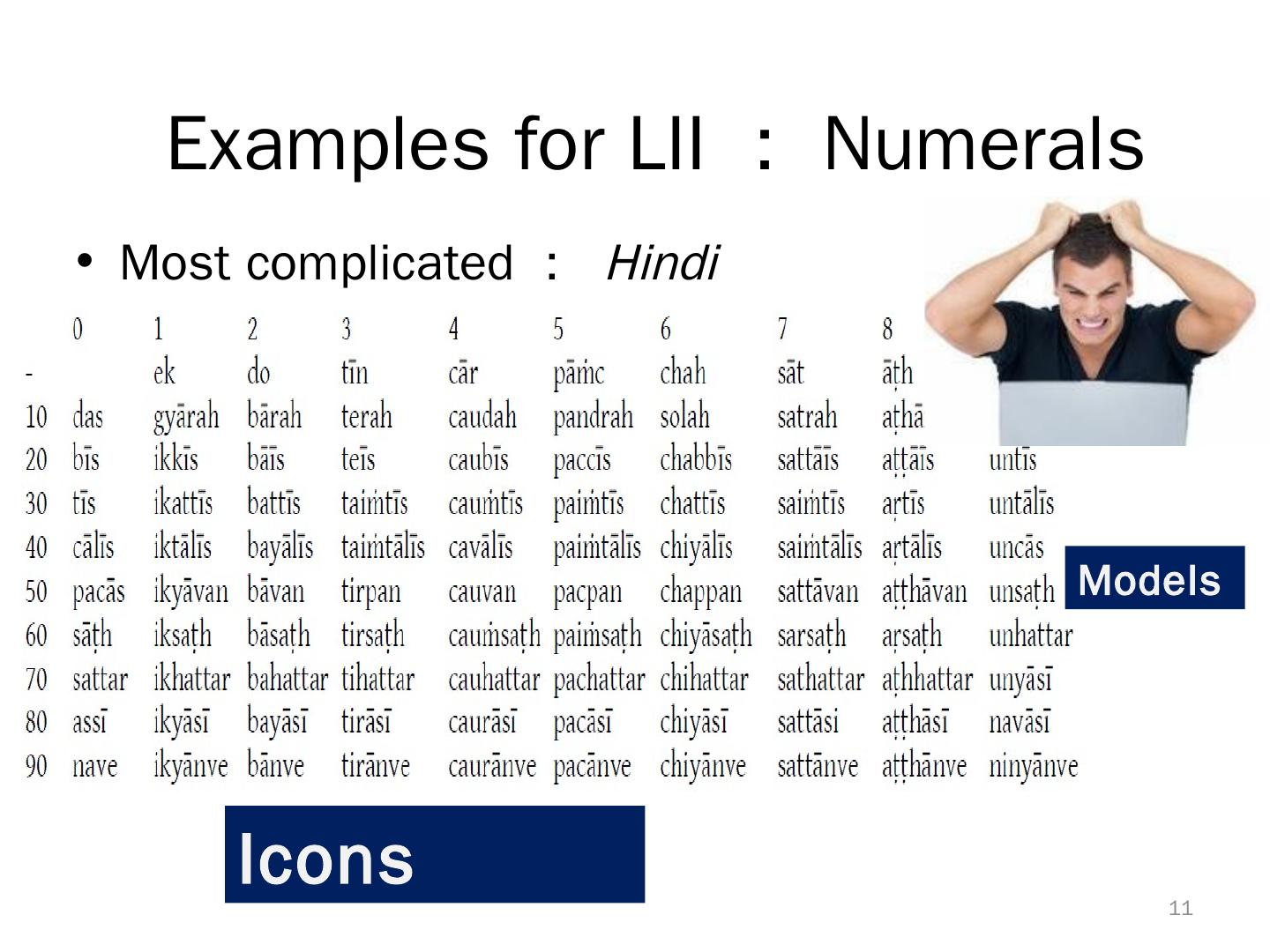
11 . Examples for LII : Numerals • Most complicated : Hindi Models Icons 11
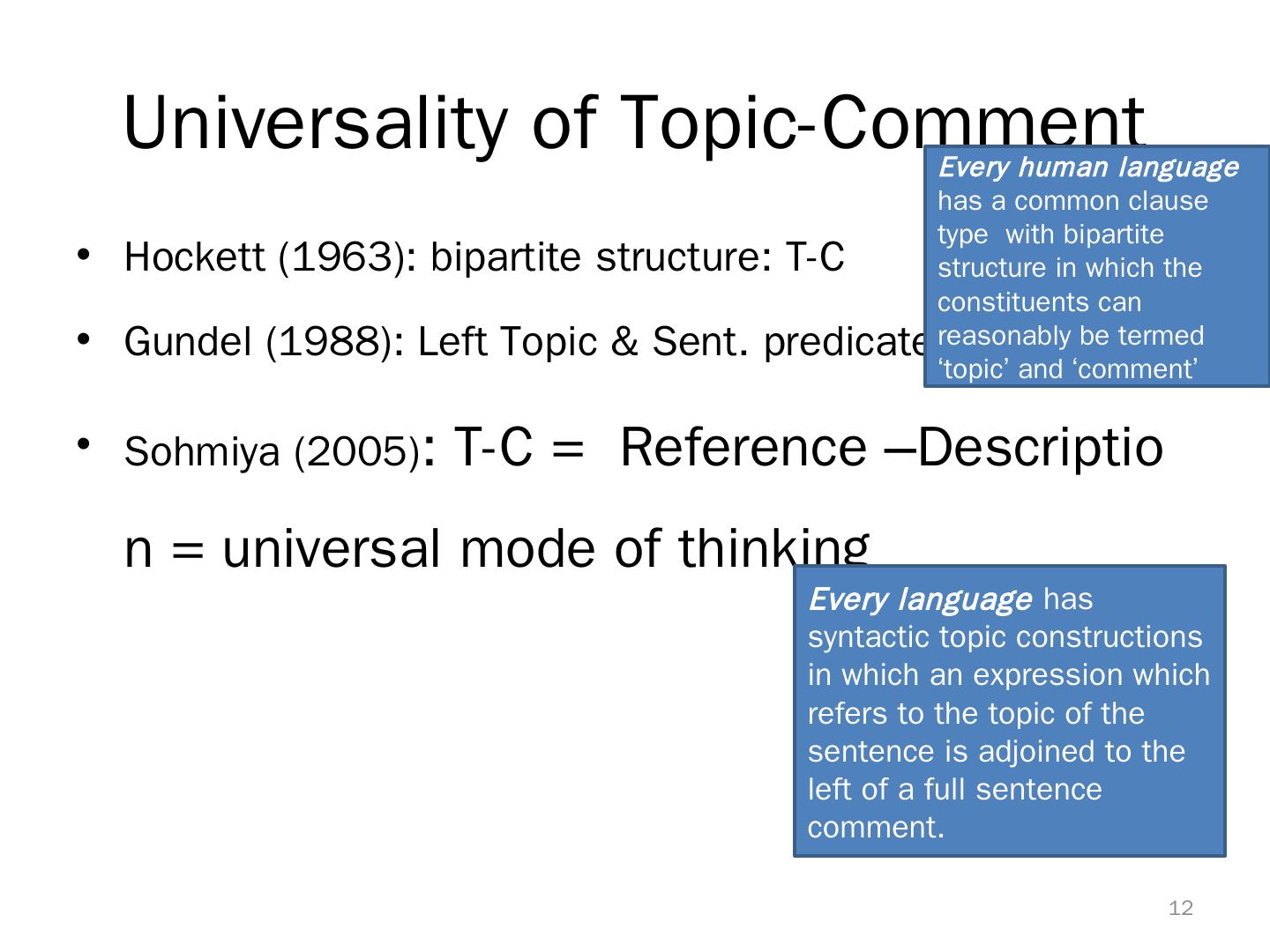
12 . Universality of Topic-Comment Every human language has a common clause type with bipartite • Hockett (1963): bipartite structure: T-C structure in which the constituents can • Gundel (1988): Left Topic & Sent. predicate reasonably be termed ‘topic’ and ‘comment’ • Sohmiya (2005): T-C = Reference –Descriptio n = universal mode of thinking Every language has syntactic topic constructions in which an expression which refers to the topic of the sentence is adjoined to the left of a full sentence comment. 12
