- 快召唤伙伴们来围观吧
- 微博 QQ QQ空间 贴吧
- 文档嵌入链接
- 复制
- 微信扫一扫分享
- 已成功复制到剪贴板
12_Expert Systems
展开查看详情
1 .EXPERT SYSTEMS
2 .Review – Classical Expert Systems Can incorporate Neural, Genetic and Fuzzy Components
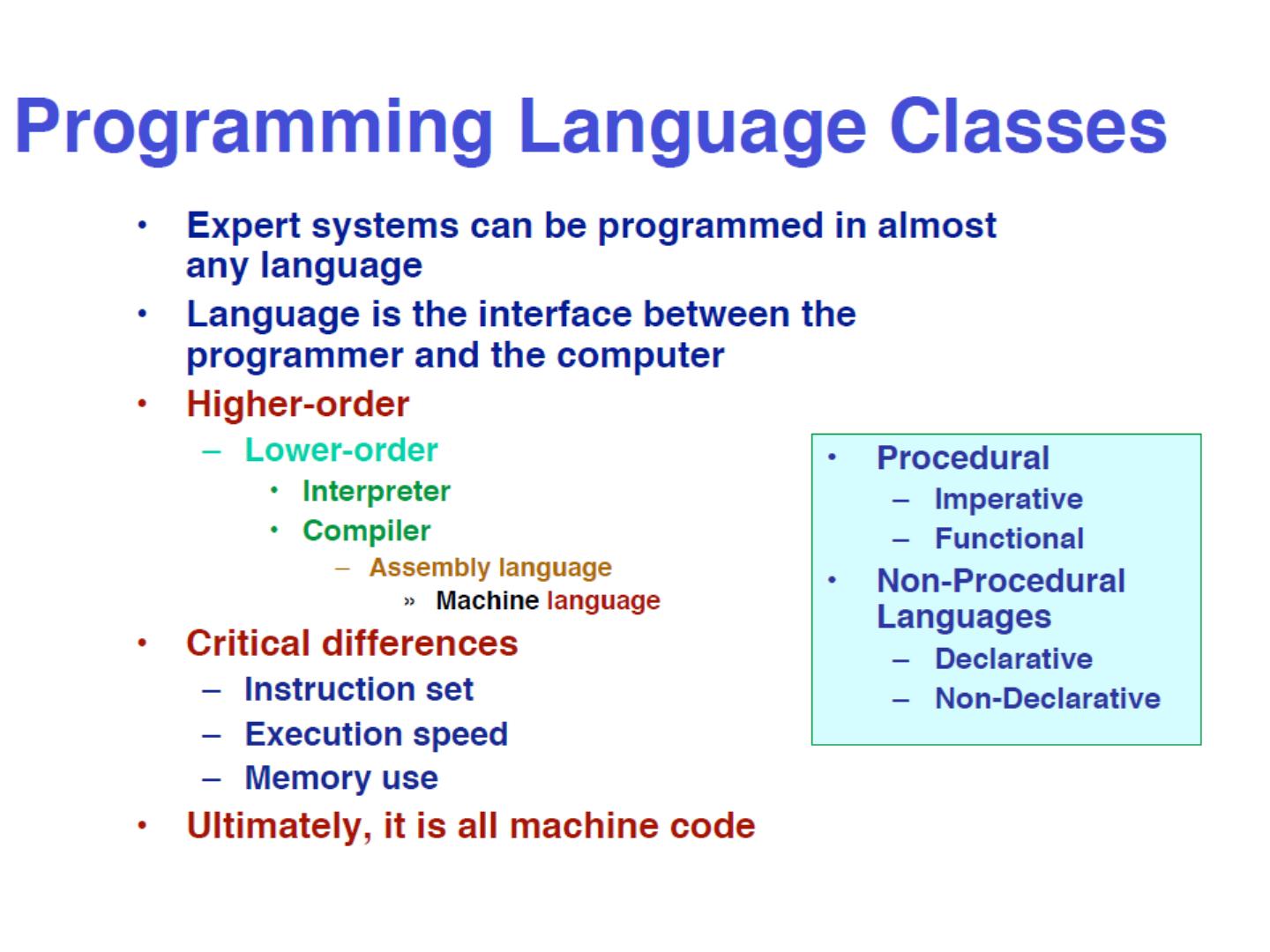
