- 快召唤伙伴们来围观吧
- 微博 QQ QQ空间 贴吧
- 文档嵌入链接
- 复制
- 微信扫一扫分享
- 已成功复制到剪贴板
KubeCon_China_Blockchain
展开查看详情
1 .Managing and Securing Blockchain Applications on Kubernetes Henry Zhang, Chief Architect, VMware China Yang Yu, Staff Engineer, VMware China
2 .Henry Zhang Yang Yu • Chief Architect, VMware China R&D • Staff Engineer, VMware China R&D • Current focus: Blockchain, Cloud Native Apps, IoT • Working on Kubernetes CNI plugin for VMware NSX transformers • Founder of Project Harbor, an open source container registry hosted by CNCF • Familiar with OpenStack’s networking component Neutron • Hyperledger Cello Contributor • Speaker of KubeCon Europe 2018 • Coauthor of two blockchain books (in Chinese) • Blockchain Technical Guides • Blockchain Core Technologies and Applications
3 .Agenda 1 Business Blockchain Overview 2 Why Kubernetes for Blockchain 3 Deploy Fabric on Kubernetes 4 Summary
4 .
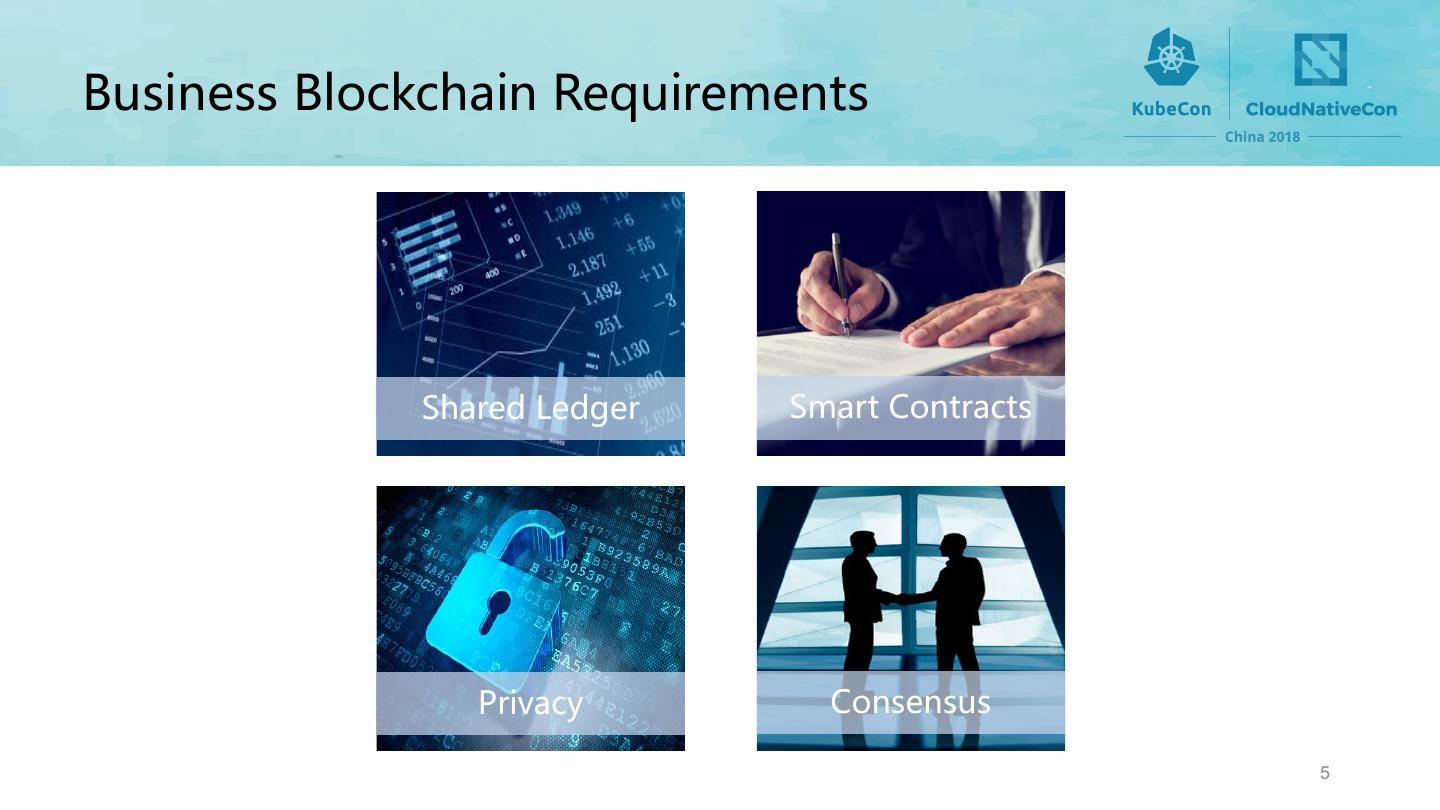
5 .5
6 . . , • . • , • , • • . . • • , 6
7 . 72 + 7 • 0 5 + 05 751 2 +0 • 5 +0 3 3 7 • Technology: IBM, Intel, Cisco, etc • Finance: JP Morgan, Well Fargos, DTCC, etc • Blockchain: R3, ConsenSys, DAH, etc. • 3 3 7 • 5 70 57 • 5330 7
8 .8
9 . ) . , • ) , , , 0 ) , 2 0) • , 2 0) ). • , ) . ) ) , ) • . , ) 0 ( 9
10 . . / / / ) ( ( / / B / /B / . // B B ( , , ) / / // . / . / . / ( , B ( ( 10
11 .11
12 .)B 2 21 2 0 • 2: 021 : 20 • 2A2 21 : ( : :1 21 0 : :2 0 2 • 2B 2 2 • : 0 : : 12: B • 002 0 : • B: 0 0 : : 12 • 2 2 5 5 • 1 2 0 : 0 05 :0 12 12
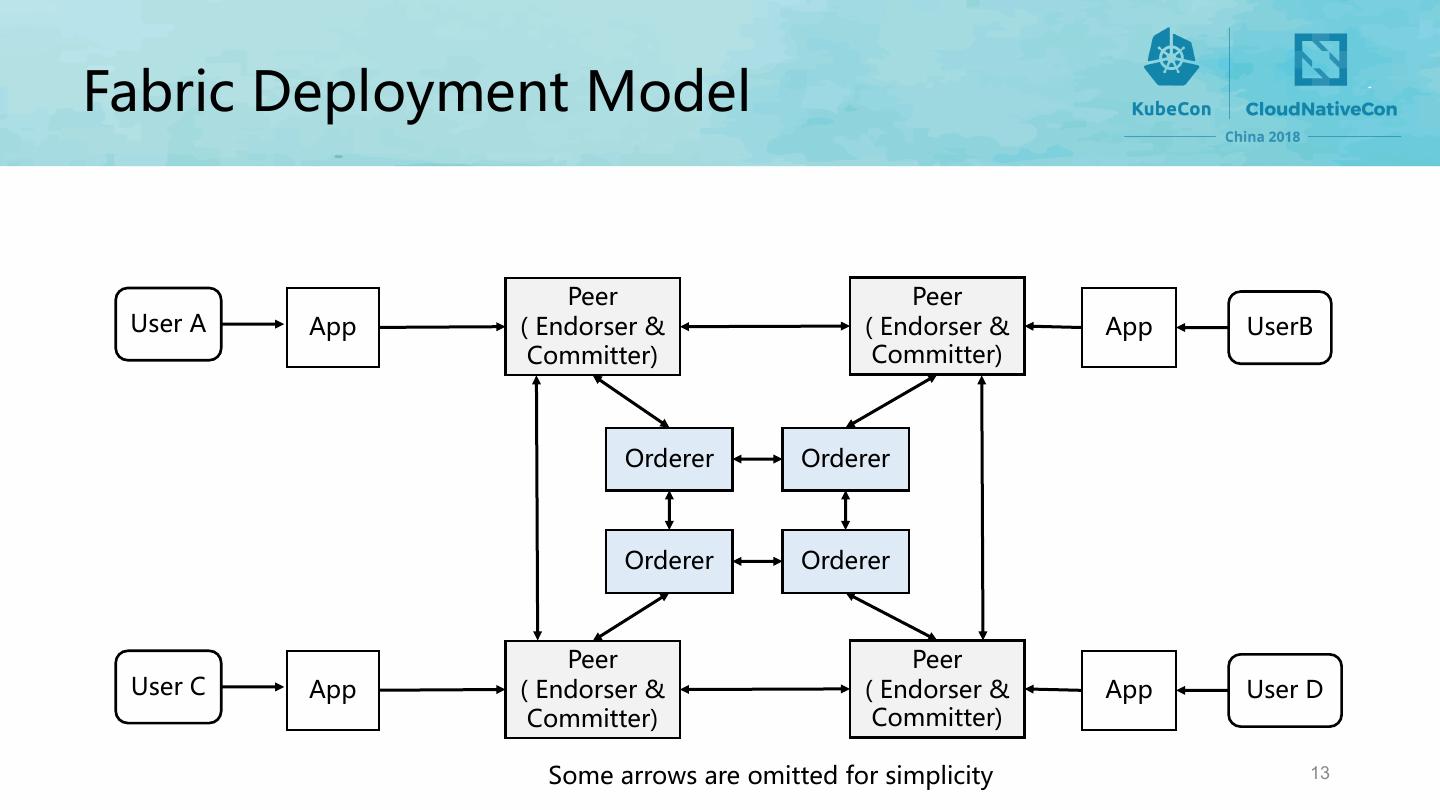
13 .) ) & & & & ) ) ( 13
14 .
