- 快召唤伙伴们来围观吧
- 微博 QQ QQ空间 贴吧
- 文档嵌入链接
- 复制
- 微信扫一扫分享
- 已成功复制到剪贴板
Tutorial 1 - Intro to LLVM
展开查看详情
1 .Introduction to LLVM Bojian Zheng CSCD70 Spring 2018 bojian@cs.toronto.edu 1
2 .What you will need for Assignment 1 … LLVM: How to write a pass that analyzes and transforms (optimizes) Intermediate Representation ( IR ) . C++ Fundamentals: Public Inheritance (Abstract Class, Dynamic Casting) , Iterator , STL Data Structures 2 Prerequisite
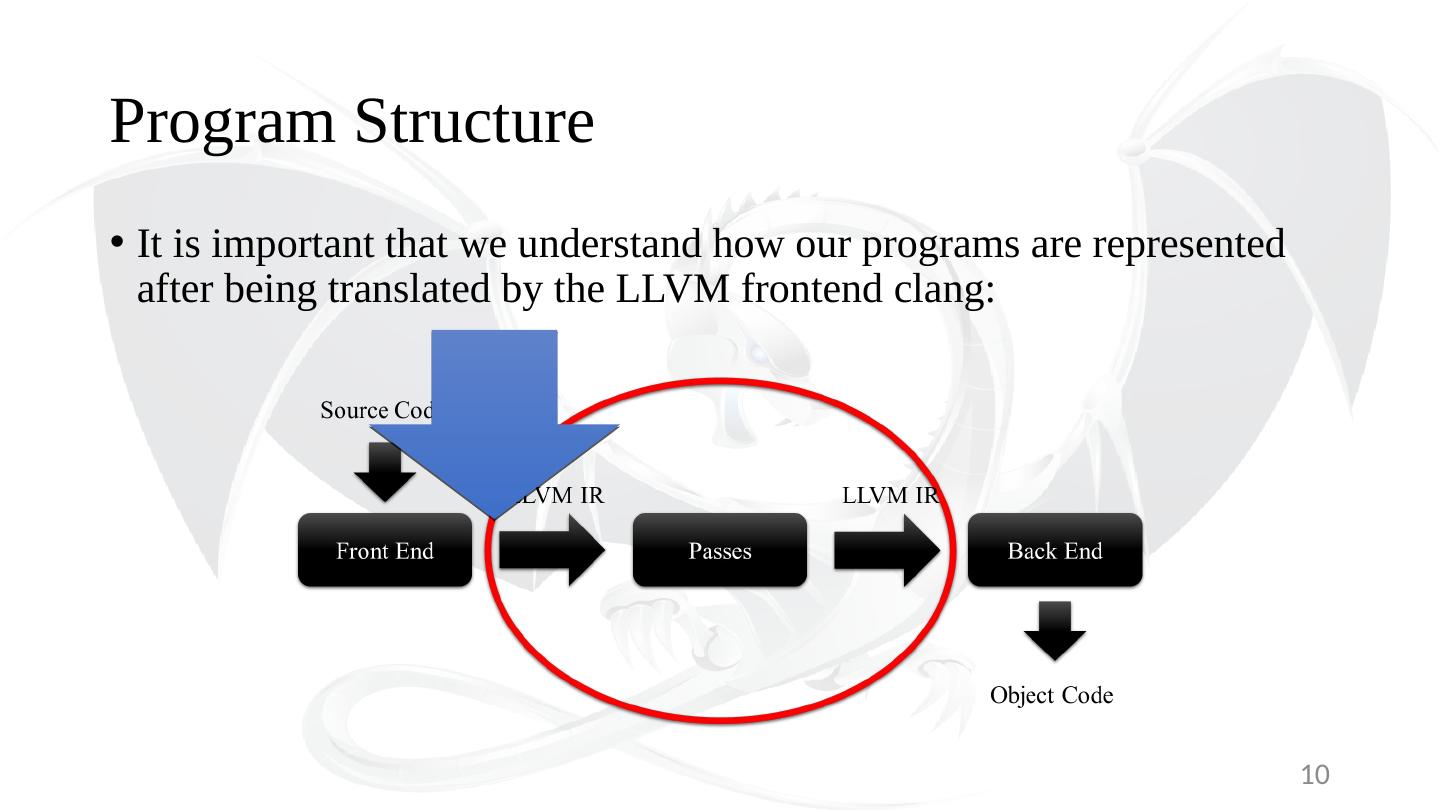
3 .Three-Phase Design – From Source to Binary 3 Front End Passes Back End LLVM IR LLVM IR Object Code Source Code
4 .Three-Phase Design – From Source to Binary C/C++ Source int main() { return 0; } LLVM IR define i32 @main() … { ret i32 0 } 4 clang
5 .Example – IR Optimization Suppose that we are hoping to replace every statement in our code with . How can we achieve this? Write a Pass that does the followings: Analyzes whether there are statements of the form in our code or not, and where are those statements located. Transforms those instructions with . 5
6 .IR Optimization The IR optimizations consist of many optimization passes. LLVM itself also has passes for analysis or transformations: https://llvm.org/docs/Passes.html In this assignment, we will be making use of the mem2reg pass. Please DON’T use the LLVM passes unless otherwise told to. 6
7 .Questions? Keywords: Intermediate Representation (IR) Optimization Pass Analysis & Transformation 7
8 .Analysis 8
9 .How to write an analysis pass? We need to understand the following three things: Program Structure : How is our program represented in LLVM? Iterators : How to traverse through such structures? Downcasting : How to retrieve more information from iterators? LLVM Pass Interface : Implement LLVM interface. 9
10 .Program Structure It is important that we understand how our programs are represented after being translated by the LLVM frontend clang: 10