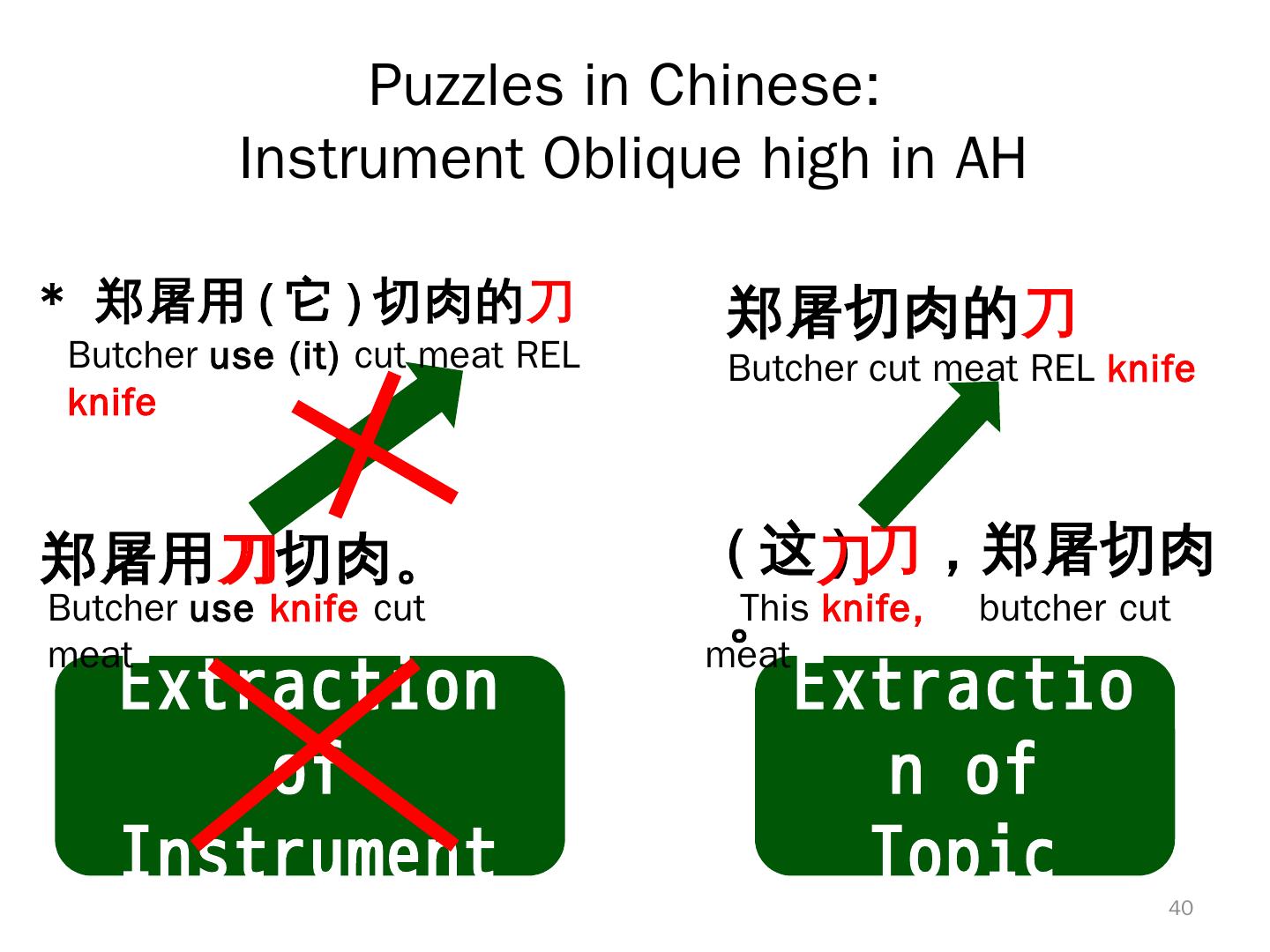
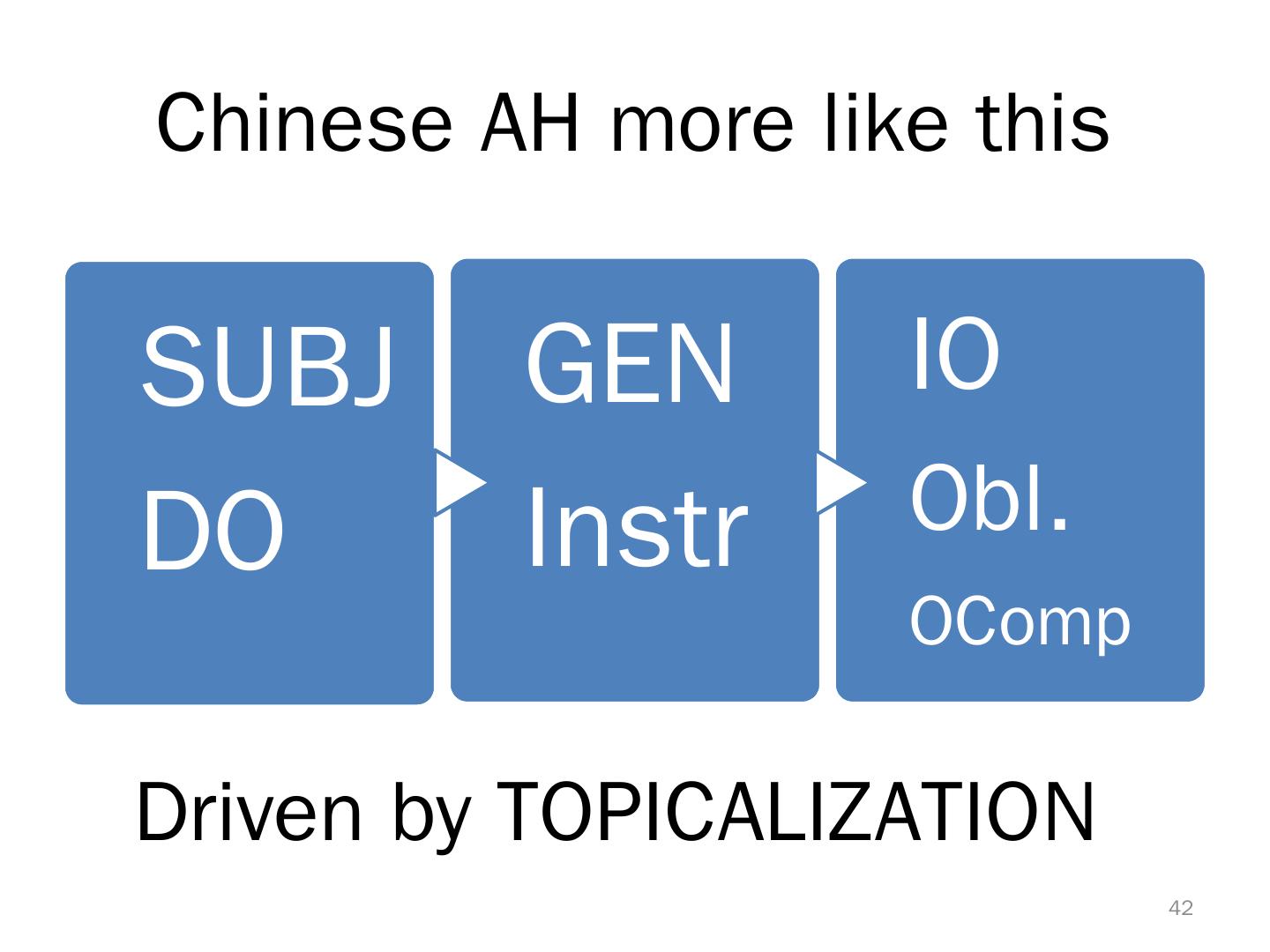
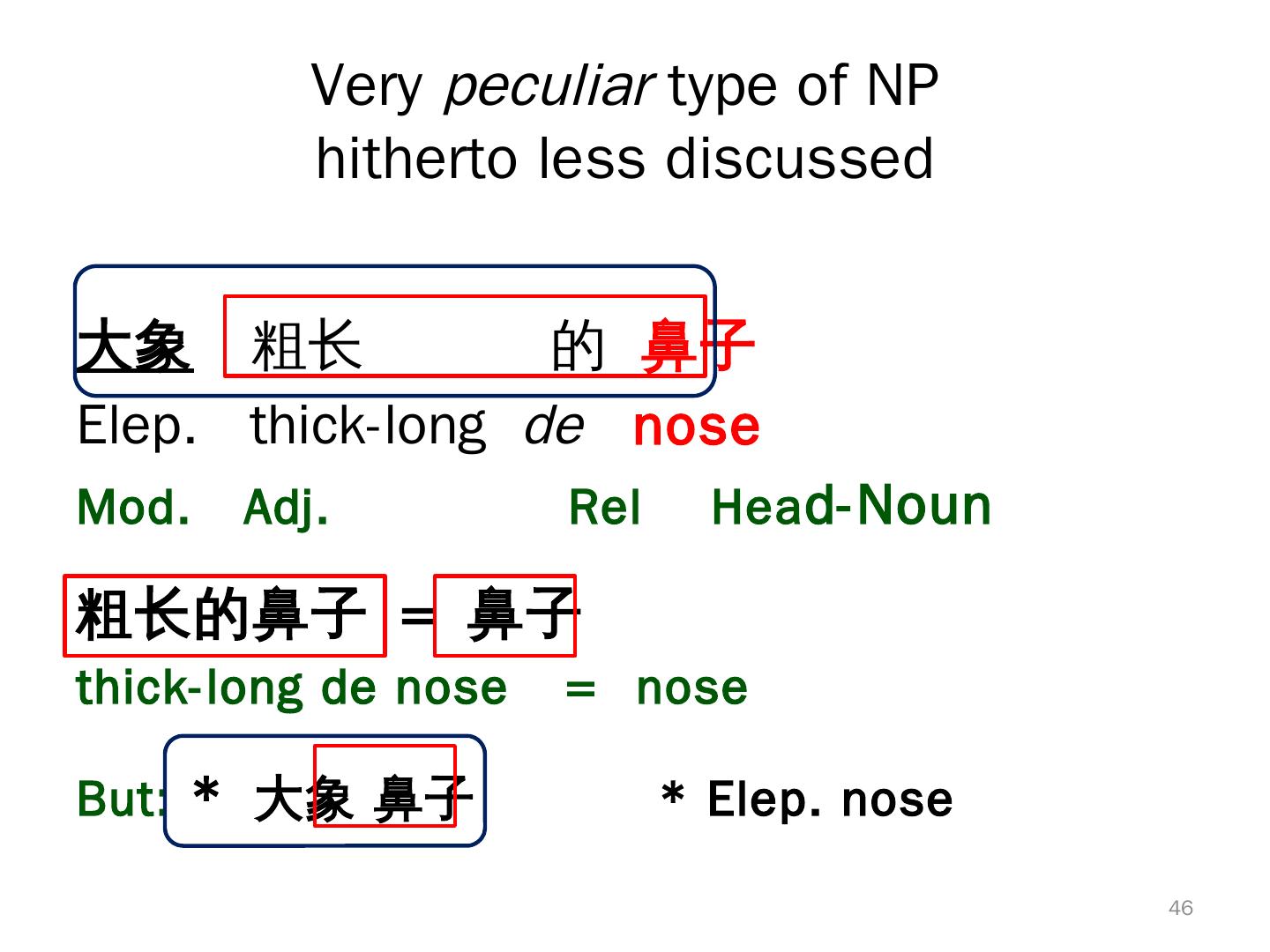
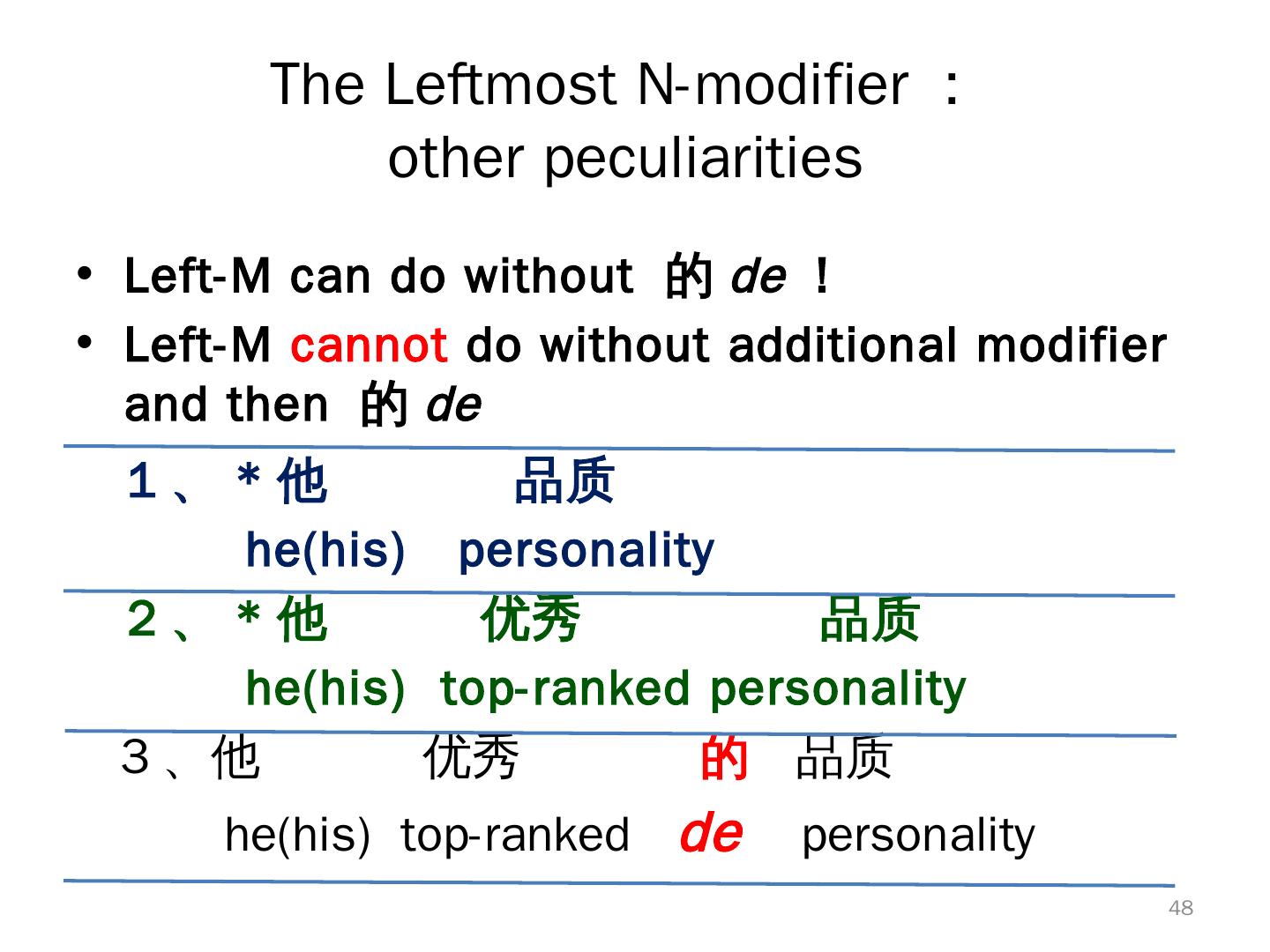
13 . Typological ‘Exceptionals’ in Chinese • Topic-prominent(L&T1981): Topic markers, but SV O • Prenominal Relative Clauses • Do not (strictly) follow Accessibility Hierarchy (K. C 1977) • Pre-verbal Prep. phrase • Topic-Comment WITHIN NPs • Defected subject complementation Interacted? Correlated? 13
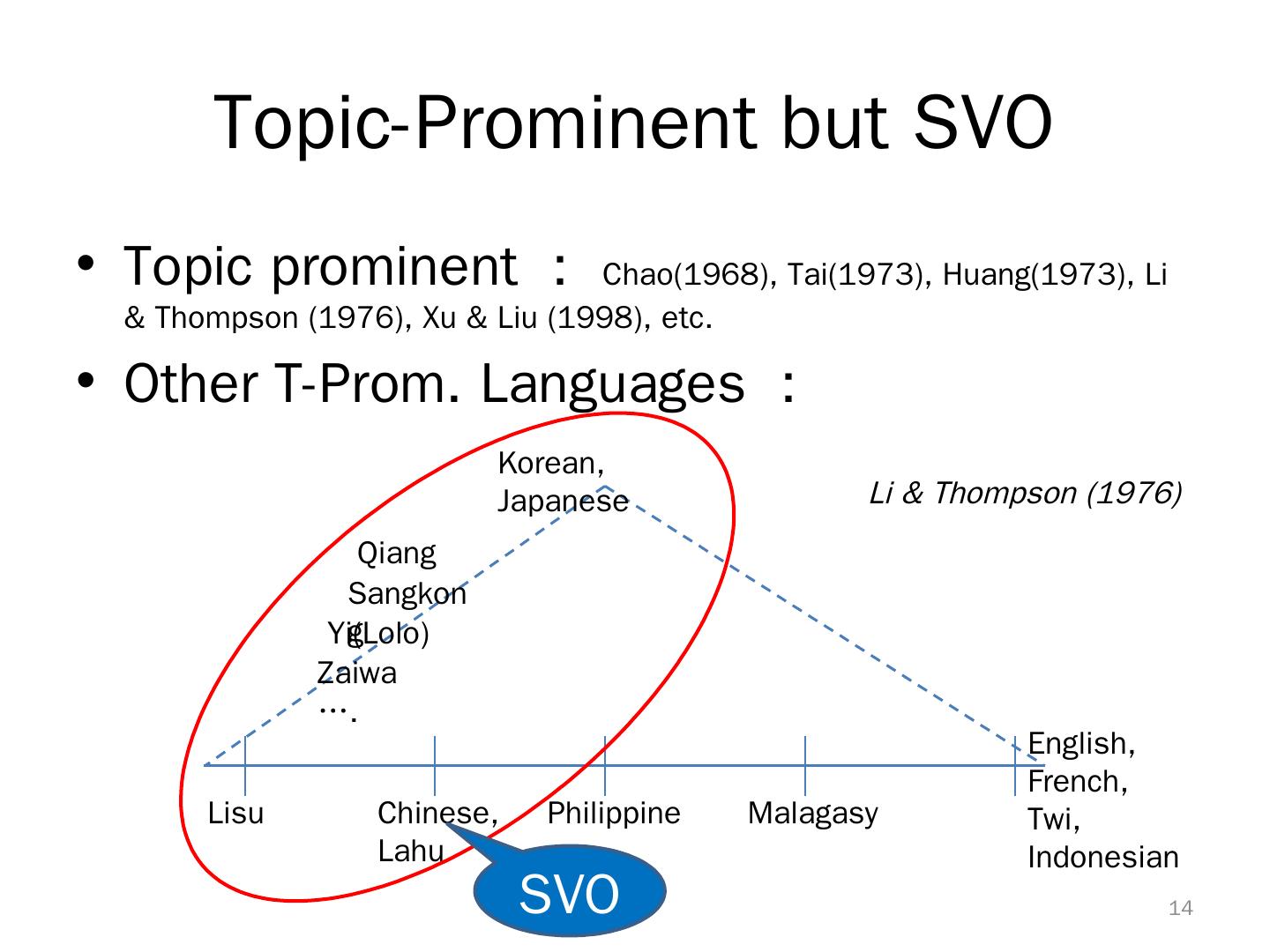