15 . What is Kubernetes • Kubernetes, is an open-source platform for managing, automating deployment, scaling, and operating containerized applications across a cluster of worker nodes. Capabilities: • Deploy your applications quickly and predictably • Scale your applications on the fly • Seamlessly roll out new features • Optimize use of your hardware by using only the resources you need Role: • K8s sits in the Container as a Service (CaaS) or Container orchestration layer 15
16 .K8s introduces a lot new concepts • 10,000 ft. View K8s Cluster Pod 1 Pod 2 Worker node 1 • Cluster • Master Pod 3 Pod 4 Master • Workers (nodes) Worker node 2 • Pods Pod 5 Pod 6 Worker node 3 16
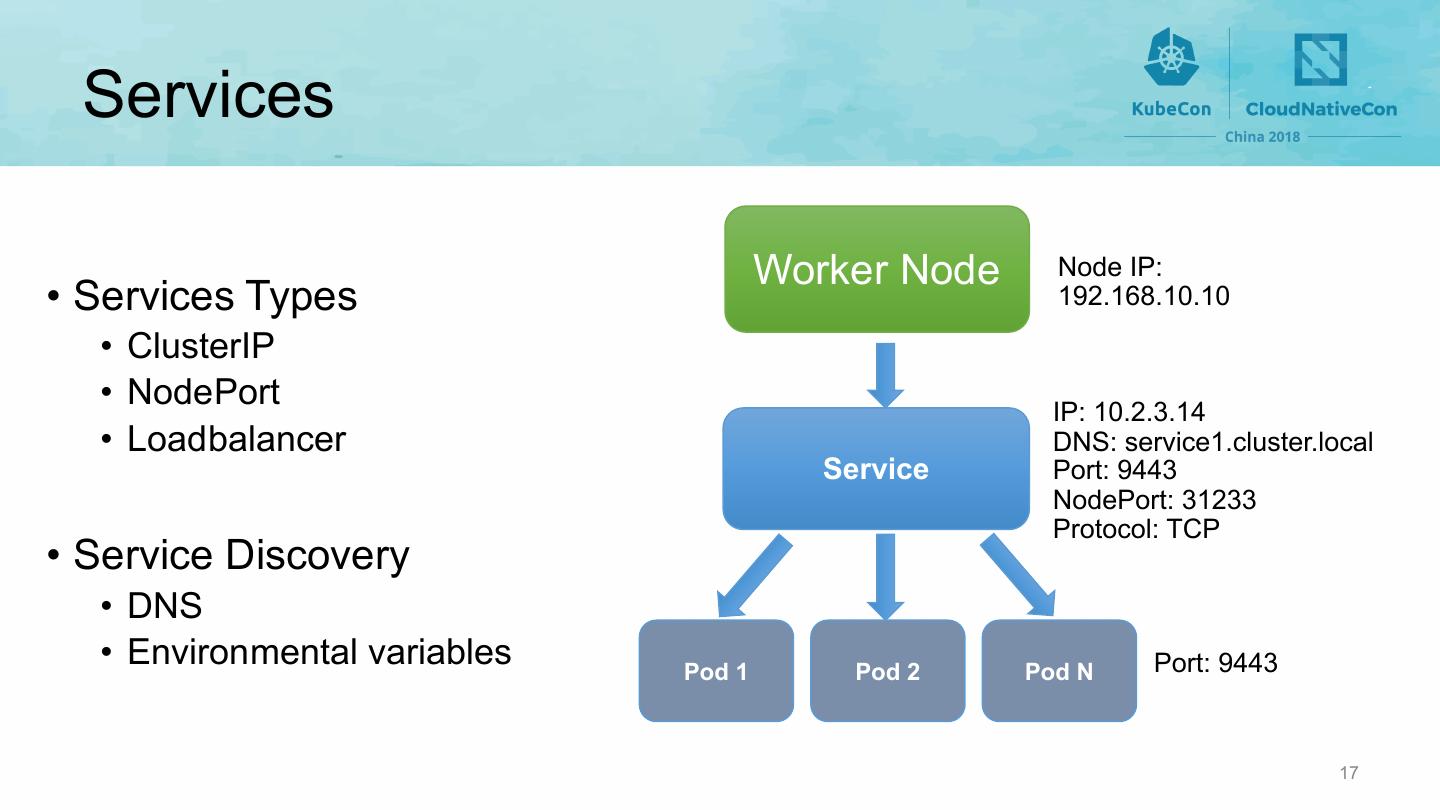
17 . Services Worker Node Node IP: • Services Types 192.168.10.10 • ClusterIP • NodePort IP: 10.2.3.14 • Loadbalancer DNS: service1.cluster.local Service Port: 9443 NodePort: 31233 Protocol: TCP • Service Discovery • DNS • Environmental variables Pod 1 Pod 2 Pod N Port: 9443 17
