- 快召唤伙伴们来围观吧
- 微博 QQ QQ空间 贴吧
- 文档嵌入链接
- 复制
- 微信扫一扫分享
- 已成功复制到剪贴板
输出级和功率放大器
展开查看详情
1 .Chapter 9 output stages and power amplifiers Introduction 9.1 Classification of output stages 9.2 Class A output stage 9.3 Class B output stage 9.4 Class AB output stage 9.5 Biasing the class AB circuit
2 .Power Amplifier Small-signal approximation and models either are not applicable or must be used with care. THD (total harmonic distortion) Deliver the power to the load in efficient manner. Ex. To provide the amplifier with a low output resistance so that it can deliver the output signal to the load without loss of gain. Power dissipation is as low as possible.
3 .Classification of Power Amplifier Power amplifiers are classified according to the collector current waveform that results when an input signal is applied. Conducting angle.
4 .Classification of Power Amplifier Collector current waveforms for transistors operating in (a) class A, (b) class B
5 .Classification of Power Amplifier class AB class C
6 .CE amplifier is not proper for using as a power amplifier DC supply power: I CQ Vcc , the area of ABCO Rc power: I CQ U Rc , the area of QBCD Collector dissipation power: I CQ U CEQ , the area of AQDO Load power:
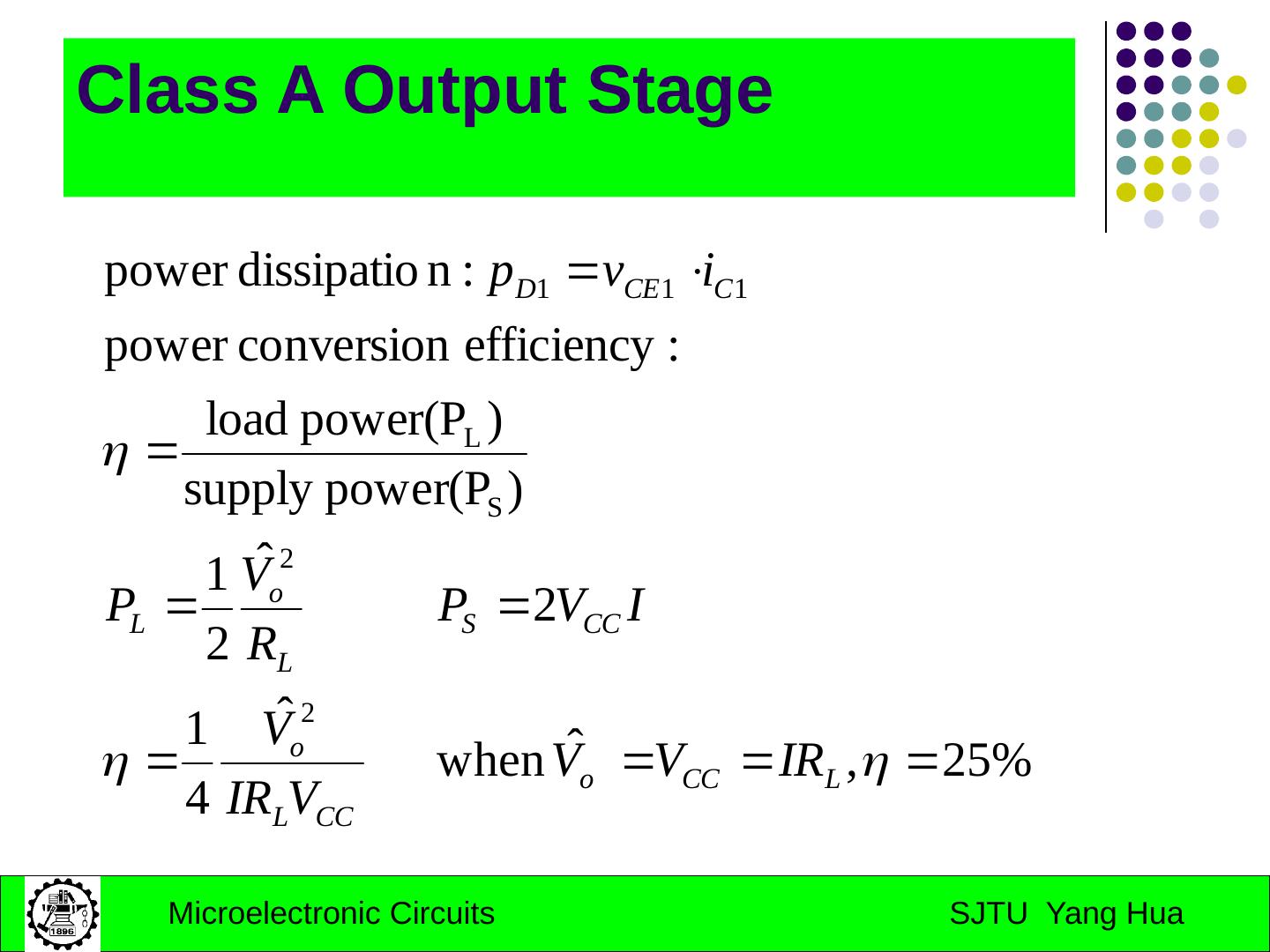
7 .Class A Output Stage
8 .Figure 14.3 Transfer characteristic of the emitter follower. This linear characteristic is obtained by neglecting the change in v BE 1 with i L . The maximum positive output is determined by the saturation of Q 1 . In the negative direction, the limit of the linear region is determined either by Q 1 turning off or by Q 2 saturating, depending on the values of I and R L .
9 .Figure 14.4 Maximum signal waveforms in the class A output stage of Fig. 14.2 under the condition I = V CC / R L or, equivalently, R L = V CC / I .
10 .Figure 14.4 Maximum signal waveforms in the class A output stage of Fig. 14.2 under the condition I = V CC / R L or, equivalently, R L = V CC / I .
11 .Class B Output Stage A class B output stage. Complementary circuits. Push-pull operation Maximum power-conversion efficiency is 78.5%
12 .Class B Output Stage When Vi=0, Q N and Qp are cut off, Vo=0 When Vi>0.5V, Q N is on and Qp is cut off, Vo=Vi-V BEN When Vi>0.5V, Qp is on and Q N is cut off, Vo=Vi-V BEP
13 .Transfer Characteristic
14 .Crossover Distortion
15 .Power –conversion efficiency The load power Maximum load power
16 .Power –conversion efficiency Total supply power Maximum total supply power
17 .Power –conversion efficiency Power-conversion efficiency Maximum power-conversion efficiency
18 .Power Dissipation Power dissipation Maximum Power dissipation
19 .Power Dissipation At the point of maximum power dissipation the efficiency can be evaluated:
20 .Example: 9.1
21 .Reducing crossover distortion
22 .Class AB Output Stage
23 .A Class AB Output Stage Utilizing Diodes for Biasing The diode biasing has an Important advantage: Thermal stabilization of Quiescent current
24 .A Class AB Output Stage Utilizing A V BE Multiplier for Biasing