3 .Many expert systems are based on rules
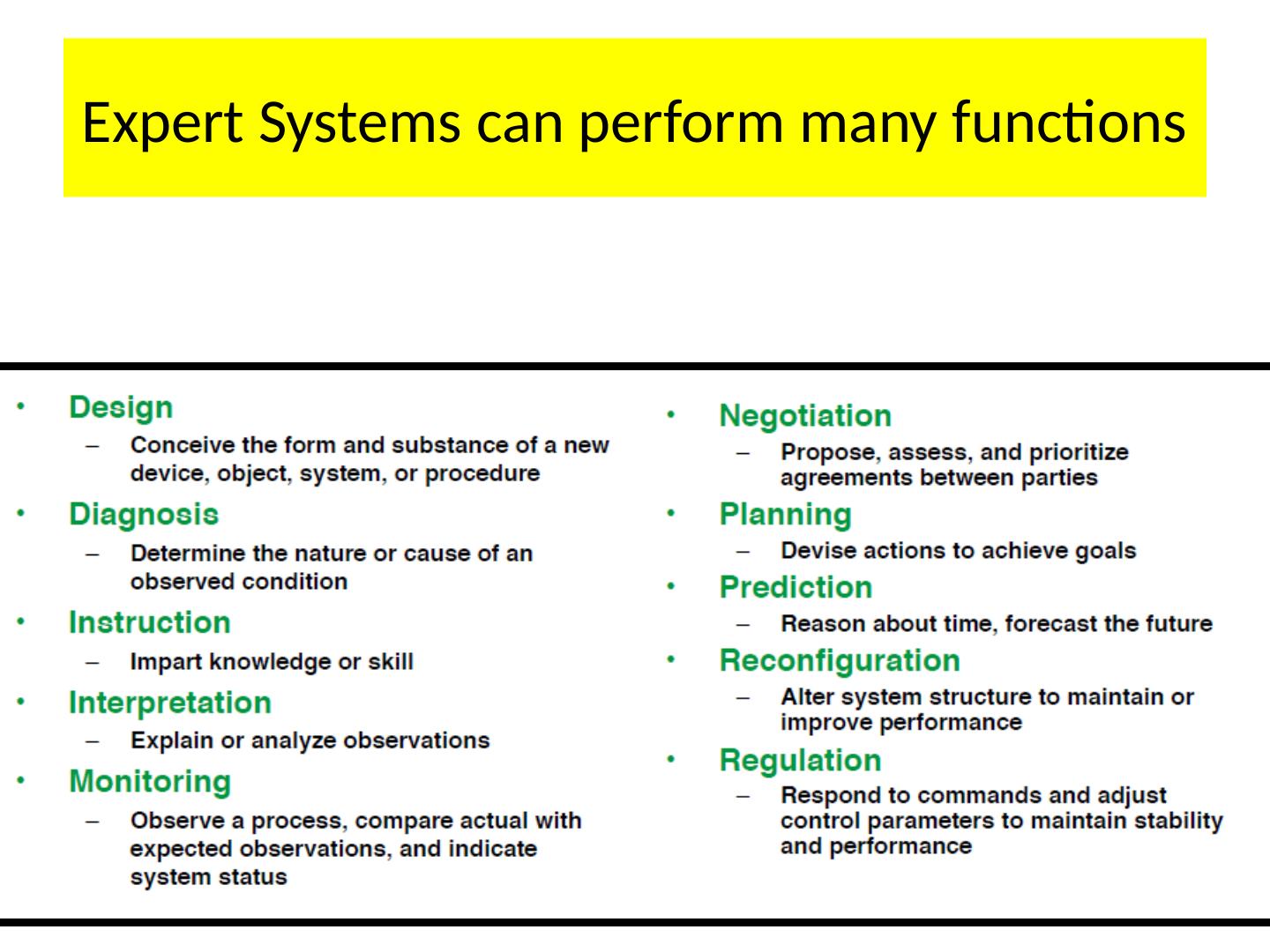
4 .Expert Systems can perform many functions
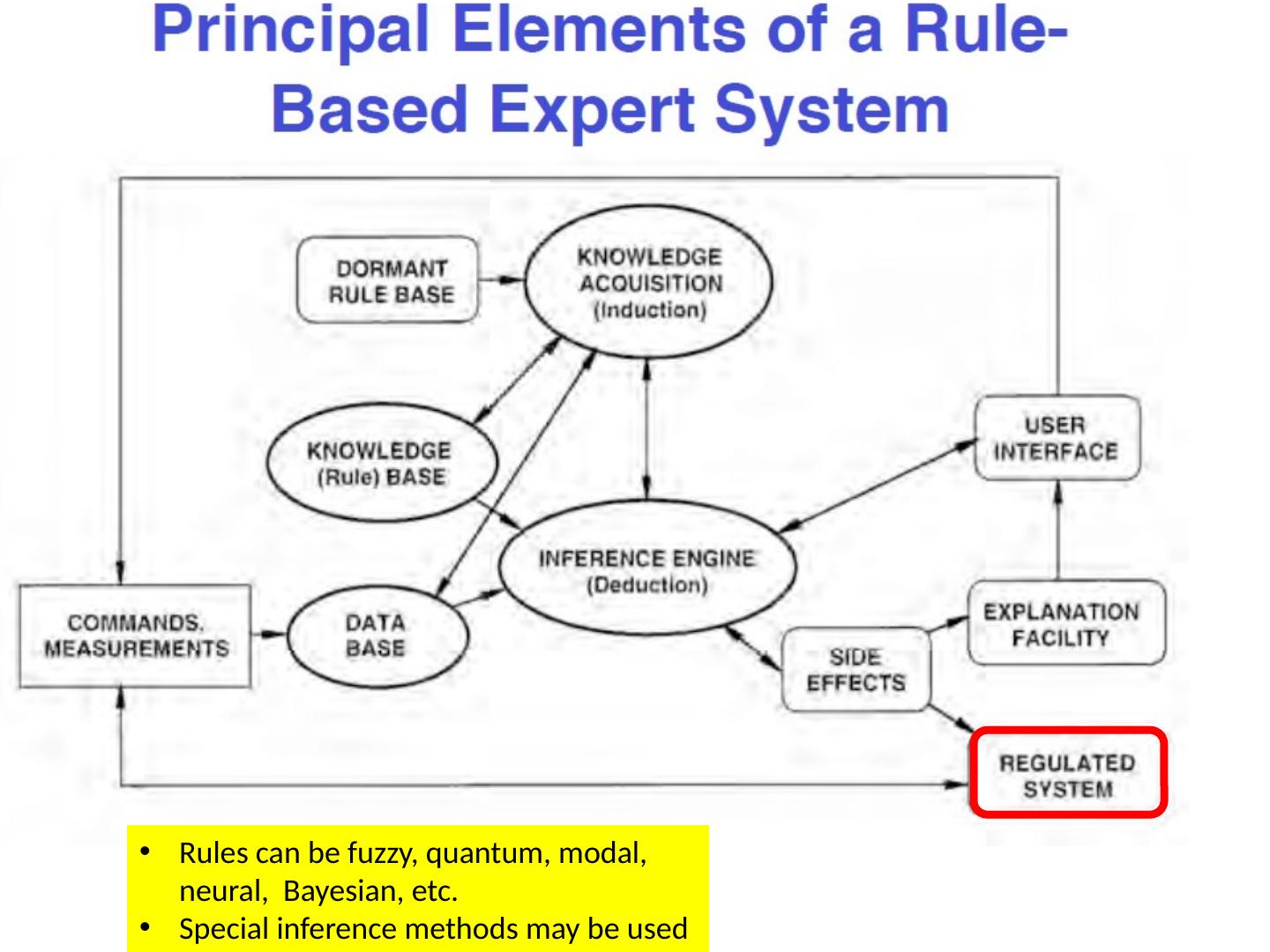
5 .Rules can be fuzzy, quantum, modal, neural, Bayesian, etc. Special inference methods may be used