14 . Topic-Prominent but SVO • Topic prominent : Chao(1968), Tai(1973), Huang(1973), Li & Thompson (1976), Xu & Liu (1998), etc. • Other T-Prom. Languages : Korean, Japanese Li & Thompson (1976) Qiang Sangkon g Yi(Lolo) Zaiwa …. English, French, Lisu Chinese, Philippine Malagasy Twi, Lahu Indonesian SVO 14
15 . Topicalization & Complementation as Subject Another case for Language Internal Iconicity 15
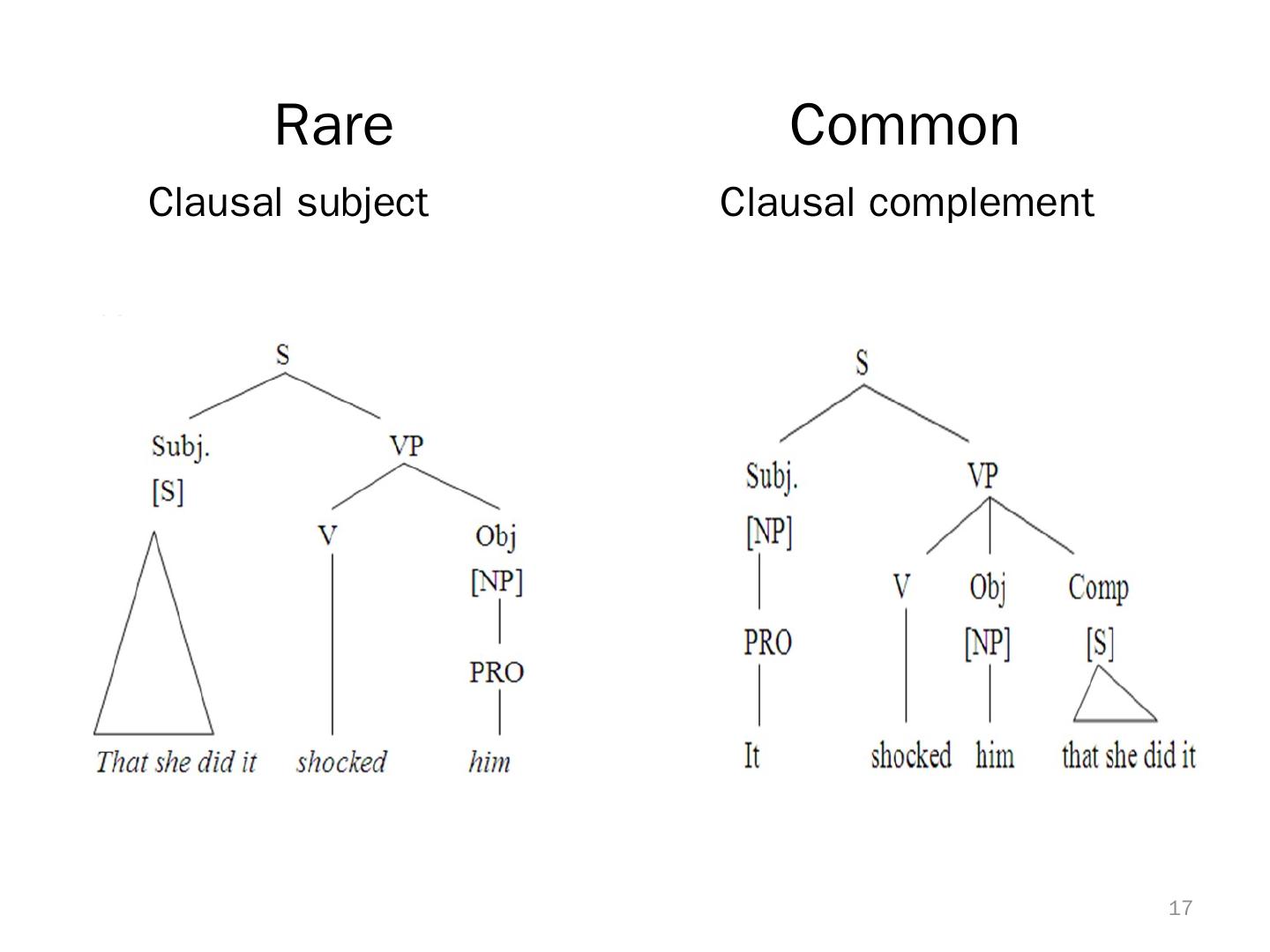
16 . Two strategies in world langugages • clausal subject Rare – That he did it shocked him. • clausal complement Common – shocked him that he did it. Hungarian , Szabolcsi 2009 16
17 . Rare Common Clausal subject Clausal complement 17