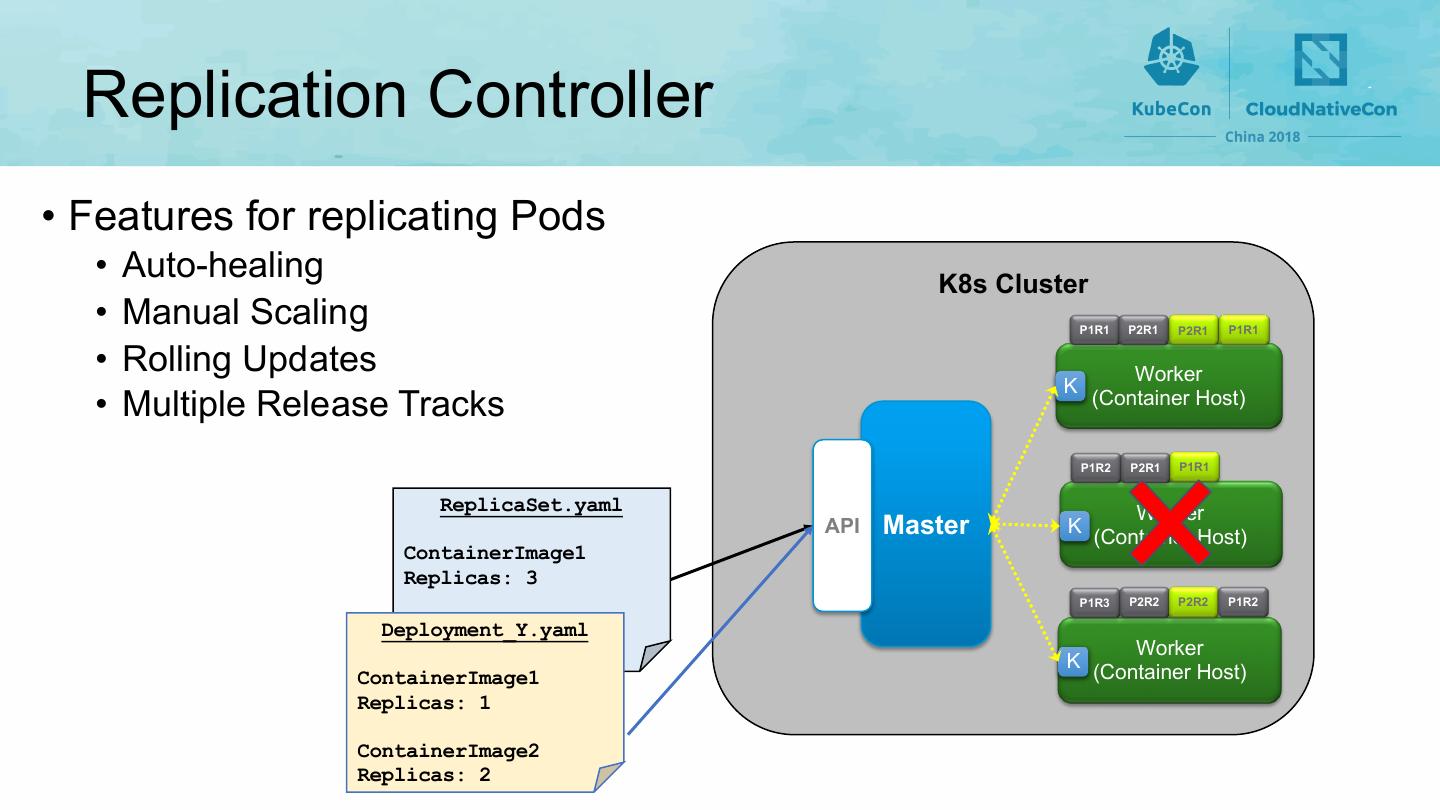
18 . Replication Controller • Features for replicating Pods • Auto-healing K8s Cluster • Manual Scaling P1R1 P2R1 P2R1 P1R1 • Rolling Updates Worker K • Multiple Release Tracks (Container Host) P1R2 P2R1 P1R1 ReplicaSet.yaml Worker API Master K (Container Host) ContainerImage1 Replicas: 3 P1R3 P2R2 P2R2 P1R2 ContainerImage2 Deployment_Y.yaml Replicas: 2 Worker K ContainerImage1 (Container Host) Replicas: 1 ContainerImage2 Replicas: 2
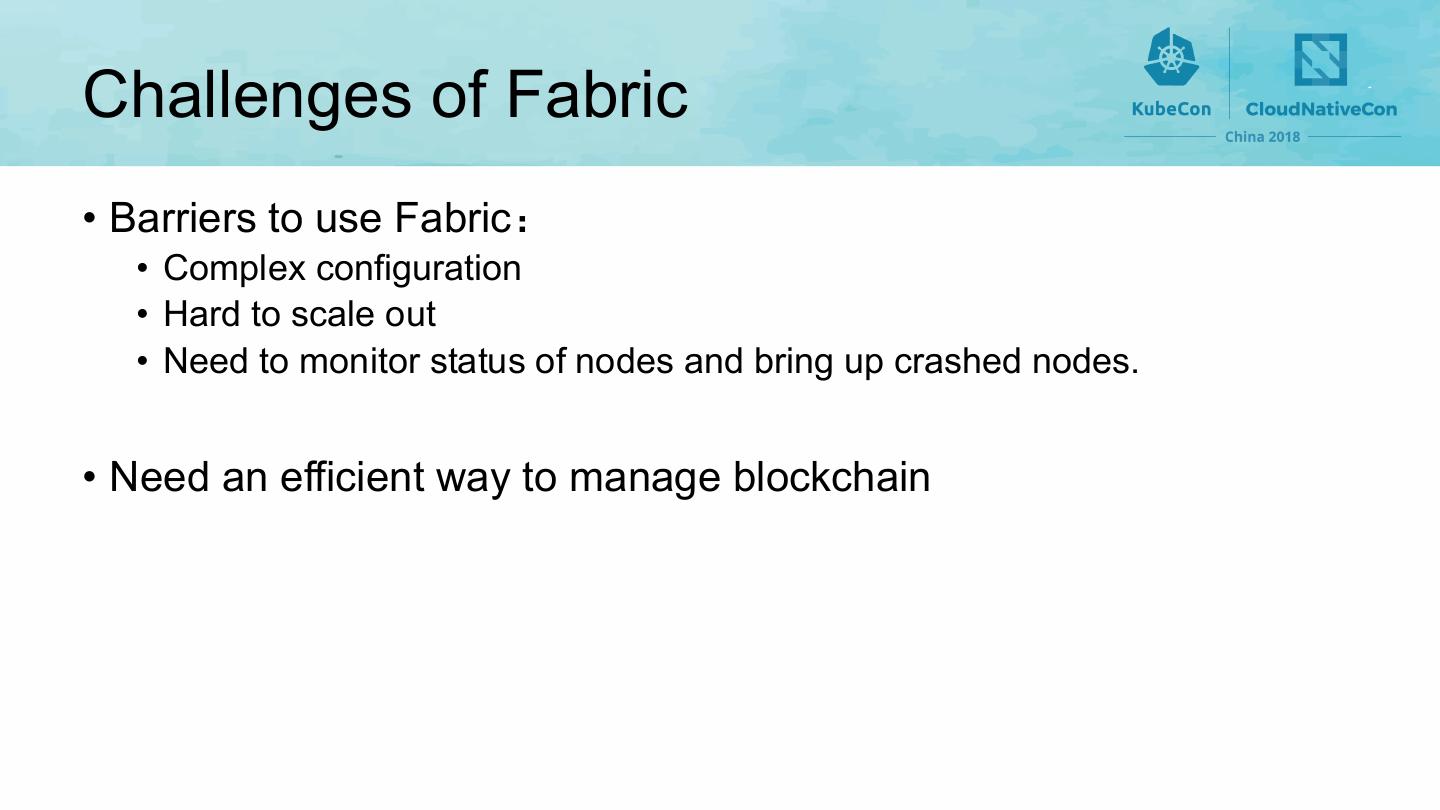
19 .Challenges of Fabric • Barriers to use Fabric • Complex configuration • Hard to scale out • Need to monitor status of nodes and bring up crashed nodes. • Need an efficient way to manage blockchain 19
20 .Why Kubernetes? • Fabric • Components are encapsulated in containers • Need the flexibility to configure and scale out • Kubernetes • Microservice oriented • Easy scaling • Tooling for operational management • Multi-tenancy support to segregation workload 20
21 .
