- 快召唤伙伴们来围观吧
- 微博 QQ QQ空间 贴吧
- 文档嵌入链接
- 复制
- 微信扫一扫分享
- 已成功复制到剪贴板
014-Knowledge, Planning and Robotics
展开查看详情
1 .• 16 April 2011 • Alan, Edison, etc , Saturday.
2 . Knowledge, Planning and Robotics 1. Knowledge 2. Types of knowledge 3. Representation of knowledge 4. Planning 5. Knowledge for planning 6. Planning in robotics 7. Logic in robot planning and behavior
3 . Knowledge Representation 1. Representational adequacy 1. declarative, procedural 2. Inferential adequacy 1. manipulate knowledge 2. incorporate new knowledge
4 . Types of Knowledge 1. Simple facts 2. Complex organized knowledge 3. procedure - how to knowledge 4. meta-knowledge
5 . Semantic Data Models • High level model of model – Model of conceptual model • Not tied to implementation concerns • Focus on – expressiveness – simplicity – concise – formality
6 . Semantic Nets • Nodes represent Objects • Links or Arcs represent Relationships – “instance of” - set membership – “is a” - inheritance – “ has a” - attribute descriptors – “part of” - aggregation
7 . Is a Has a Part-of Instance of
8 . Semantic Nets Advantages Disadvantages • Flexible • Hard to deal with • easy to understand exceptions • support inheritance • procedural knowledge • difficult to represent “natural” way to represent knowledge • no standards for defining nodes or relationships