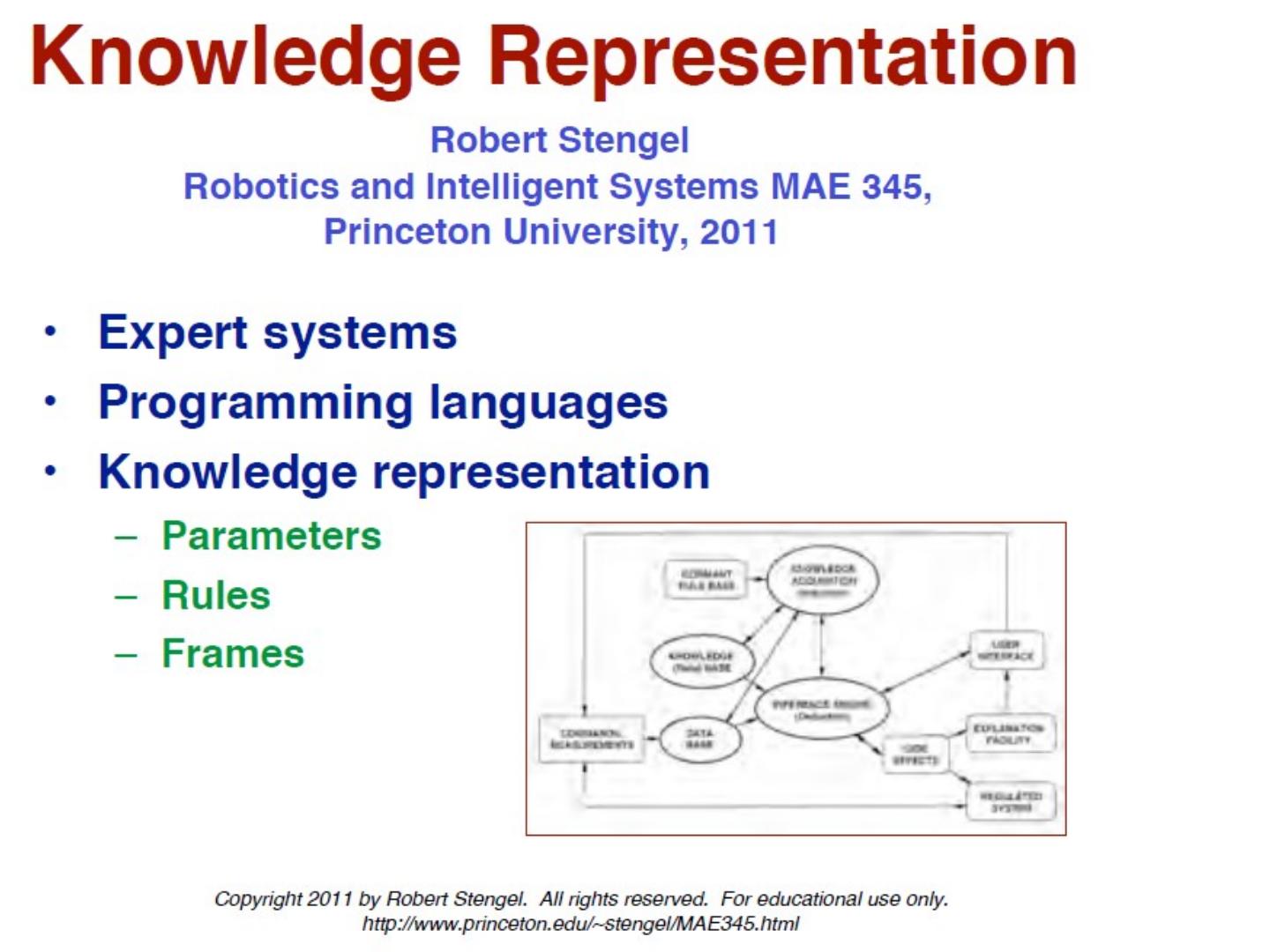
6 .Concepts of Knowledge Representation: INFERENCE
7 .Inference versus Knowledge Representation
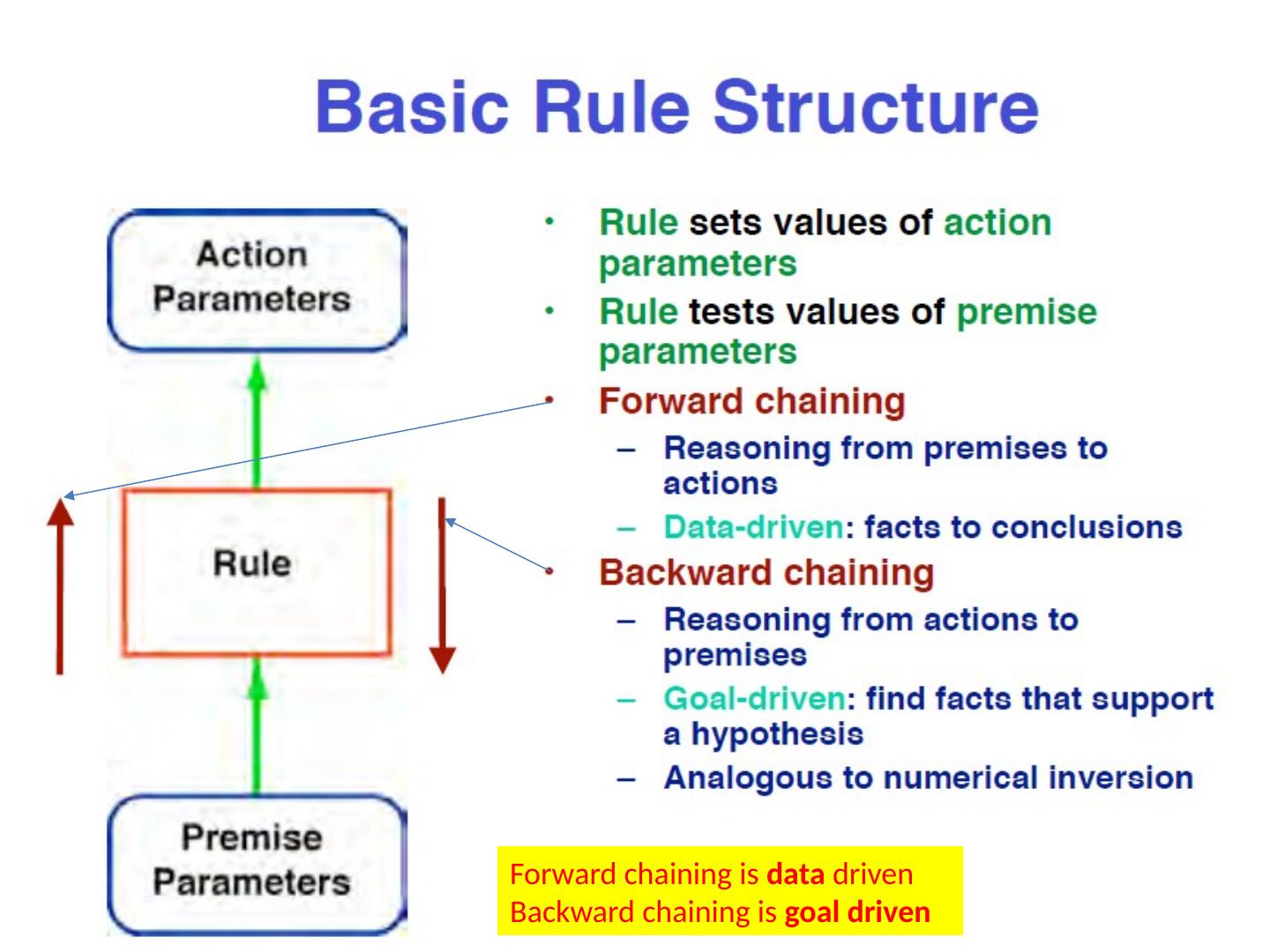
8 .Forward chaining is data driven Backward chaining is goal driven
9 .