18 . Chinese: Clausal Subject only • Clausal Subject 他 打 小孩 激怒 - 了 围观者 。 he beat kid infuriate-PST onlooker ‘That he beat the kid make the onlookers angry.’ • Clausal-Complement *这/它 激怒 - 了 围观者 他打 小孩。 this/it infuriate-PST onlooker he beat kid 18
19 .Chinese clausal Subject: Clause reduct ion Non-finite, infinitival, nominalized 他 踢 小孩 不 - 可信。 he kick kid not-reliable/true ‘His kicking kids/the kid is not true.’ * 他 踢 - 了 小孩 不 - 可信。 he kick-PAST kid not-reliable/true ‘That he kicked the kid is not true.’ Semantically self-contradicte: 了 is a trigger of existence presp. 19
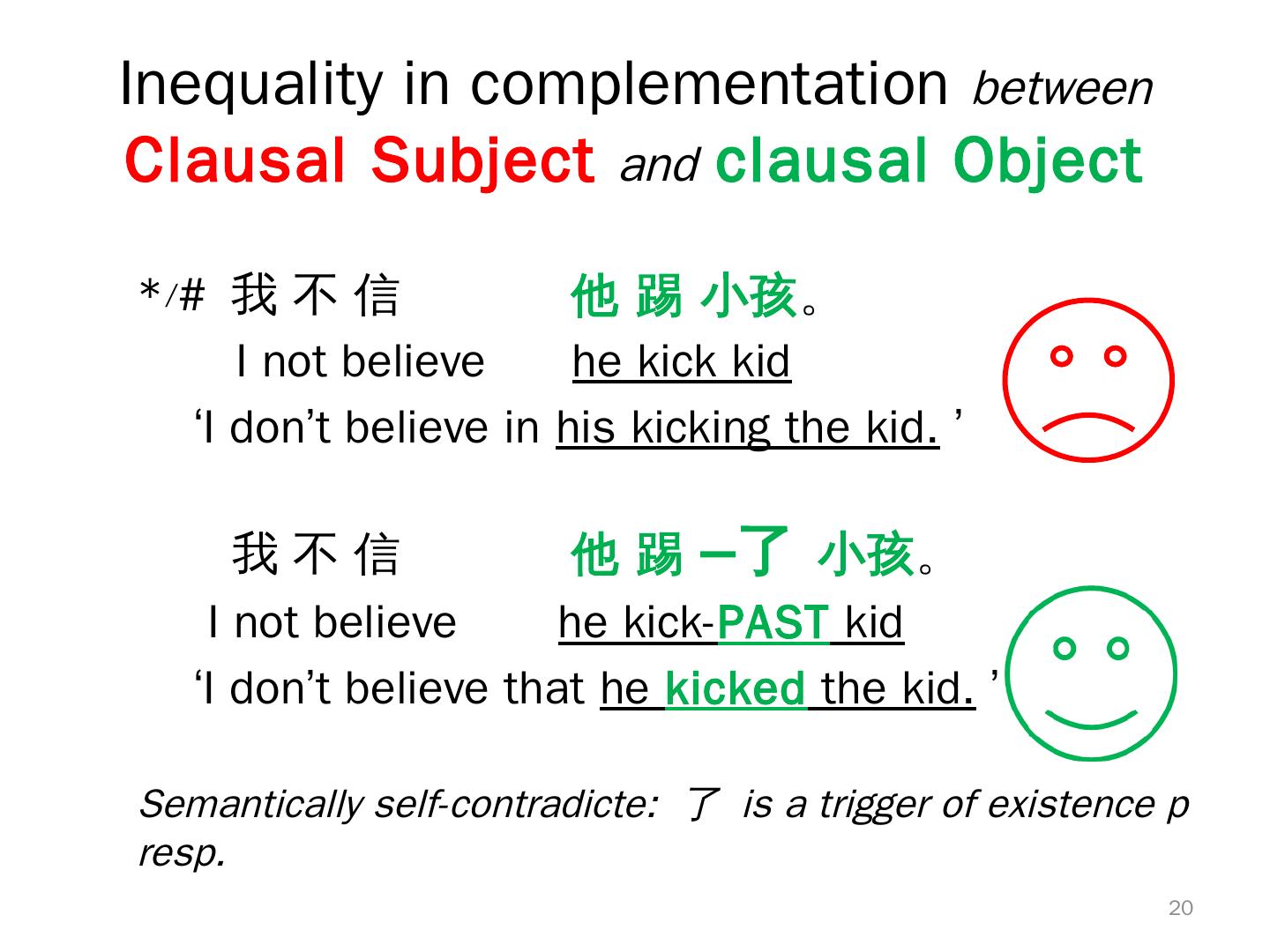
