- 快召唤伙伴们来围观吧
- 微博 QQ QQ空间 贴吧
- 视频嵌入链接 文档嵌入链接
- 复制
- 微信扫一扫分享
- 已成功复制到剪贴板
青年论坛第六期-多模态3D目标检测
摘要
3D目标检测是计算机视觉领域的热点话题之一,在自动驾驶场景中具有广泛应用。目前,在自动驾驶场景中,激光雷达和相机是两种常用的传感器。激光雷达返回的点云能够提供高精度的定位信息,而RGB图像能为目标检测提供丰富的语义信息。因此,如何有效的融合多个模态用于3D目标检测是一个值得深入探讨的问题。
我们提出了一种多模态的3D目标检测算法。一方面,我们将点云投影到图像上获取相应图像特征,并设计了一种后融合机制用于处理点云特征和图像特征。另一方面,我们设计了一种新的数据增强方法用于多模态3D目标检测。我们的方法在大型自动驾驶数据集nuScenes上获得了单模型第一的结果。
王春微,上海交通大学人工智能研究院在读硕士生,主要研究兴趣集中于多模态3D目标检测、3D目标检测的域迁移问题等深度学习理论与方法研究。目前以第一作者身份已在CVPR会议发表论文1篇。
展开查看详情
1 . PointAugmenting: Cross-Modal Augmentation for 3D Object Detection Chunwei Wang, Chao Ma, Ming Zhu, Xiaokang Yang Shanghai Jiao Tong University CVPR 2021
2 . Background: 3D Object Detection LiDAR Camera ? Fusion • Modality:Point cloud • Modality:2D Image • Input: (X, Y, Z, I, …) • Input:(R, G, B, …) • Advantages:accurate location • Advantages:dense, rich semantics • Disadvantages:sparse, unordered • Disadvantages:lack of depth 1 Lidar-only 2 Fusion-based
3 . Lidar-based 3D Object Detection 1 Grid-based 2 Point-based Methods: Divide point clouds into Methods: Employ PointNet++ for regular 3D voxels or BEV maps feature extraction VoxelNet 2018 CVPR PointRCNN 2019 CVPR SECOND 2018 Sensors Fast Point RCNN 2019 ICCV PointPillars 2019 CVPR STD 2019 ICCV SASSD 2020 CVPR 3DSSD 2020 CVPR Advantages: PV-RCNN 2020 CVPR • computationally efficient • high recall Advantages: Problems: • larger receptive field by the point set • Voxelization - degrade localization abstraction accuracy • high localization accuracy • Downscaled features - lose spatial Disadvantages : information • higher computation cost • Uneven distribution in BEV – get sparser with increasing depth
4 . Lidar-based 3D Object Detection Grid-based: VoxelNet 2018 CVPR • Voxelization • Conv middle layer → Conv3D → reshape to BEV • RPN SECOND 2018 Sensors: 3D sparse convolution - computation efficient Grid-based: PointPillars 2019 CVPR
5 . Lidar-based 3D Object Detection 1 Grid-based 2 Point-based Methods: Divide point clouds into Methods: Employ PointNet++ for regular 3D voxels or BEV maps feature extraction VoxelNet 2018 CVPR PointRCNN 2019 CVPR SECOND 2018 Sensors Fast Point RCNN 2019 ICCV PointPillars 2019 CVPR STD 2019 ICCV SASSD 2020 CVPR 3DSSD 2020 CVPR Advantages: PV-RCNN 2020 CVPR • computationally efficient • high recall Advantages: Problems: • larger receptive field by the point set • Voxelization - degrade localization abstraction accuracy • high localization accuracy • Downscaled features - lose spatial Disadvantages : information • higher computation cost • Uneven distribution in BEV – get sparser with increasing depth
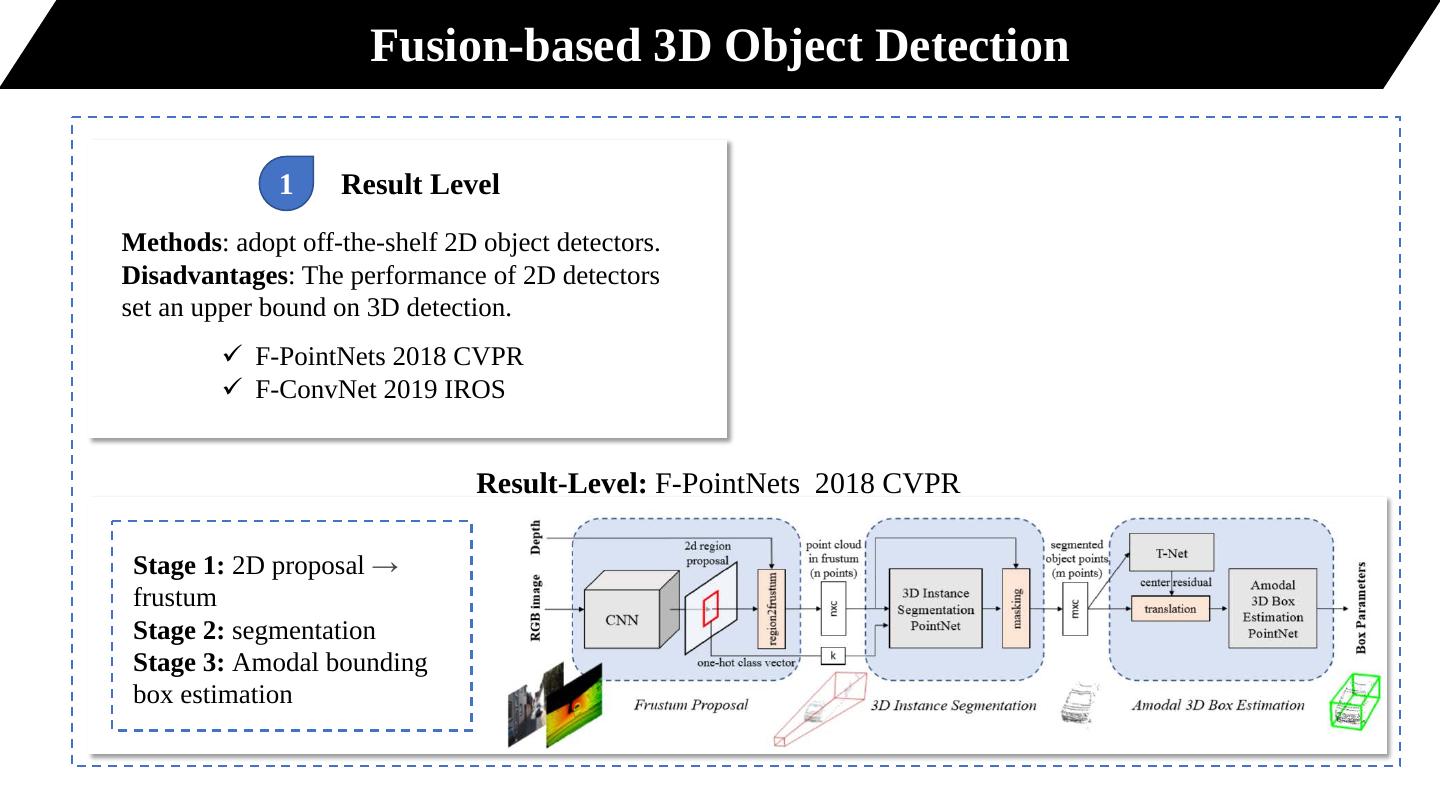
6 . Fusion-based 3D Object Detection 1 Result Level Methods: adopt off-the-shelf 2D object detectors. Disadvantages: The performance of 2D detectors set an upper bound on 3D detection. F-PointNets 2018 CVPR F-ConvNet 2019 IROS Result-Level: F-PointNets 2018 CVPR Stage 1: 2D proposal → frustum Stage 2: segmentation Stage 3: Amodal bounding box estimation