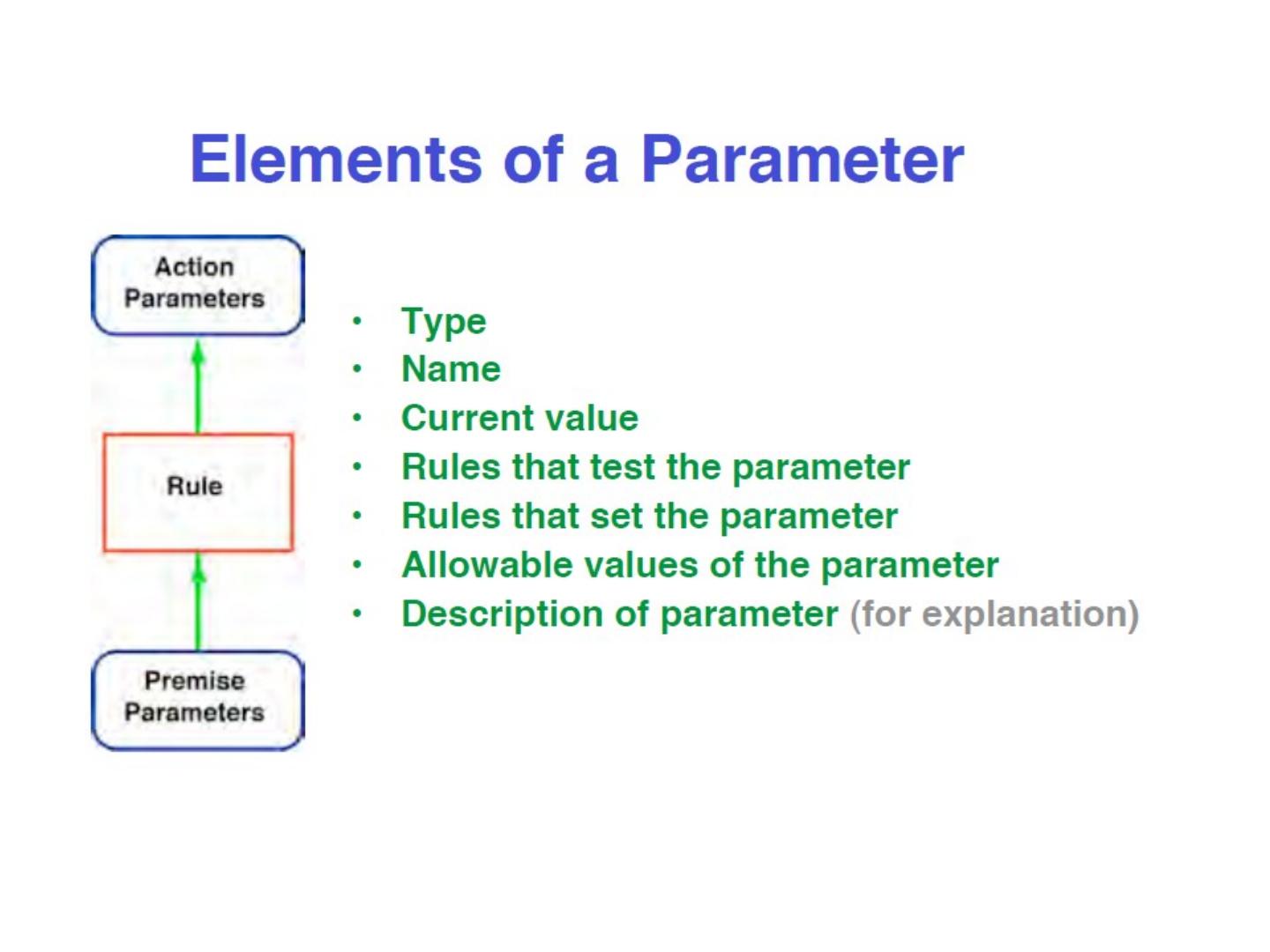
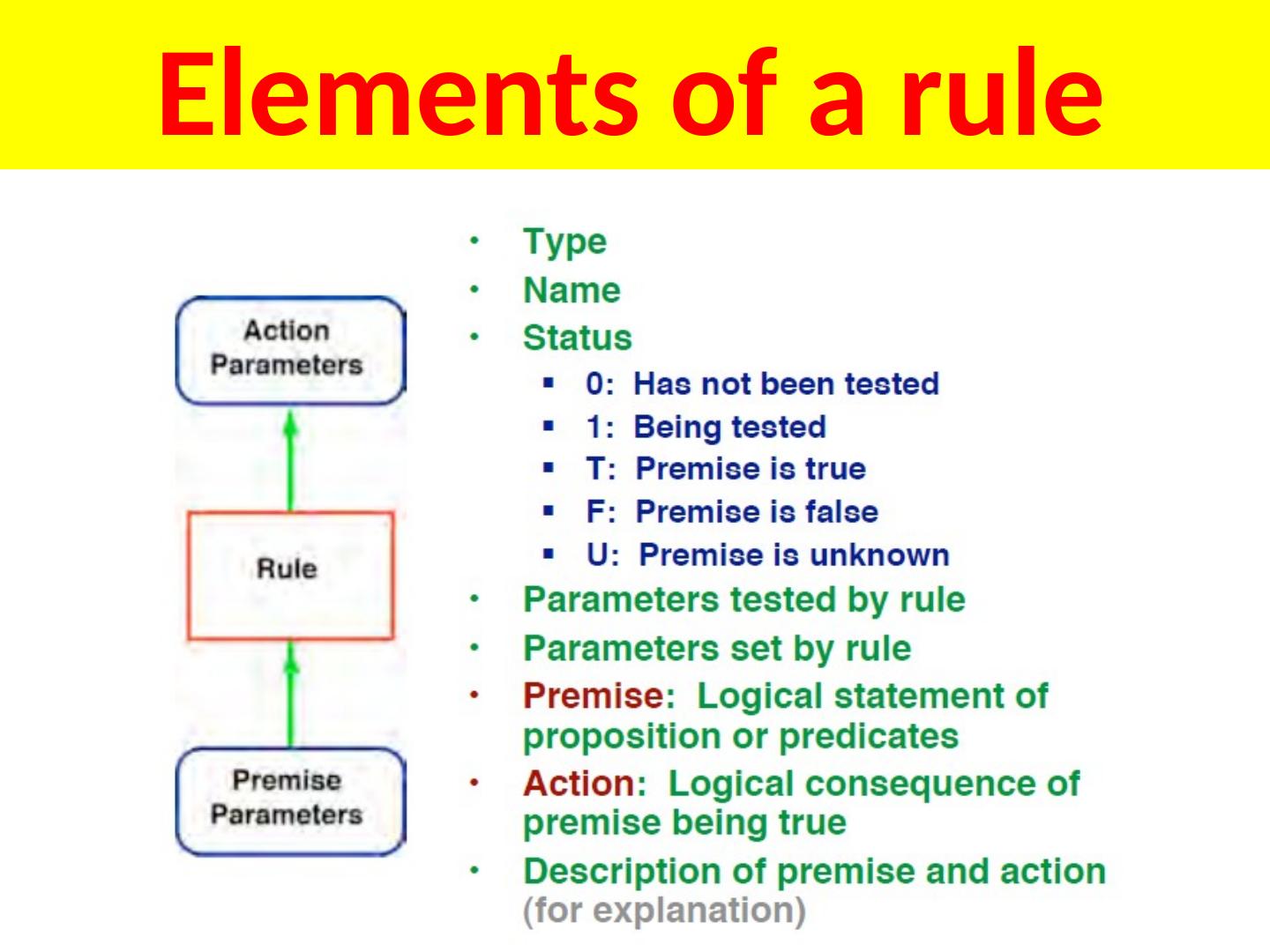
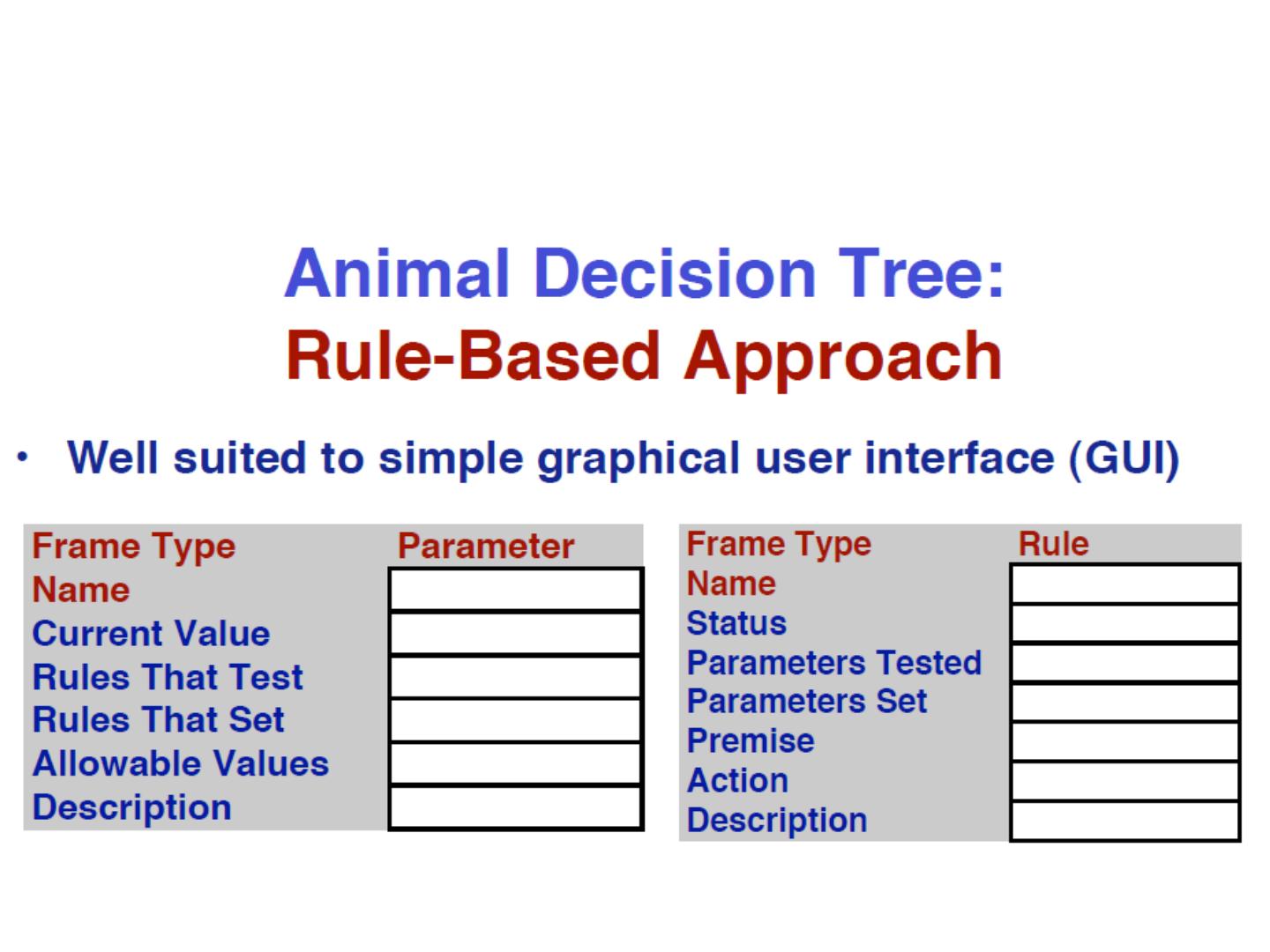
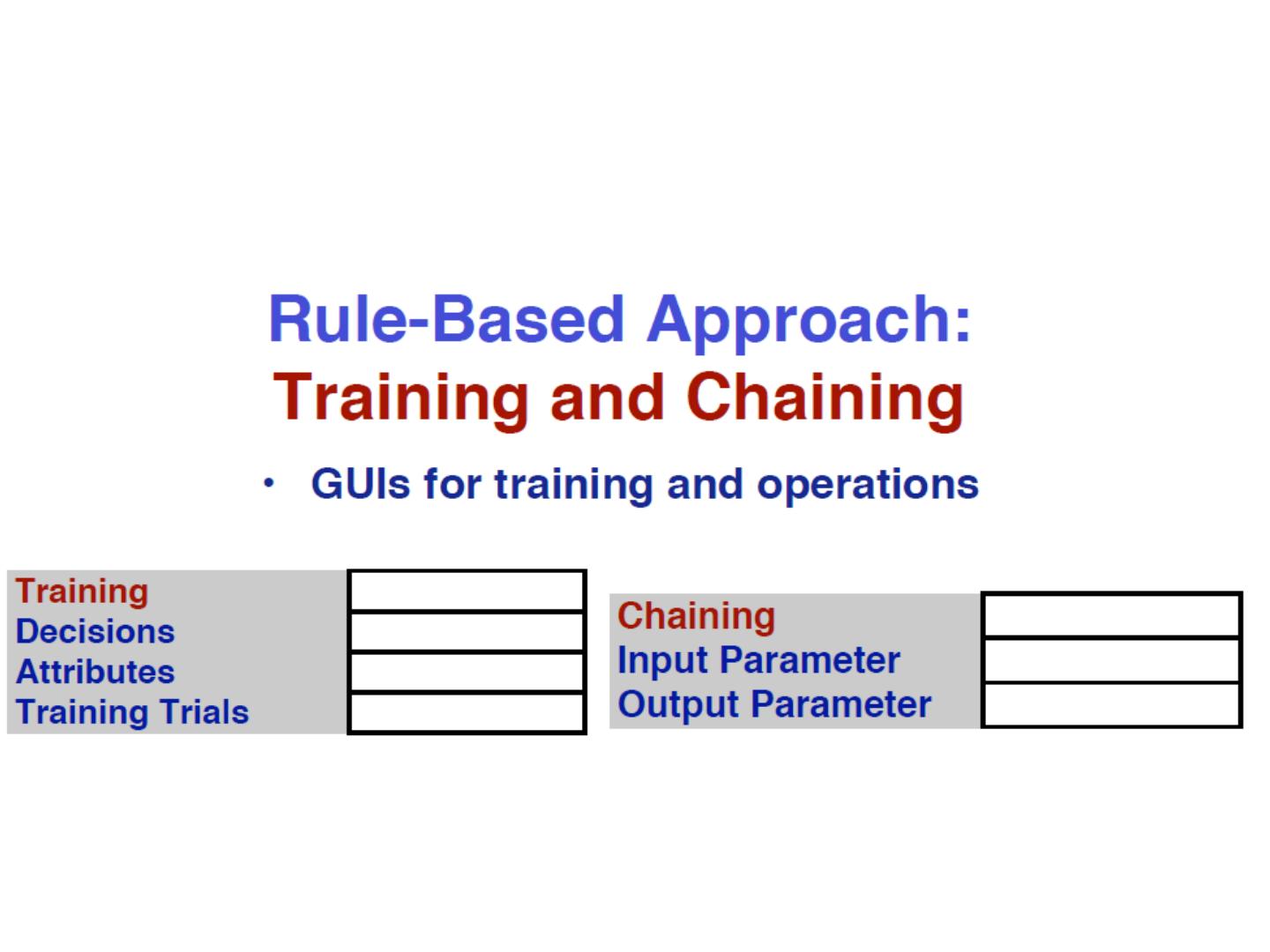
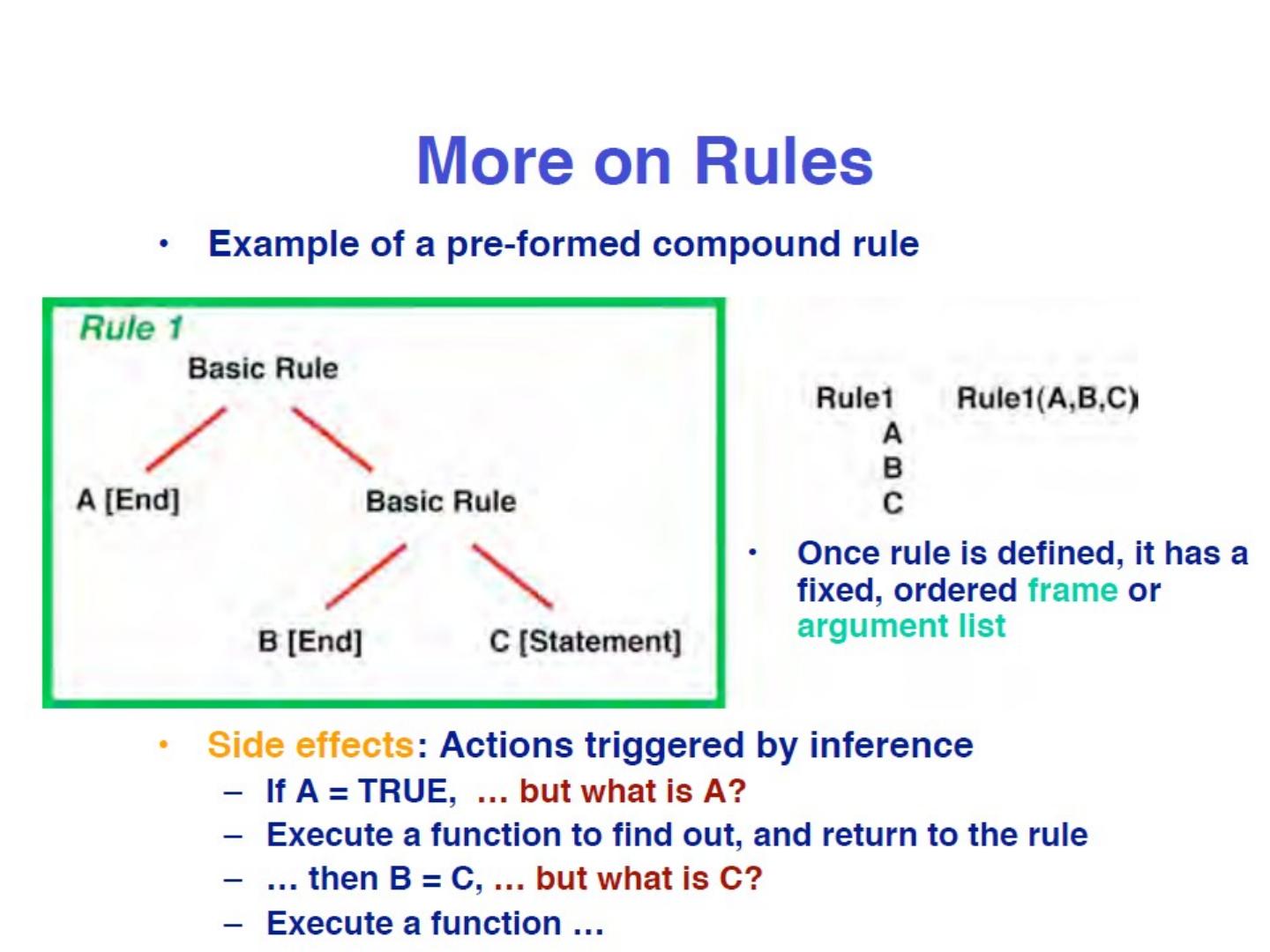
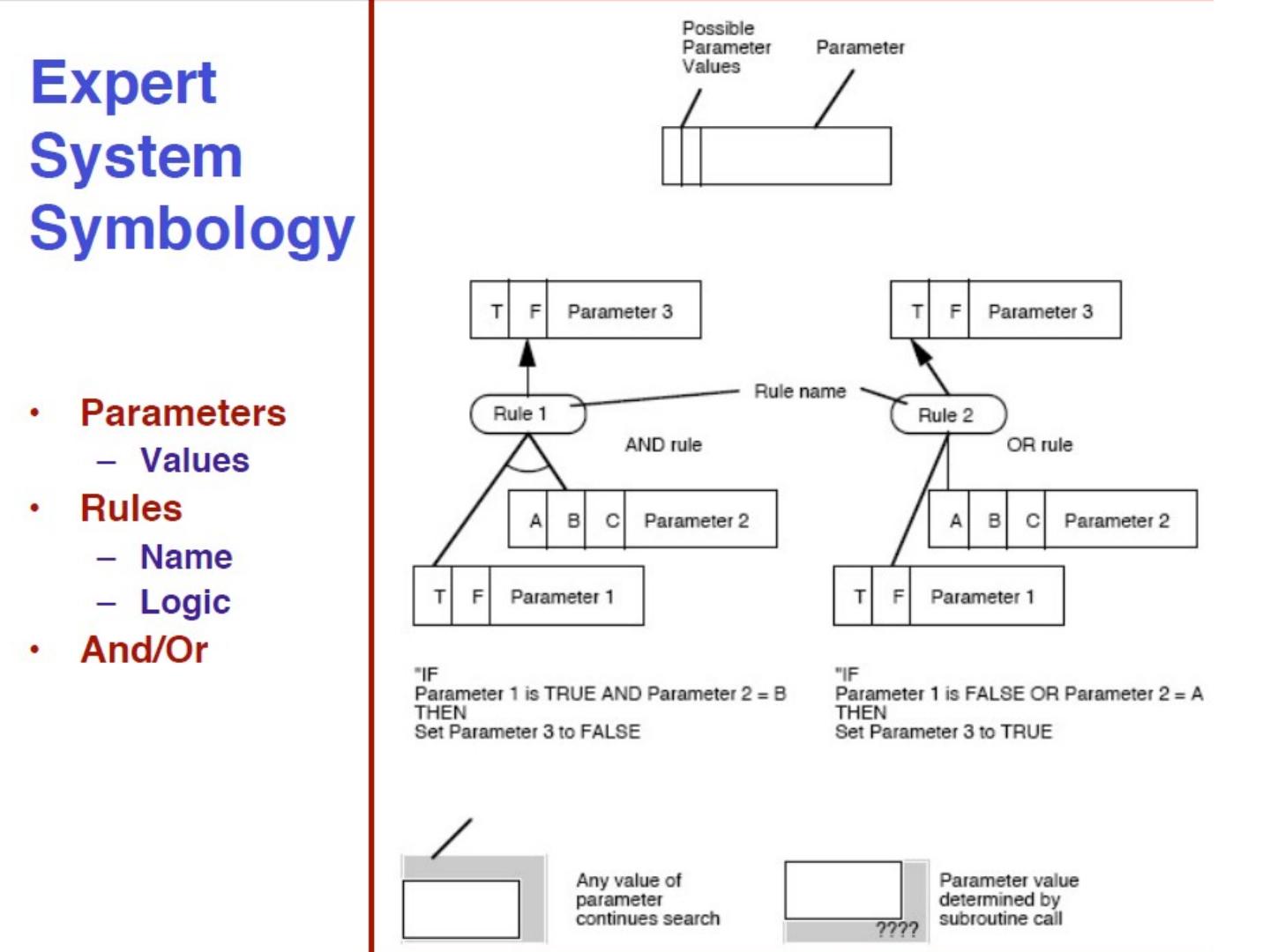
10 .Elements of a rule