20 .Inequality in complementation between Clausal Subject and clausal Object */# 我 不 信 他 踢 小孩。 I not believe he kick kid ‘I don’t believe in his kicking the kid. ’ 我不信 他 踢 –了 小孩。 I not believe he kick-PAST kid ‘I don’t believe that he kicked the kid. ’ Semantically self-contradicte: 了 is a trigger of existence p resp. 20
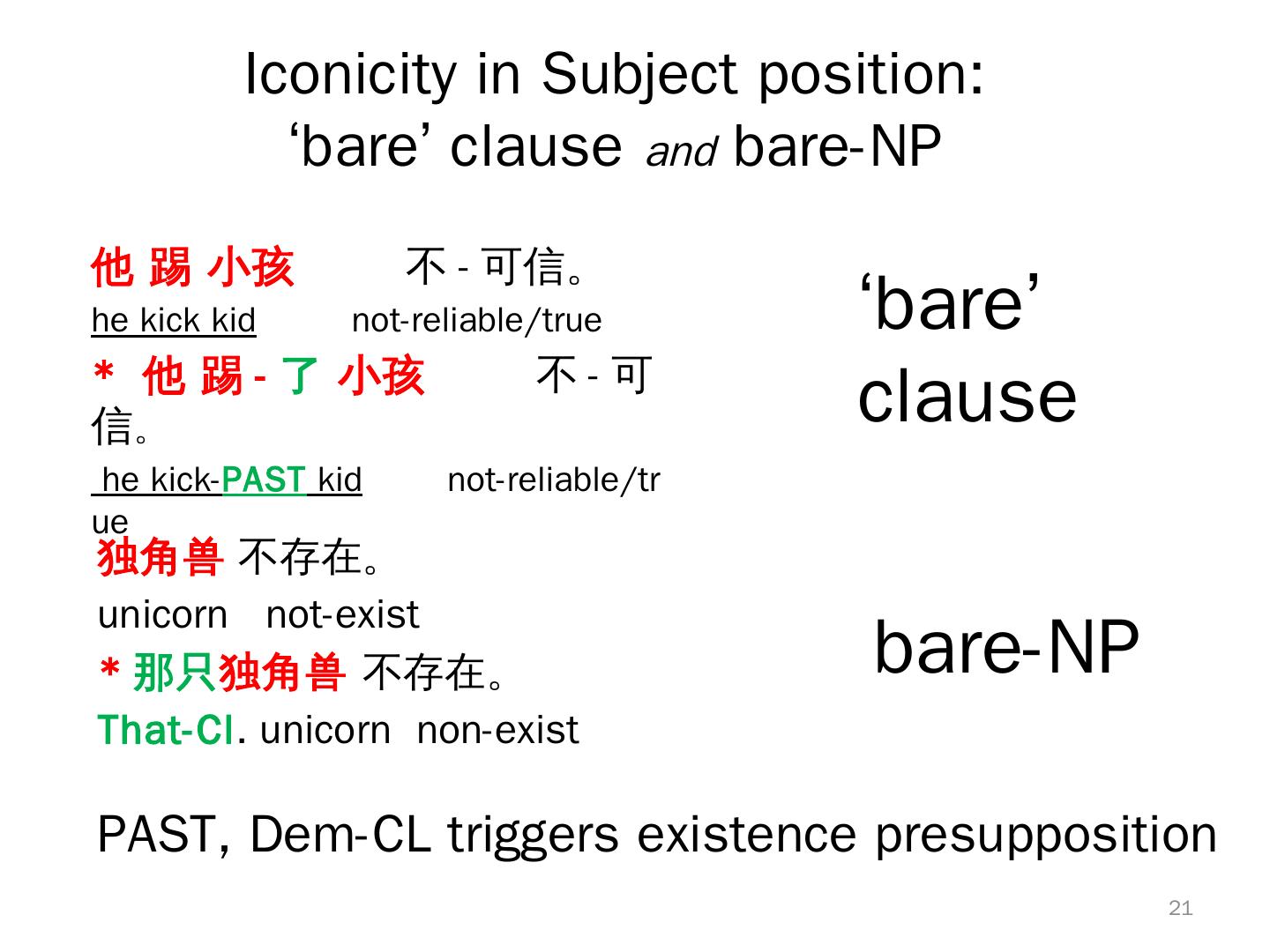
21 . Iconicity in Subject position: ‘bare’ clause and bare-NP 他 踢 小孩 不 - 可信。 he kick kid not-reliable/true ‘bare’ * 他 踢 - 了 小孩 信。 不-可 clause he kick-PAST kid not-reliable/tr ue 独角兽 不存在。 unicorn not-exist * 那只独角兽 不存在。 bare-NP That-Cl. unicorn non-exist PAST, Dem-CL triggers existence presupposition 21