9 . Classes, Objects, Attributes, Values - Object Orientation • Classes describe common properties of objects • Objects may be physical or conceptual • Attributes are characteristics of objects • Values are specific measures of Attributes for specific instances
10 . Classes • Specify common properties of instances • support hierarchical classification • superclass / subclass – subclass may be more refined version – each subclass inherits operations and attributes of its ancestors – subclass may have its own operations and attributes
11 . Objects or Instances • Refers to things identified in model of conceptual model – may be tangible (equipment, part, orders, squashed bananas) – may be mental constructs
12 .Class vs instances instances
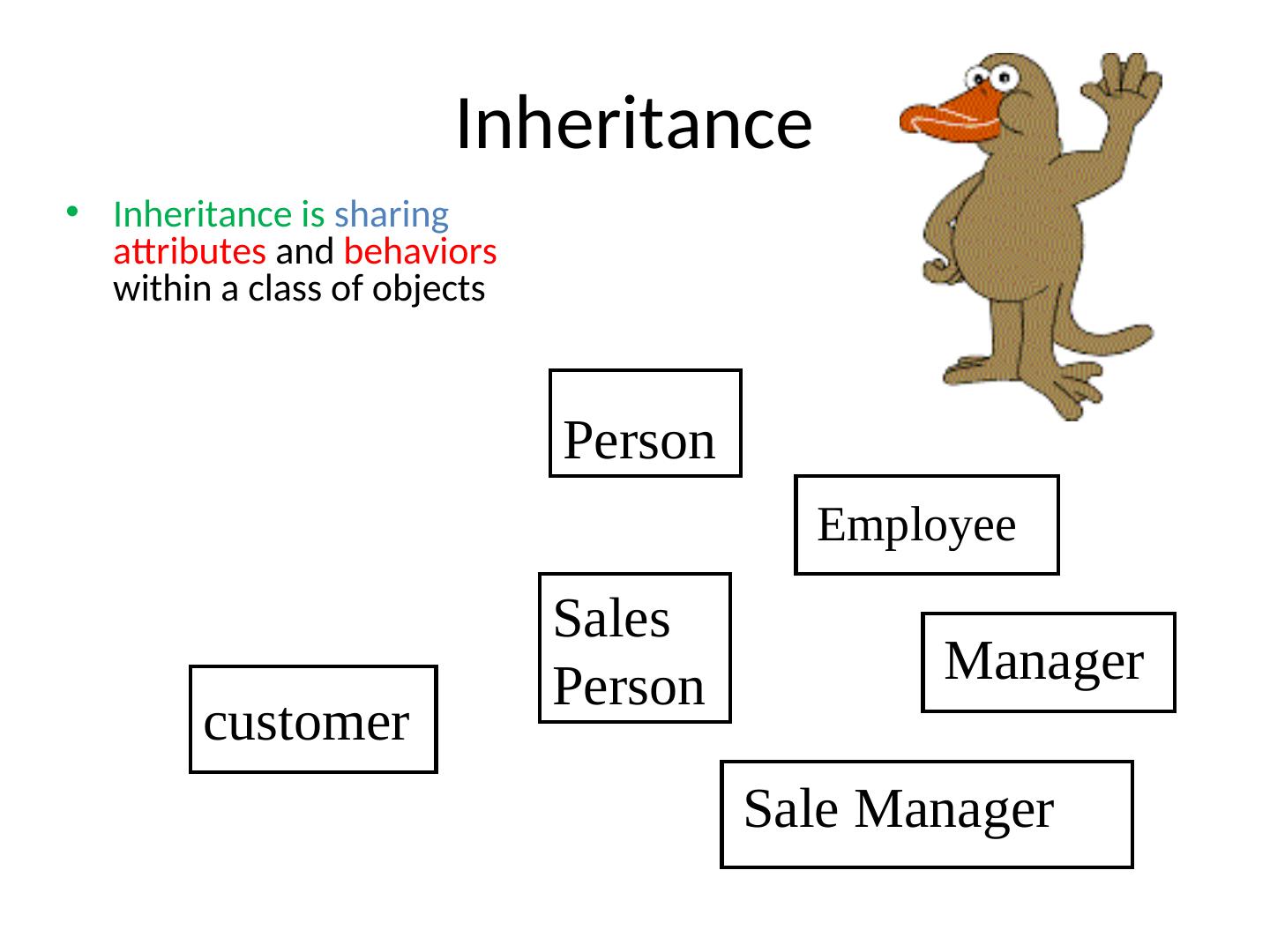