11 .Example Chinook 47 Helicopter System for testing and control
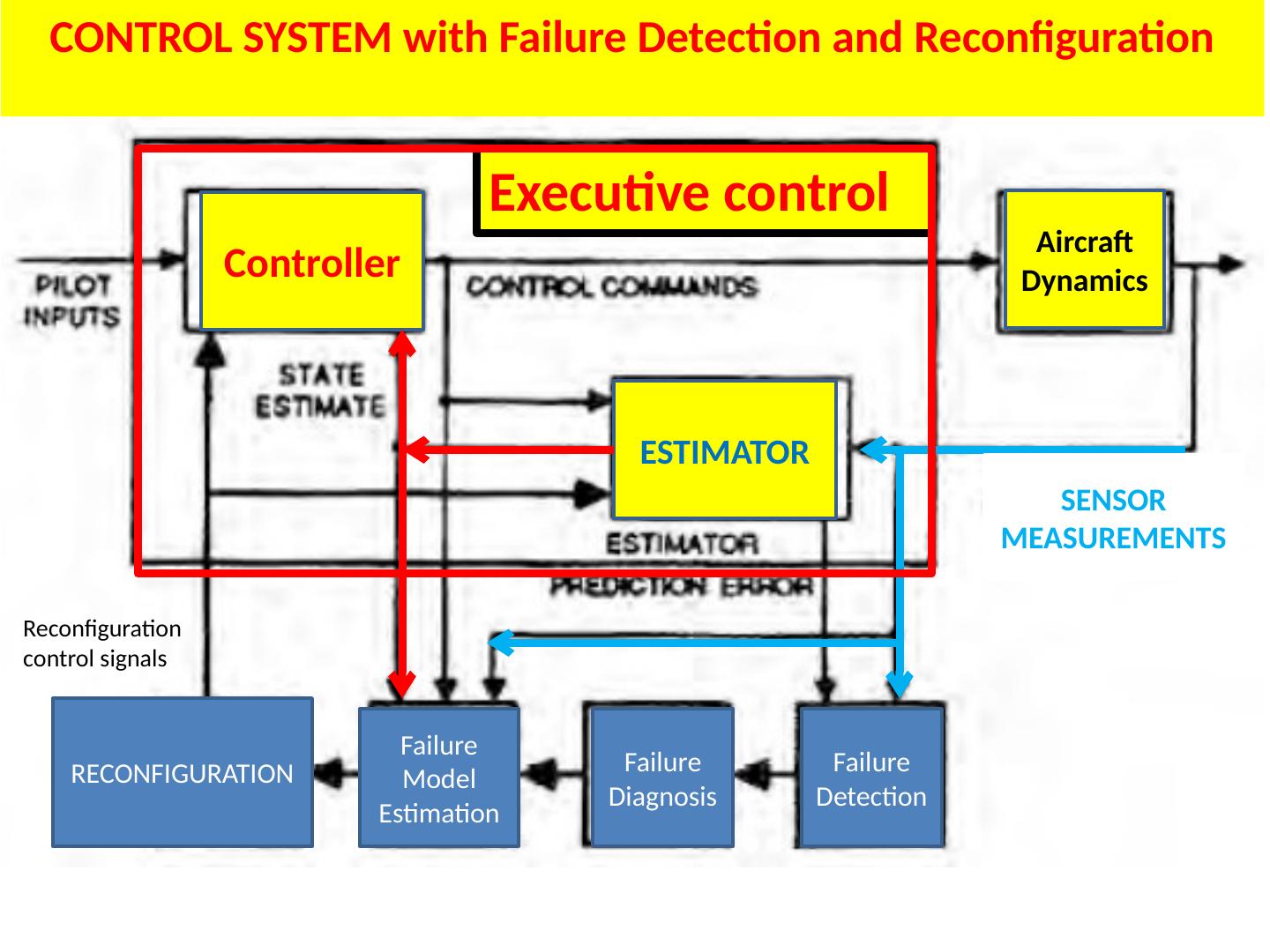
12 .CONTROL SYSTEM with Failure Detection and Reconfiguration Executive control Aircraft Dynamics Controller ESTIMATOR SENSOR MEASUREMENTS Reconfiguration