22 .Network topology of Fabric Deployment Fabric Fabric Fabric Fabric kube_dns Pod Pod Pod Pod Pod NFS CMD client 10.0.0.10 Server flannel flannel flannel Master 10.0.0.1/16 Worker1 10.0.0.1/16 Worker2 10.0.0.1/16 192.168.0.1/24
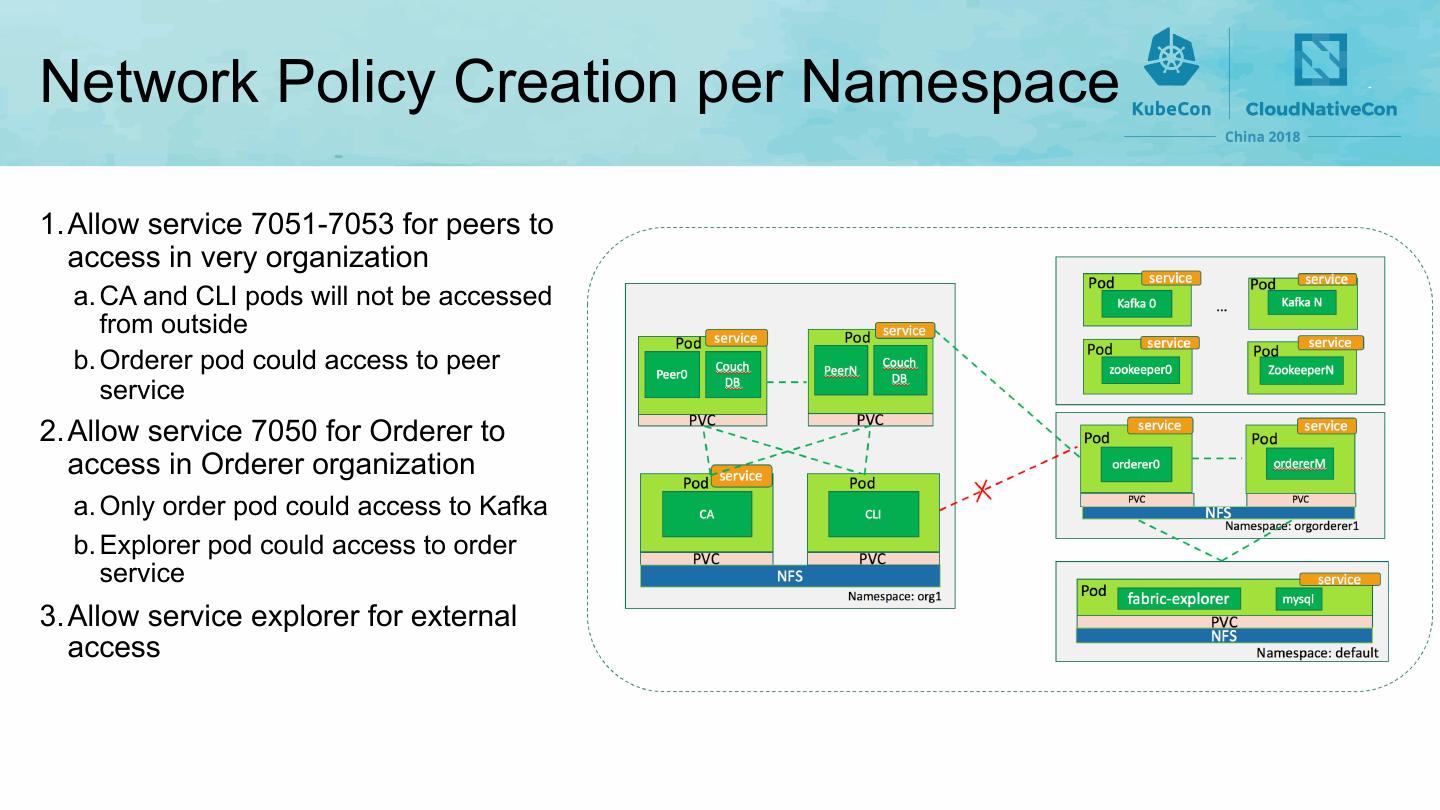
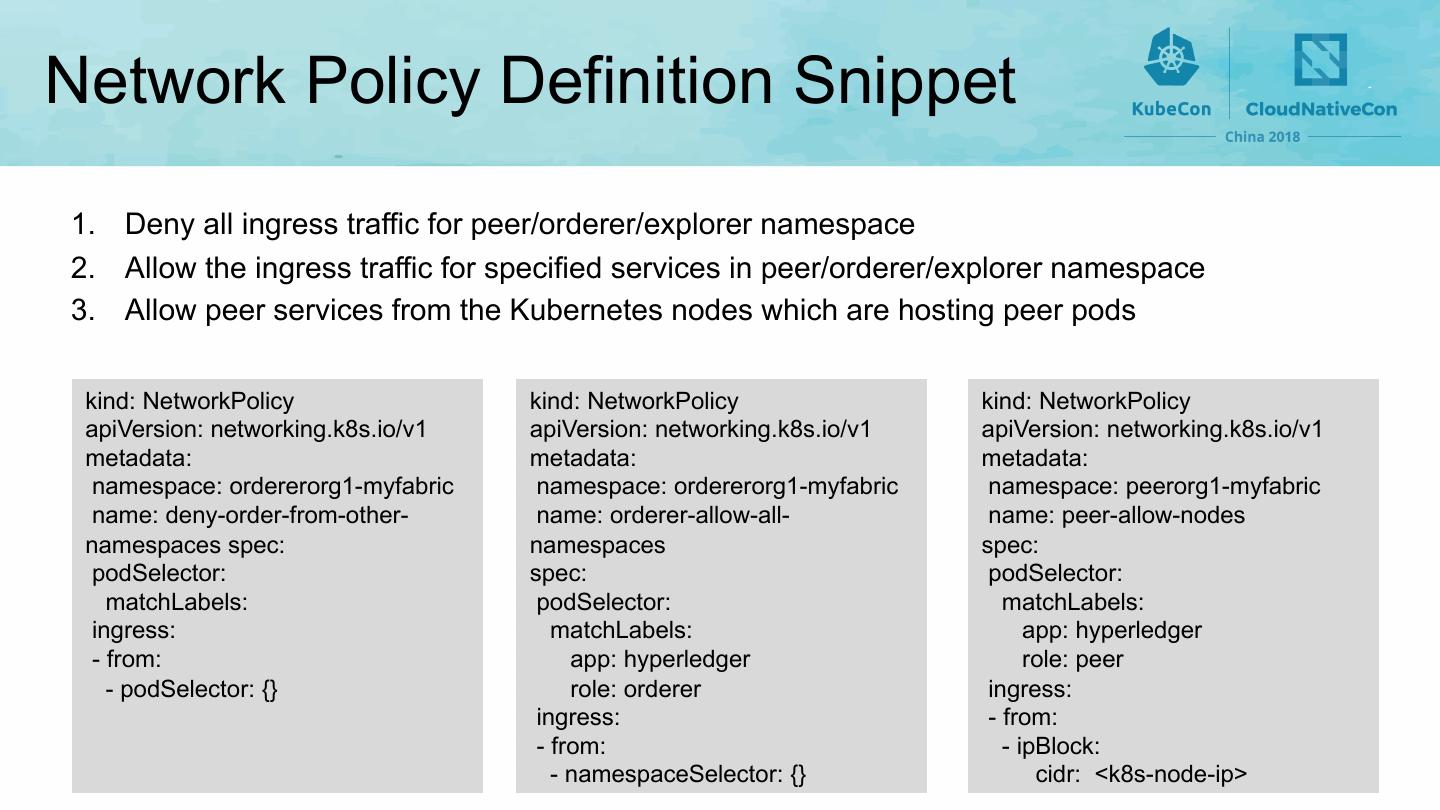
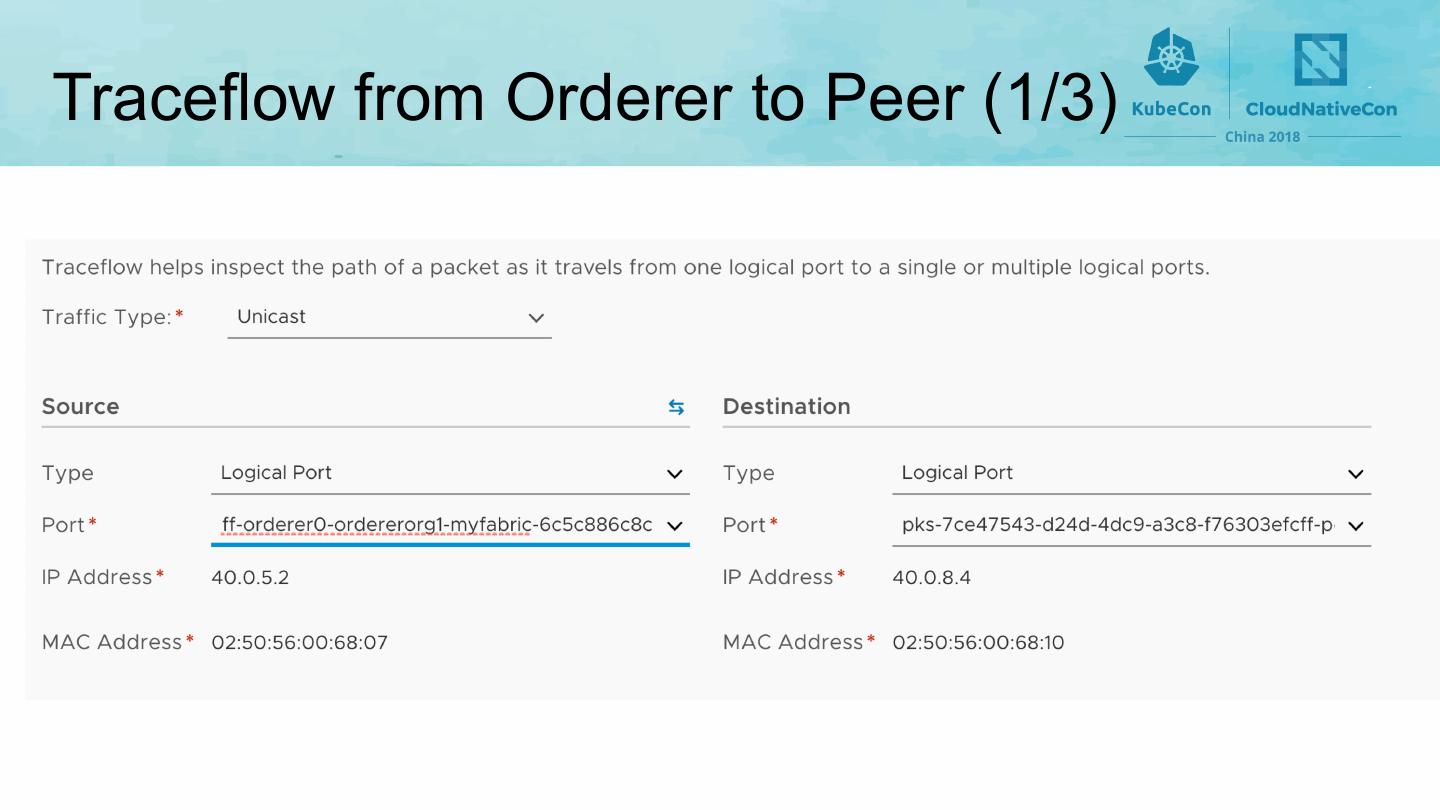
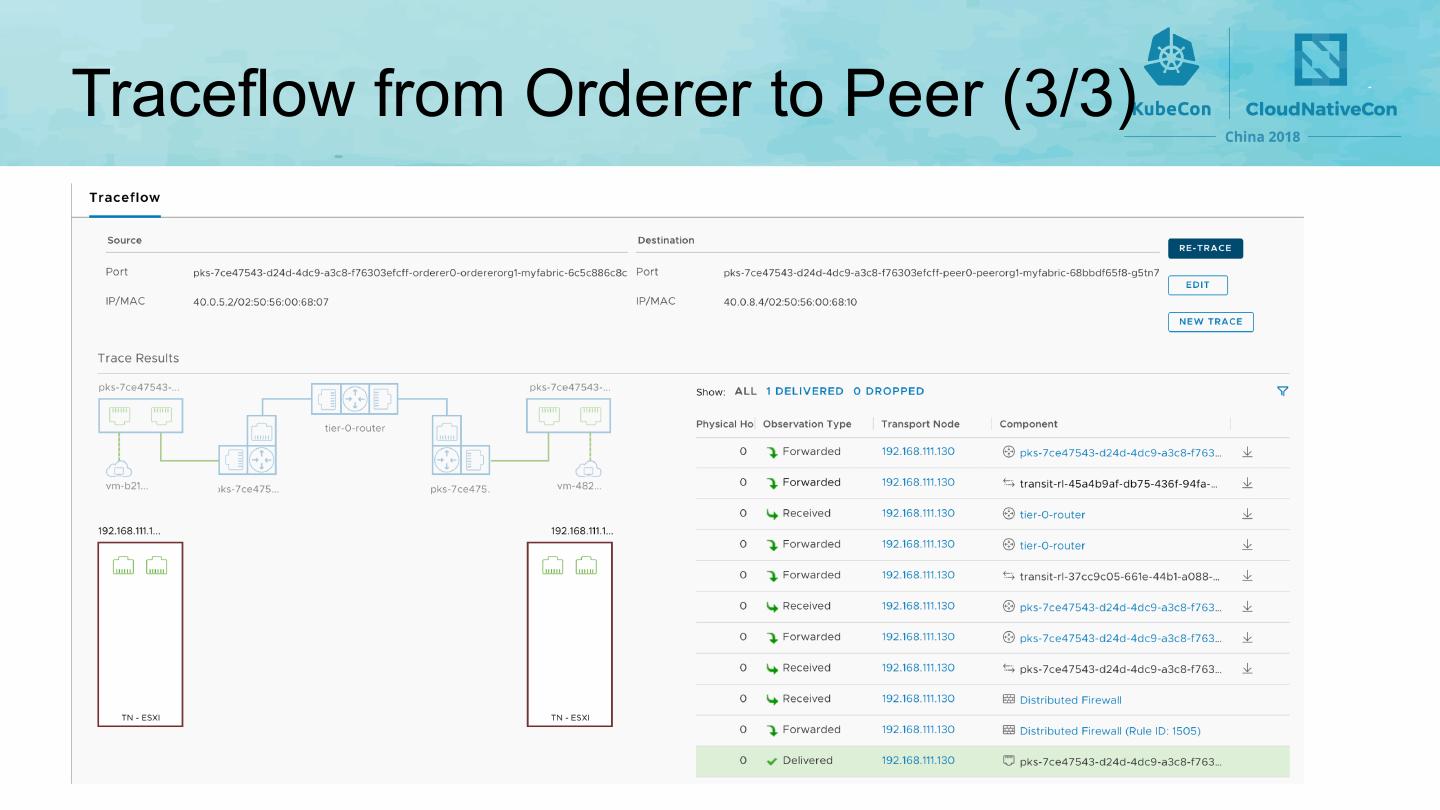
23 .Network • All pods are deployed on Kubernetes’ overlay network (such as flannel) • Mapping Kubernetes’ namespace to Fabric organization • Using namespaces to separate components of different organizations • Applying network policy to enforce isolation between organizations 23