13 . Inheritance • Inheritance is sharing attributes and behaviors within a class of objects Person Employee Sales Person Manager customer Sale Manager
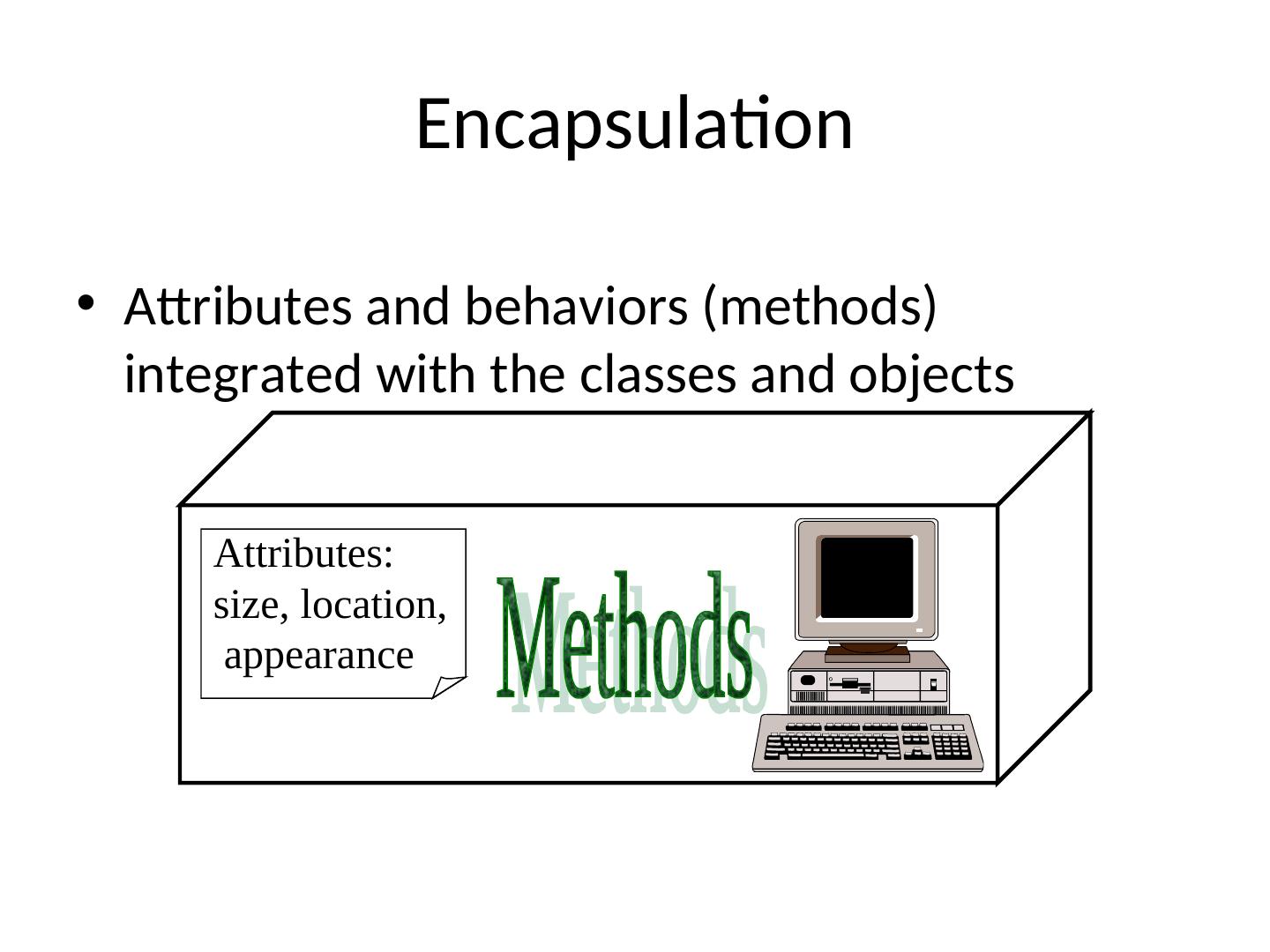
14 . Encapsulation • Attributes and behaviors (methods) integrated with the classes and objects Attributes: size, location, appearance
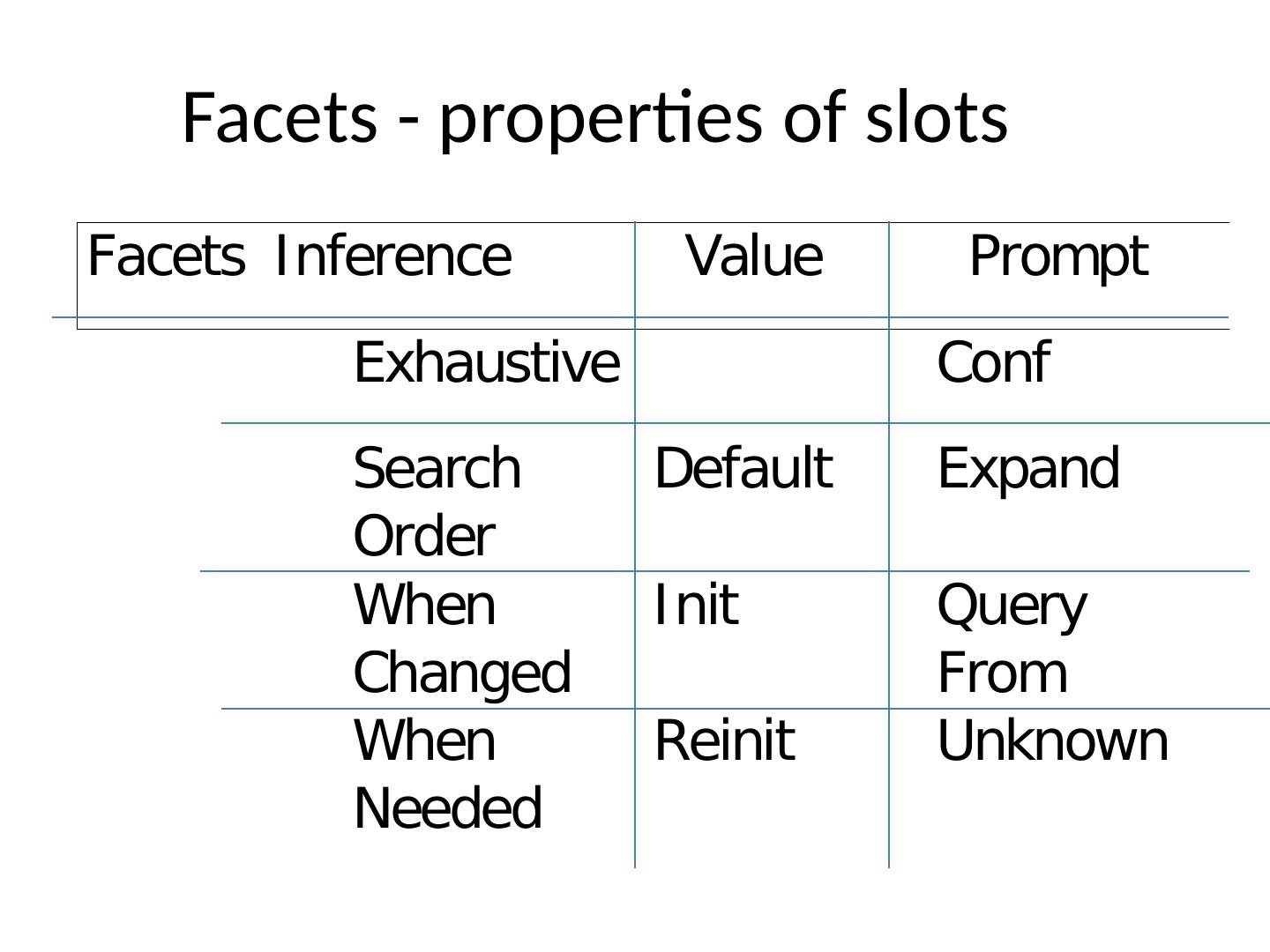
15 . Polymorphism • Each object responds in its unique way to messages When changed method When needed method
16 . Object-Orientation • Tool for managing complexity 1. emphasis on object structure 2. specify “what is” 3. mapped directly from semantic net