22 .Topicalization: the hidden power 他 踢 小孩 –呢 不 - 可信。 he kick kid -TOP not-reliable/true 独角兽 - 呢 不存在。 unicorn -TOP not-exist Model Icon Bare NP Subject Clausal subject Generic topic generic sentence 22
23 . Case of Ancient Chinese 杀人者 死, 伤人 及 盗 抵罪 。 Kill-man-NOM/TOP die injure-man and steal be-held-gui lty Three for one: ‘One who murders be put to death, and who injures and steals be held g uilty’ Nominalization, Complementation = topicalization Two strategies for complemantation, as one: Nominalizer( 者 ), Clausal reduction = topicalization Topic-Comment as the Model 23
24 . Differing and Similar S-complementation strate gies in Tibeto-Burman Languages 24
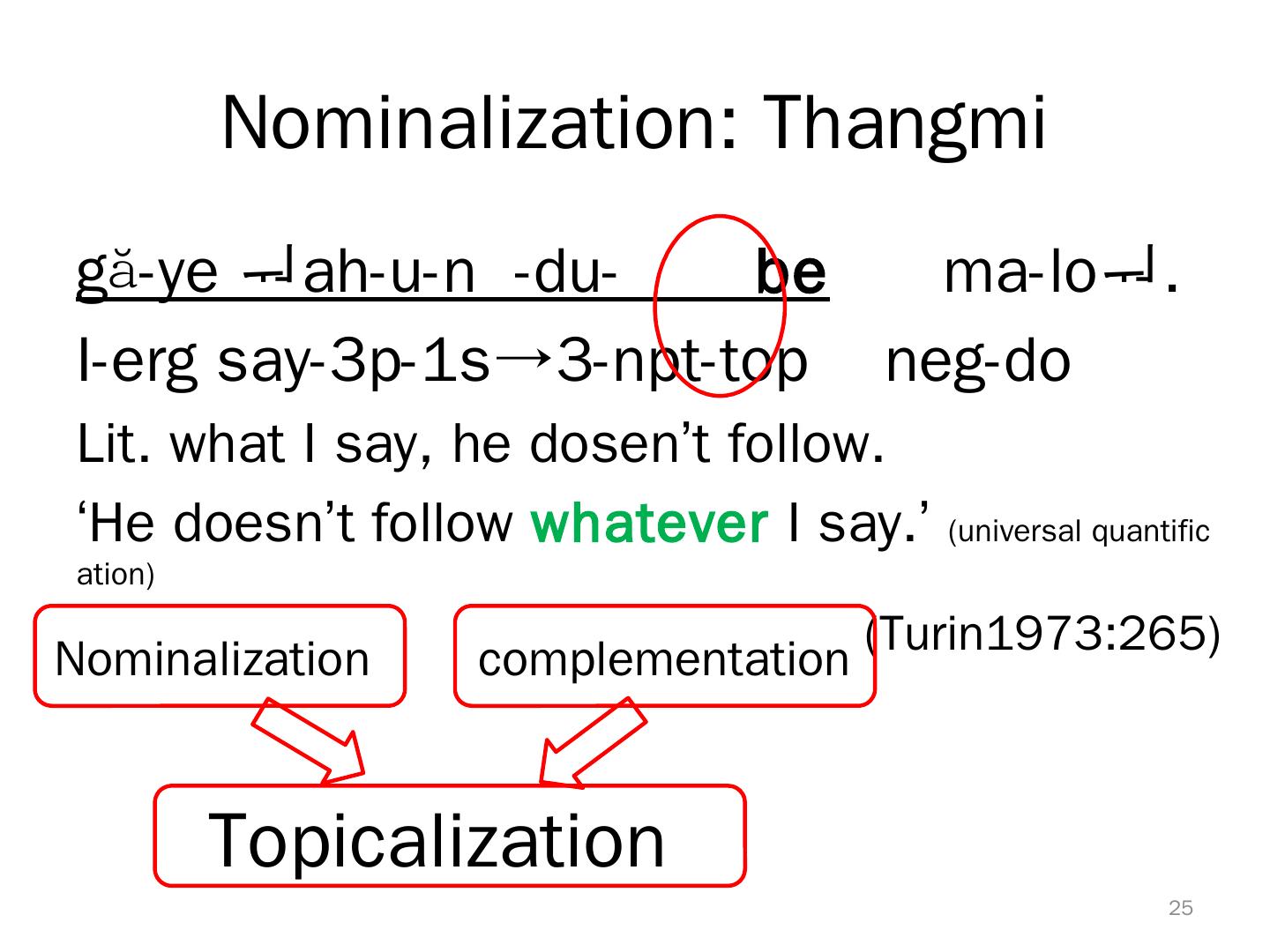
25 . Nominalization: Thangmi gă-ye ah-u-n -du- be ma-lo. I-erg say-3p-1s→3-npt-top neg-do Lit. what I say, he dosen’t follow. ‘He doesn’t follow whatever I say.’ (universal quantific ation) (Turin1973:265) Nominalization complementation Topicalization 25
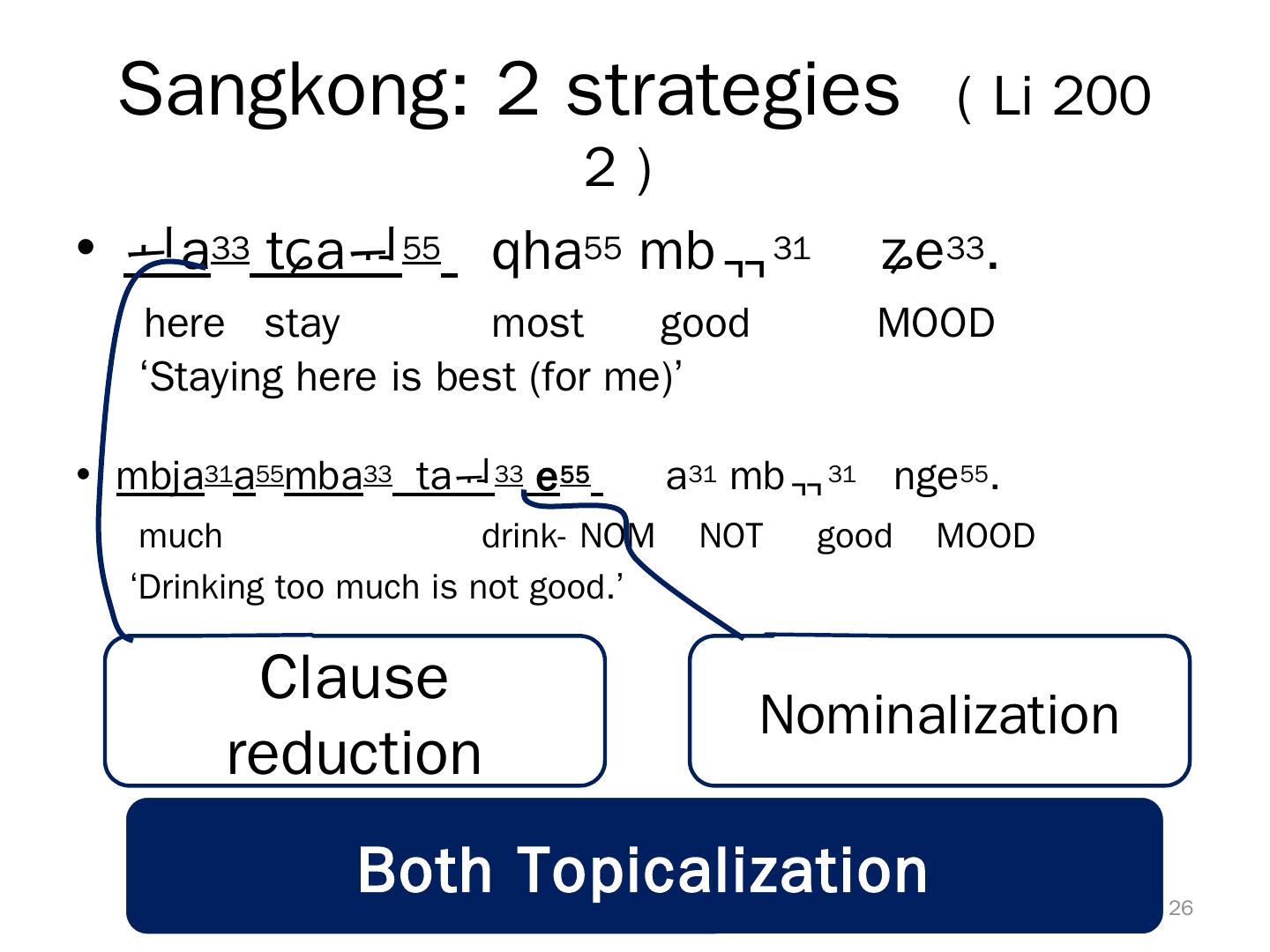
26 . Sangkong: 2 strategies ( Li 200 2) • a33 tɕa55 qha55 mb31 ʑe33. here stay most good MOOD ‘Staying here is best (for me)’ • mbja31a55mba33 ta33 e 55 a31 mb31 nge55. much drink- NOM NOT good MOOD ‘Drinking too much is not good.’ Clause Nominalization reduction Both Topicalization 26