7 . Fusion-based 3D Object Detection 1 Result Level 2 Proposal Level Methods: adopt off-the-shelf 2D object detectors. Methods: perform fusion at the region proposal level Disadvantages: The performance of 2D detectors Disadvantages: slow and cumbersome set an upper bound on 3D detection. F-PointNets 2018 CVPR MV3D 2017 CVPR F-ConvNet 2019 IROS AVOD 2018 IROS Proposal Level: AVOD 2018 IROS
8 . Fusion-based 3D Object Detection 1 Result Level 3 Point Level Methods: fetch point-wise image features by Methods: adopt off-the-shelf 2D object detectors. projecting point clouds onto image plane. Disadvantages: The performance of 2D detectors set an upper bound on 3D detection. Methods: construct BEV camera features F-PointNets 2018 CVPR before fusing with LiDAR BEV features. F-ConvNet 2019 IROS a Disadvantages: Feature blurring ContFuse 2018 ECCV MMF 2019 CVPR 3D-CVF 2020 ECCV 2 Proposal Level Methods: perform fusion at the region proposal level Methods: augment each LiDAR point with Disadvantages: slow and cumbersome b image features or segmentation scores. MVX-Net 2019 ICRA MV3D 2017 CVPR PointPainting 2020 CVPR AVOD 2018 IROS
9 .Fusion-based 3D Object Detection Point-Level: PointPainting 2020 CVPR
10 . Image Representation for Lidar Points Segmentation Scores CNN Features • Provide semantic labels • Provide richer semantic cues • Straightforward and compact VS rather than the object class only semantic cues • Larger receptive field • PointPainting fails due to segmentation failures on • CNN Feature is better than Segmentation scores small objects
11 . PointAugmenting Network Architecture Classification LiDAR Feature Extraction Feature to BEV Per-cell Pooling Voxelization Head RPN C C Regression to BEV Camera + Feature Camera Feature LiDAR Feature Point-wise Feature Fetching 3D Backbone • Lidar only Baseline: CenterPoint • Point-wise Feature Fetching: . LiDAR points are projected onto image plane and then appended by the fetched point-wise CNN features • 3D Detection: a late fusion mechanism across modalities
12 . Data Augmentation for Cross-modality • Data Augmentation for Lidar Points GT-Paste: pastes virtual objects in the forms of ground-truth boxes and LiDAR points from other scenes to the training scenes. Extend to Cross-modality – Consistency Destruction propose a simple yet effective cross-modal augmentation method to make GT-Paste applicable to both point clouds and images.
13 . Data Augmentation for Cross-modality • Methods: simultaneously attach a virtual object onto Lidar scene and images. • Challenge: consistency preservation between camera and LiDAR data.
14 . Experiments Results nuScenes datatset • Rank 2 on nuScenes Leaderboard (rank 1 with single model) +8.0 +20.2 +5.2 Waymo datatset
15 . Ablation Study 1 Cross-Modal Network Design 2 Cross-Modal Data Augmentation
16 .Ablation Study Runtime
17 .Result Comparison