control signals Failure Detection Failure Diagnosis Failure Model Estimation RECONFIGURATION
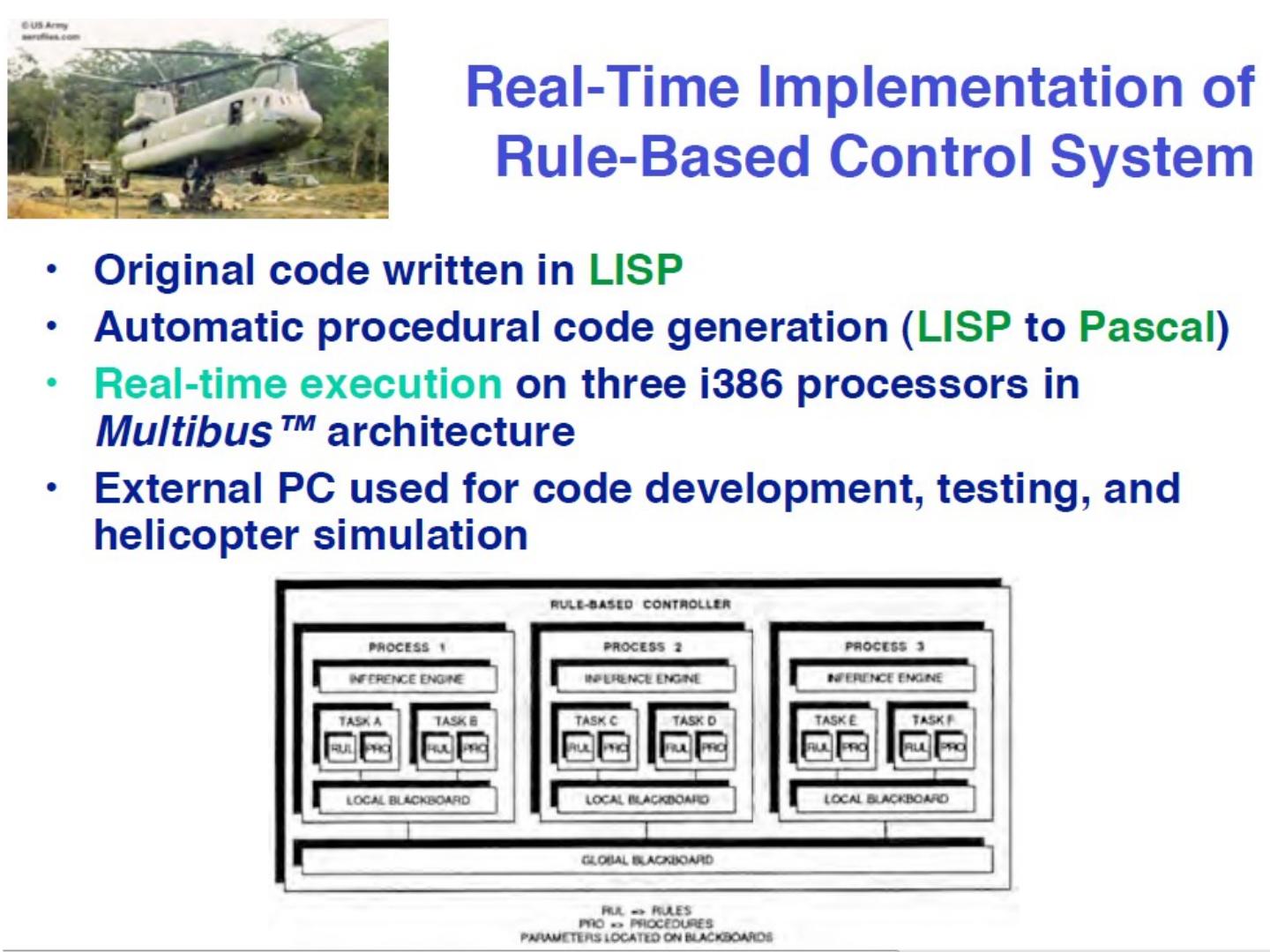
13 .Real-Time Implementation of Rule-Based Control System. Handelman and Stengel 1989