17 . Rule Representations • Rules are called productions • Rule have two parts – condition part, premise -> IF – action part ,conclusion-> THEN • The action can: – add a fact to the knowledge base, – start a procedure – or display a screen
18 . Rules represent knowledge • Apply O-A-V framework (object-attribute- value) • IF air vehicle is a plane AND plane maximum altitude is 40000 AND plane manufacturer is Boeing THEN ASK Flight Display 15
19 . Representing knowledge • Abstracting with rules – translate quantitative to qualitative – define technical terms – support generalized reasoning • make rules for user – easy to understand – help user follow decision logic
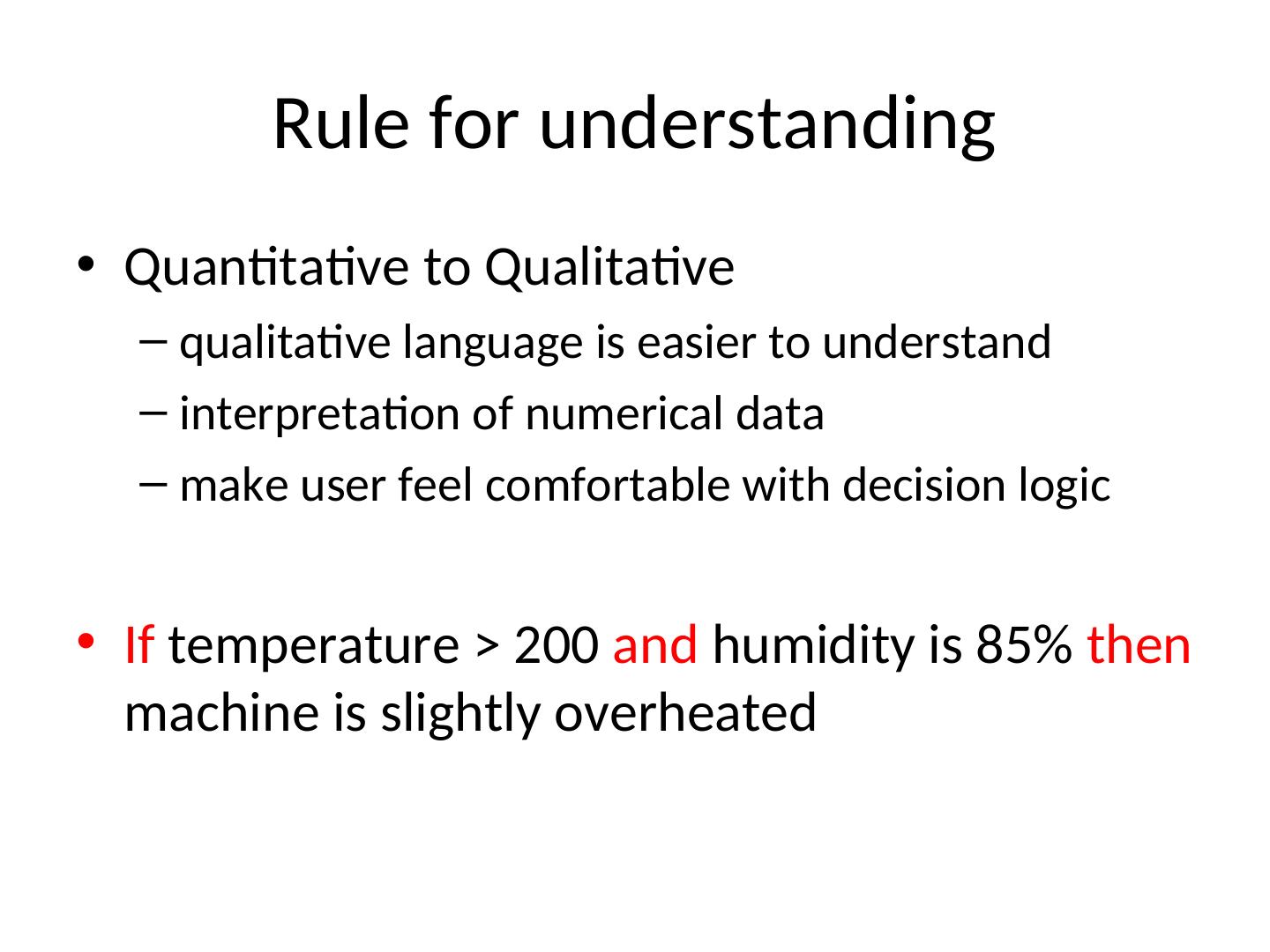