27 . Eastern Kayan (SVO, Tibeto-B? Mon-Khmer?) Solnit 1986 • [a sí trē] se o k ū tcɤ t o 3 ashamed useful COM 3 one-CLF NEG Being ashamed isn’t any use to him! Clause reduction 全量性、类指性话题 27
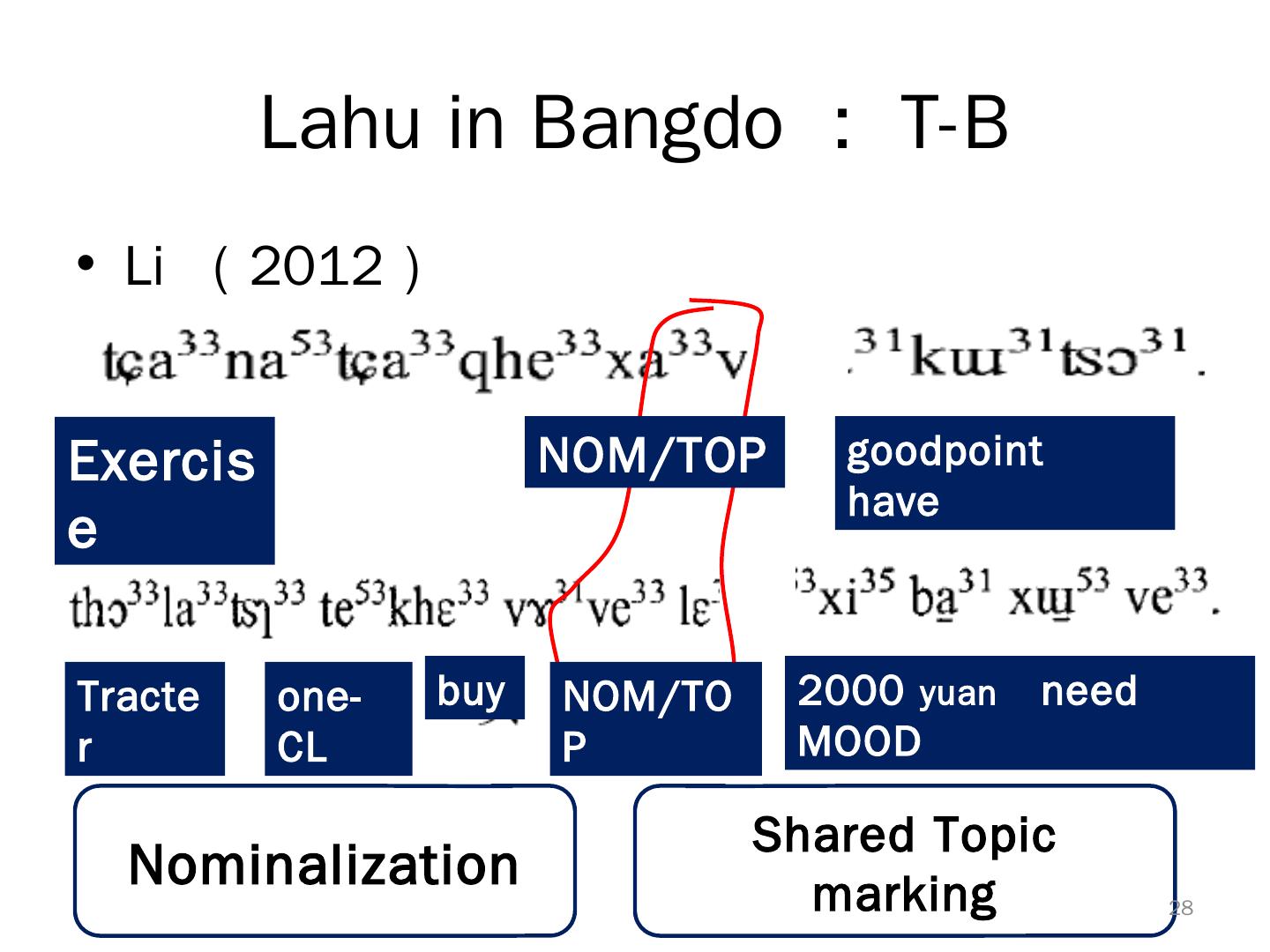
28 . Lahu in Bangdo : T-B • Li ( 2012 ) Exercis NOM/TOP goodpoint have e Tracte one- buy NOM/TO 2000 yuan need r CL P MOOD Shared Topic Nominalization marking 28
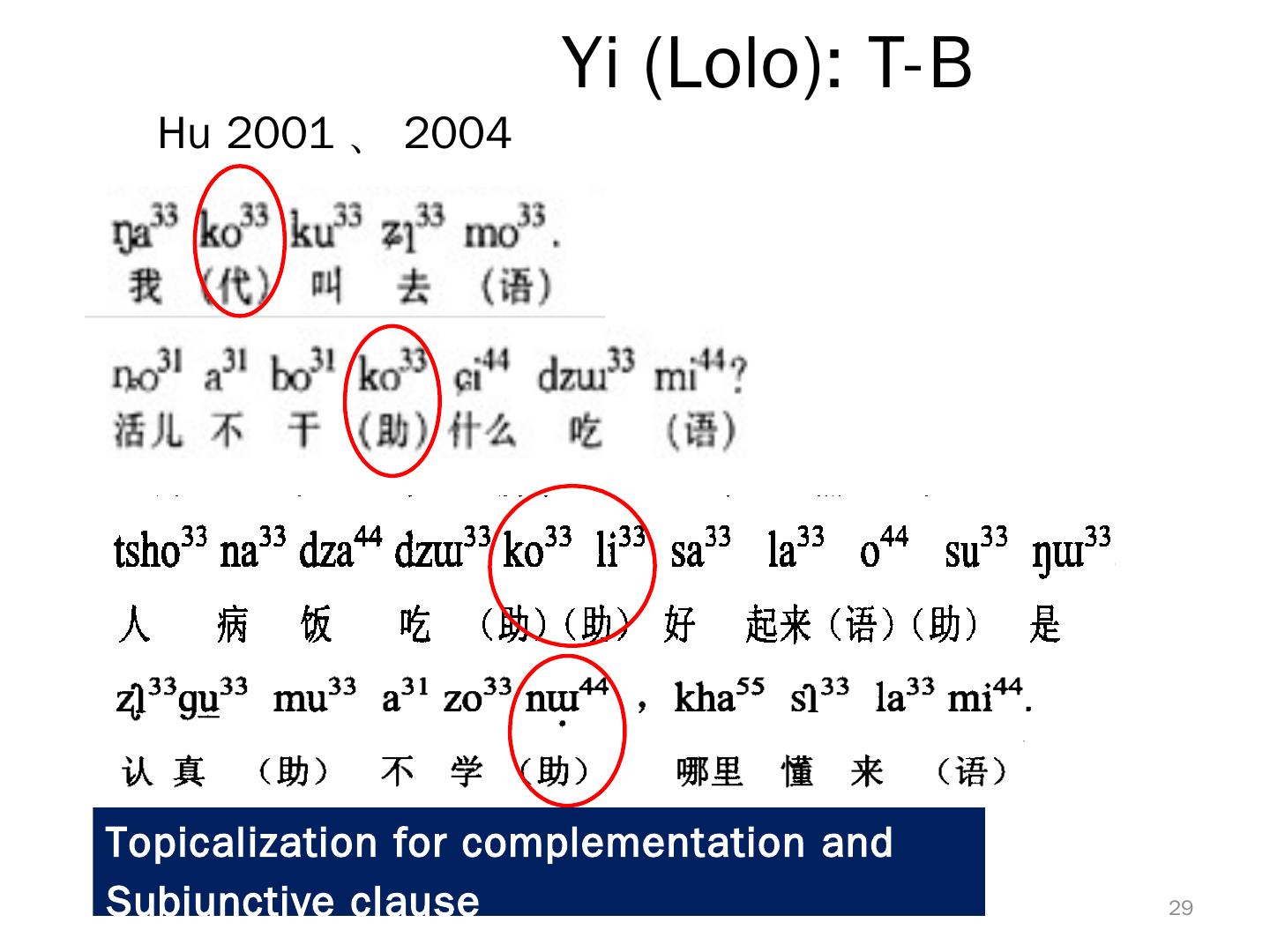
29 . Yi (Lolo): T-B Hu 2001 、 2004 Topicalization for complementation and Subjunctive clause 29