14 .Real-Time Implementation of Rule-Based Control System. Handelman and Stengel 1989
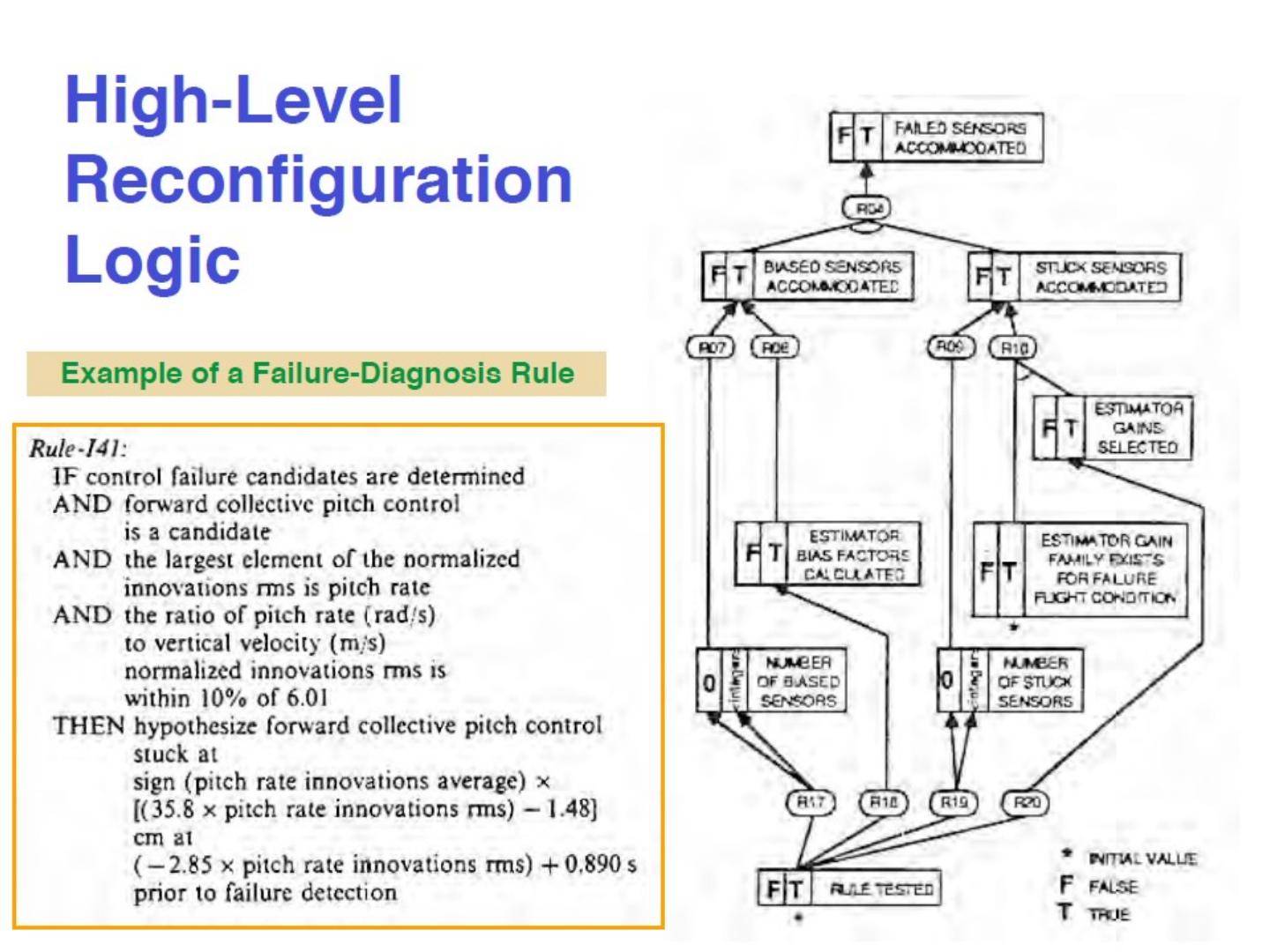
15 .High level control logic High level reconfiguration logic
16 .True/False signal is propagated bottom up
17 .True/False signal is propagated bottom up