11 .Program Structure C/C++ Source Source File Function Code Block Statement LLVM IR Module contains Functions and Global Variables . Function contains Basic Blocks and Arguments . Basic Block contains a list of Instructions . Instruction is an Opcode plus vector of Operands . 11
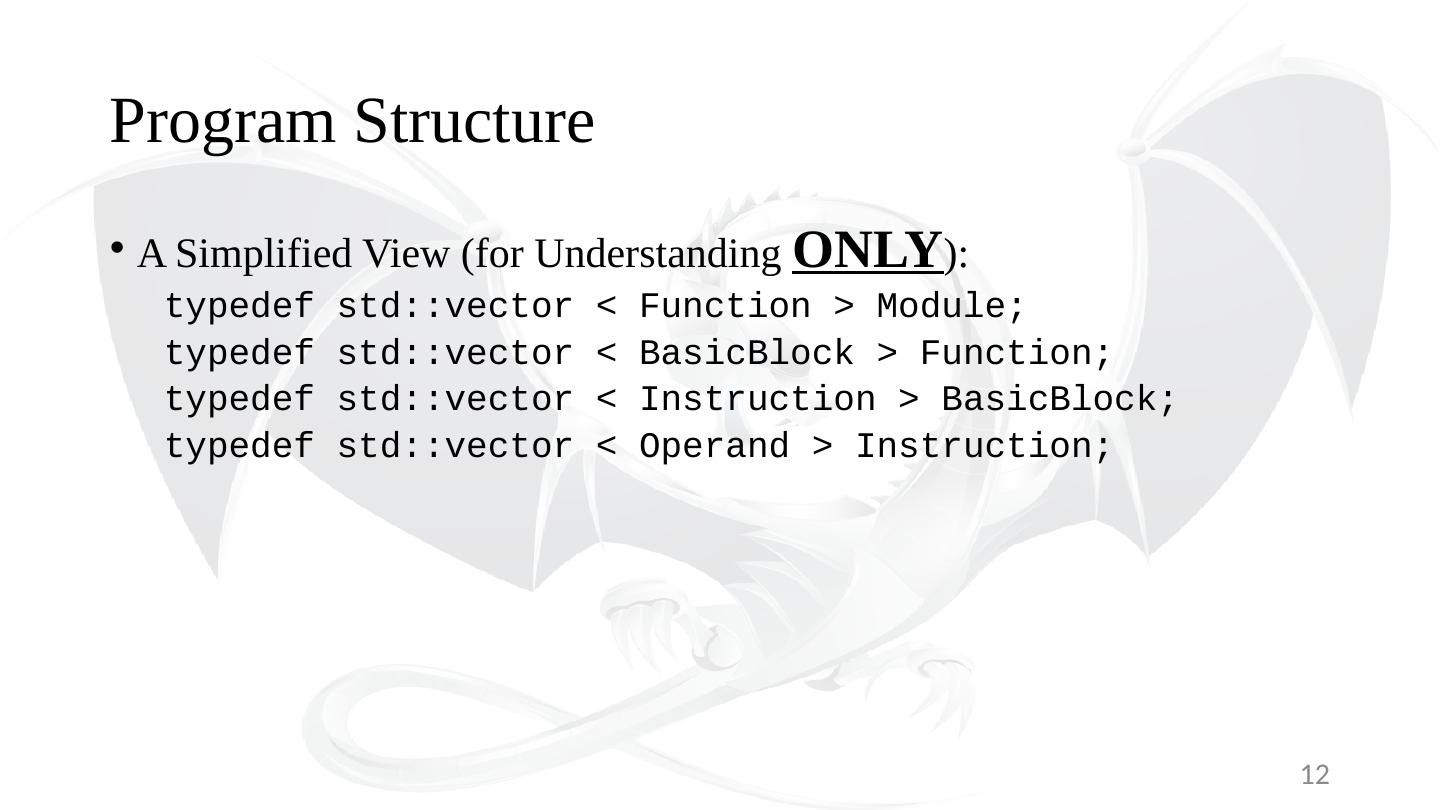
12 .Program Structure A Simplified View (for Understanding ONLY ): typedef std ::vector < Function > Module; typedef std ::vector < BasicBlock > Function; typedef std ::vector < Instruction > BasicBlock ; typedef std ::vector < Operand > Instruction; 12
13 .How to iterate through the Structures? Iterators! Recall how you traverse through std ::vector std ::vector < unsigned > vec ; for (auto iter = vec.begin (); iter != vec.end (); ++ iter ) {/* do something */} 13
14 .How to iterate through the Structures? Similarly, … Module M; for (auto iter = M.begin (); iter != M.end (); ++ iter ) {/* do something */} 14
15 .Downcasting – Getting More Details Suppose that we have an instruction, how can we know whether it is an unary instruction? a binary instruction? a call instruction? … Dynamic Casting! Consider the statement UnaryInstruction * unary_inst = dyn_cast < UnaryInstruction > ( inst ); 15
16 .LLVM Pass Interface LLVM Interface class ModulePass { bool runOnModule (Module & M) = 0; }; Implementation class MyModulePass : public ModulePass { bool runOnModule (Module & M) { for ( iter = … } }; 16
17 .Questions? Keywords: Program Structure Iterators Downcasting LLVM Pass Interface 17
18 .Transformations 18
19 .Insert/Remove/Move/Replace Instructions Three Options Instruction class methods: insertBefore () , insertAfter () , moveBefore () , moveAfter () , eraseFromParent () , removeFromParent () , … Ask parent ( BasicBlock ) to do this: inst.getParent ()-> getInstList () .insert/erase/remove/…() Make use of BasicBlockUtils (defined in header llvm /Transforms/ Utils / BasicBlockUtils.h ): ReplaceInstWithValue () , ReplaceInstwithInst () 19