24 .Storage • Configuration and data files are placed in shared storage (NFS) • Support pod portability between worker nodes • Use PV and PVC to limit visibility of data for peer nodes of Fabric 24
25 .Mapping Fabric Components into Pods • Peer Pod Fabric peer couchDB • CA Server Pod Fabric CA Server • CLI Pod: (Optional) CLI environment for the org • Orderer Pod: Orderer nodes • Kafka Pod Nodes of Kafka • Zookeeper Pod: Nodes of Zookeeper 25
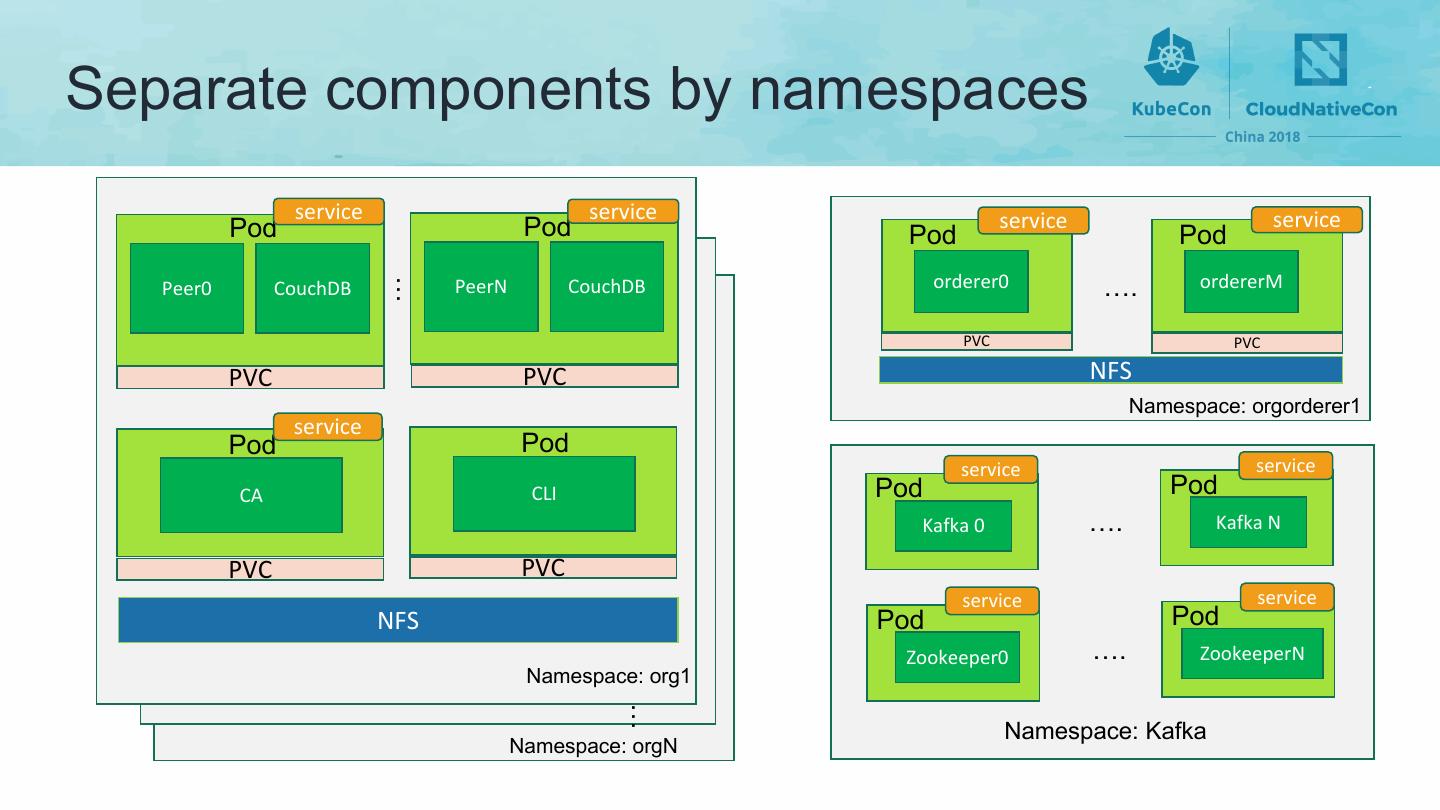
26 .Separate components by namespaces service service service service Pod Pod Pod Pod Peer0 CouchDB PeerN