20 . Rule for understanding • Quantitative to Qualitative – qualitative language is easier to understand – interpretation of numerical data – make user feel comfortable with decision logic • If temperature > 200 and humidity is 85% then machine is slightly overheated
21 . Definitional Rules • Help communicate and train users • Help user understand vocabulary • Promotes common agreement on terms for expert, user and knowledge engineer • IF you want more than one source file of classes THEN use package keyword
22 . Rules support Generalizations • Allow reasoning with from specialization to generalizations • Support classification of objects at higher levels • Support refinements
23 . Surface Knowledge 1. Hard to understand 2. Difficult to learn reasoning strategies 3. hard to update and expand knowledge base If pump operation temperature is over 300 AND water mixture pH > 5.2 THEN replace pump bearing and oil
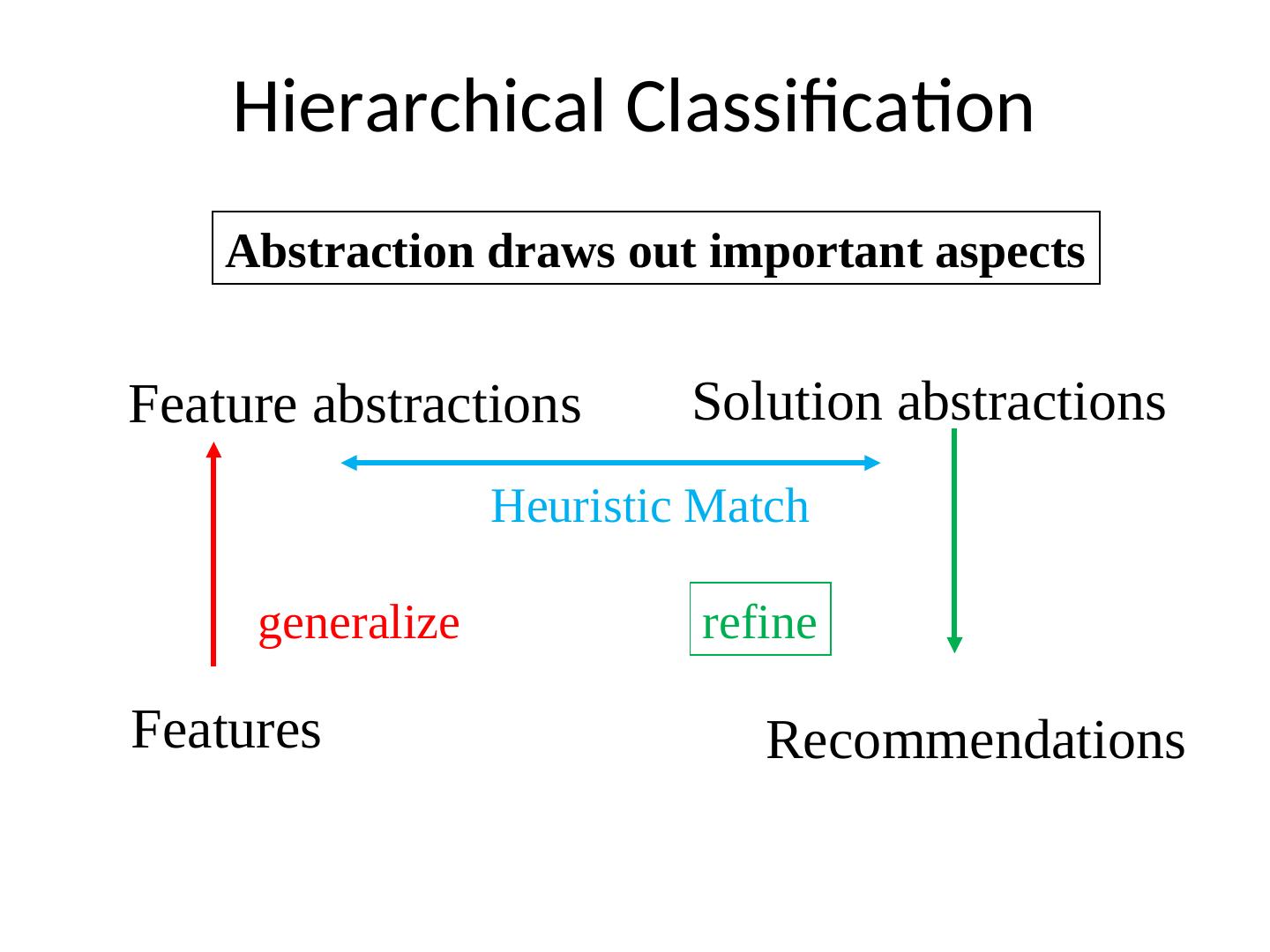
24 . Hierarchical Classification Abstraction draws out important aspects Feature abstractions Solution abstractions Heuristic Match generalize refine Features Recommendations
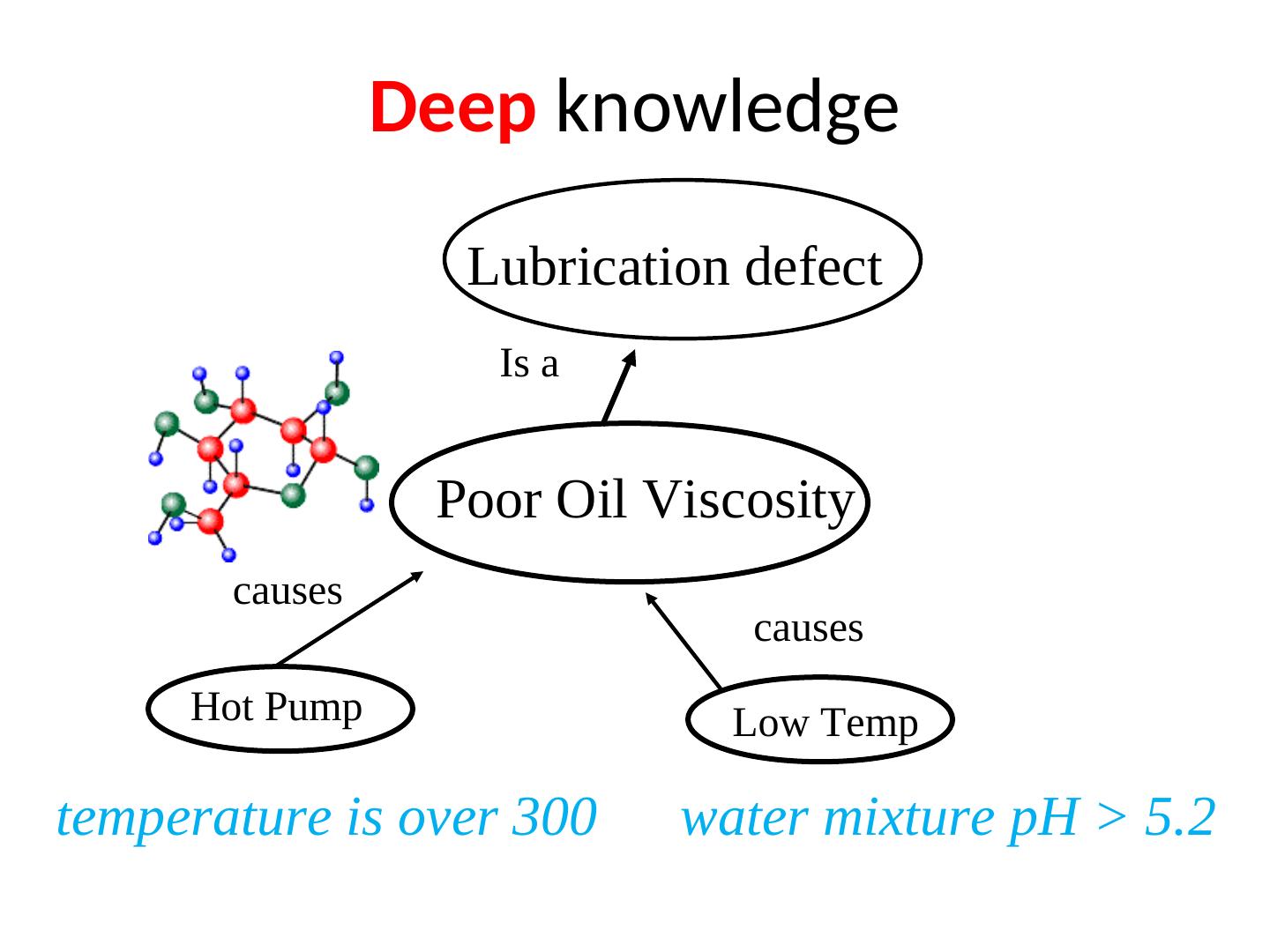
25 . Deep knowledge Lubrication defect Is a Poor Oil Viscosity causes causes Hot Pump Low Temp temperature is over 300 water mixture pH > 5.2
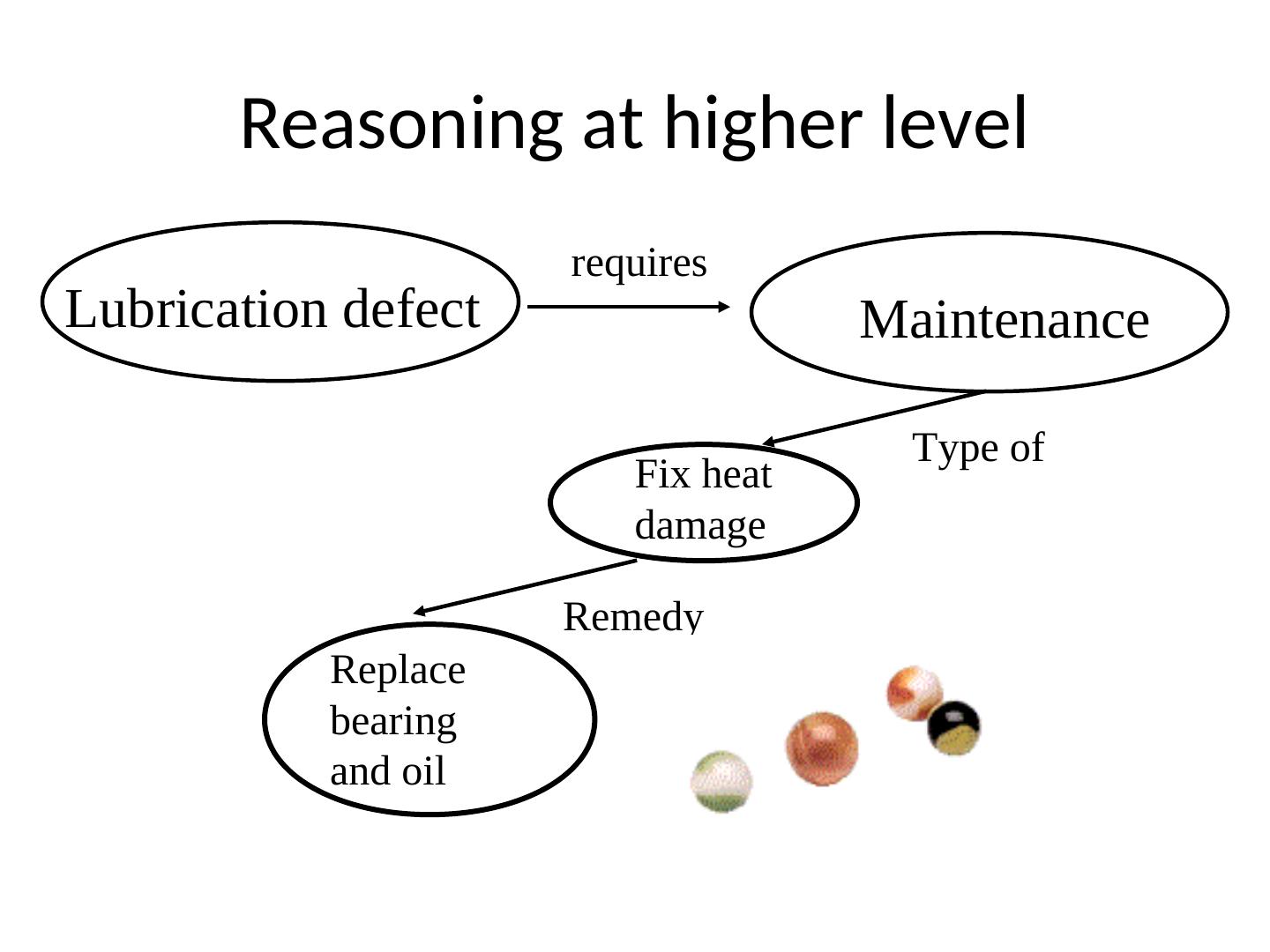
26 . Reasoning at higher level requires Lubrication defect Maintenance Type of Fix heat damage Remedy Replace bearing and oil
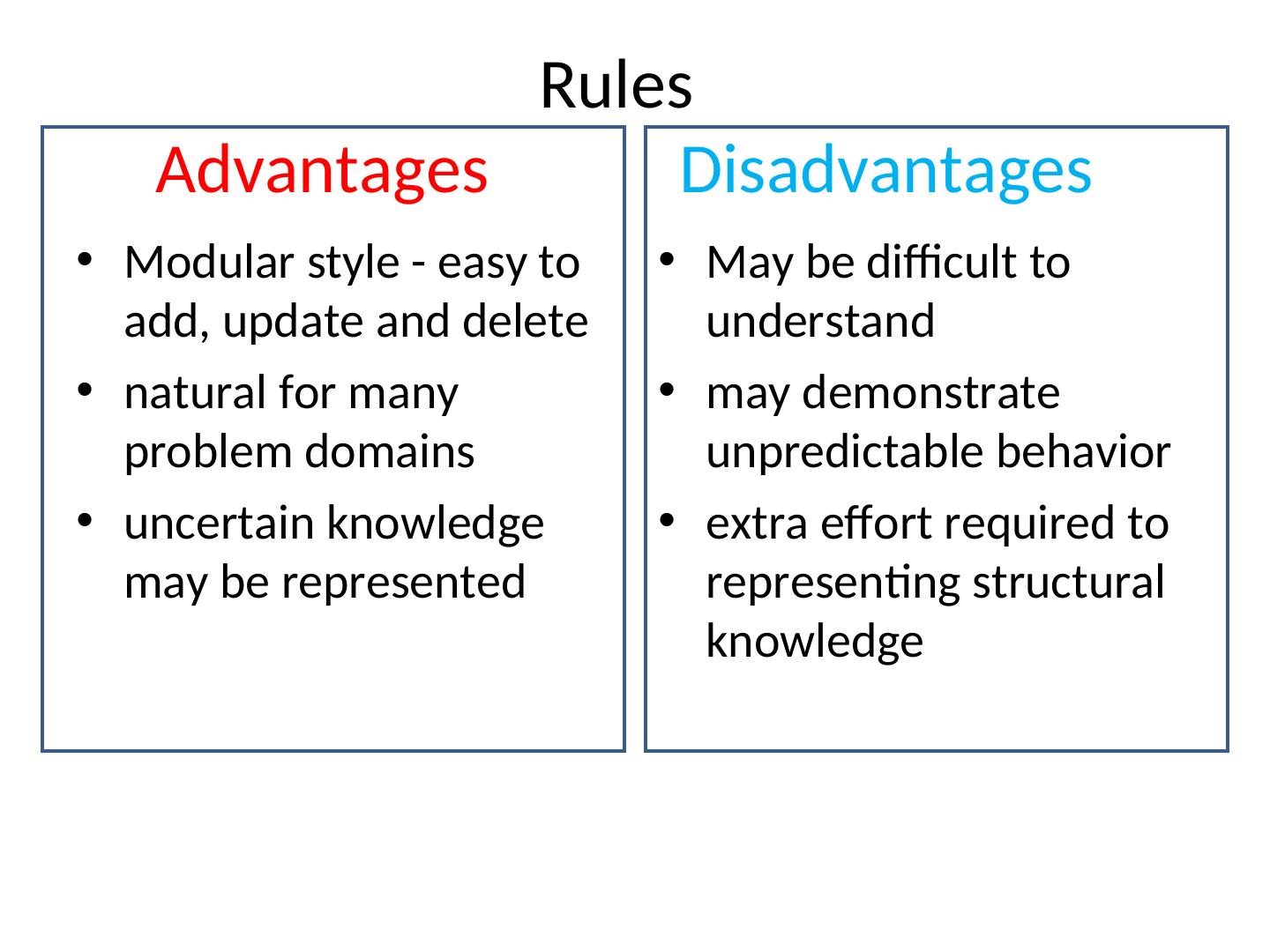
27 . Rules Advantages Disadvantages • Modular style - easy to • May be difficult to add, update and delete understand • natural for many • may demonstrate problem domains unpredictable behavior • uncertain knowledge • extra effort required to may be represented representing structural knowledge
28 . Predicate Logic • Programming by description • describe the problem’s facts • built in inference engine combines and uses facts and rules to make inferences
29 . Prolog Programming • Declaring facts about objects and their relationships -> likes (john,mary) • Defining rules about objects and relationships • Asking Questions about objects sister-of(X,Y) :- female(X), parents(X,M,F), parent(Y,M,F)