CouchDB orderer0 …. ordererM … Container PVC PVC PVC PVC NFS Namespace: orgorderer1 service Pod Pod service service CA CLI Pod Pod Kafka 0 …. Kafka N PVC PVC service service NFS Pod Pod Zookeeper0 …. ZookeeperN Namespace: org1 … Namespace: Kafka Namespace: orgN
27 .Exposing Services • Using NodePort for CA peer and Orderer services • Port mapping rules :( N>=1, M>=0) • Organization orgN port ranges 30000+(N-1)*100 ~ 30000+(N)*100-1 • orgN’s CA service port ca.orgN:7054 -> worker:30000+(N-1)*100 • Peer M of orgN exposes two ports: 7051, 7052 peerM.orgN:7051 -> worker:30000+(N-1)*100 + 2 * M + 1 peerM.orgN:7052 -> worker:30000+(N-1)*100 + 2 * M + 2 • ordererN port ordererN:7050 -> worker:33700+N
28 .Launching Fabric Cluster • Automate the process by scripts • Generate configuration files of Fabric components • Generate Pod definitions • Create definitions of PV and PVC • Start the cluster using kubectl commands 28
29 .Using Fabric Cluster • List all pods under namespace of org1 $ kubectl get pods –namespaces org1 • Enter cli-2586364563-vclmr Pod $ kubectl exec -it cli-2586364563-vclmr bash --namespace=org1 • Run Fabric command e.g. create a new channel $ peer channel create -o orderer0.orgorderer1:7050 \ -c mychannel -f ./channel-artifacts/channel.tx