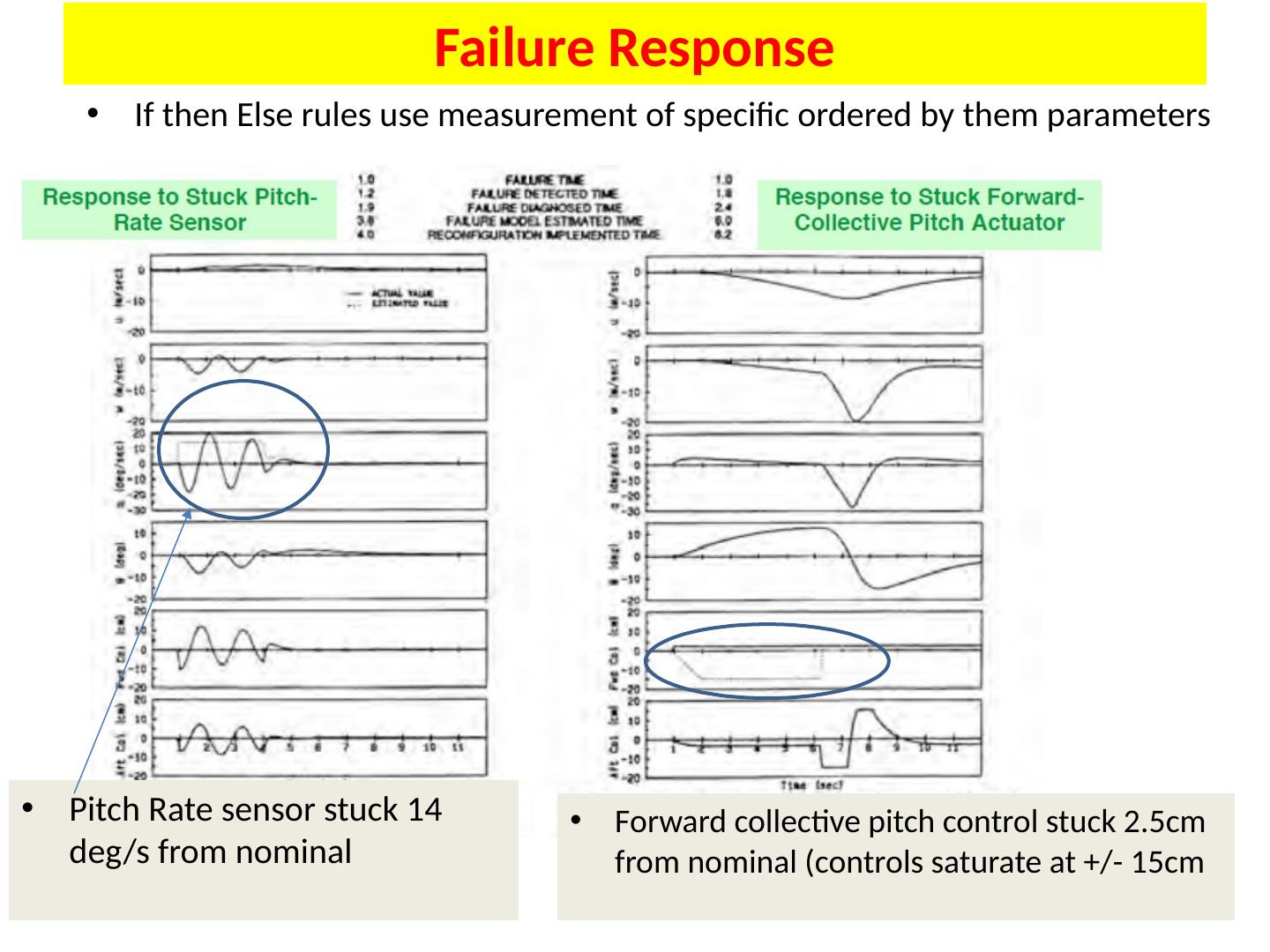
18 .Failure Response If then Else rules use measurement of specific ordered by them parameters Pitch Rate sensor stuck 14 deg /s from nominal Forward collective pitch control stuck 2.5cm from nominal (controls saturate at +/- 15cm
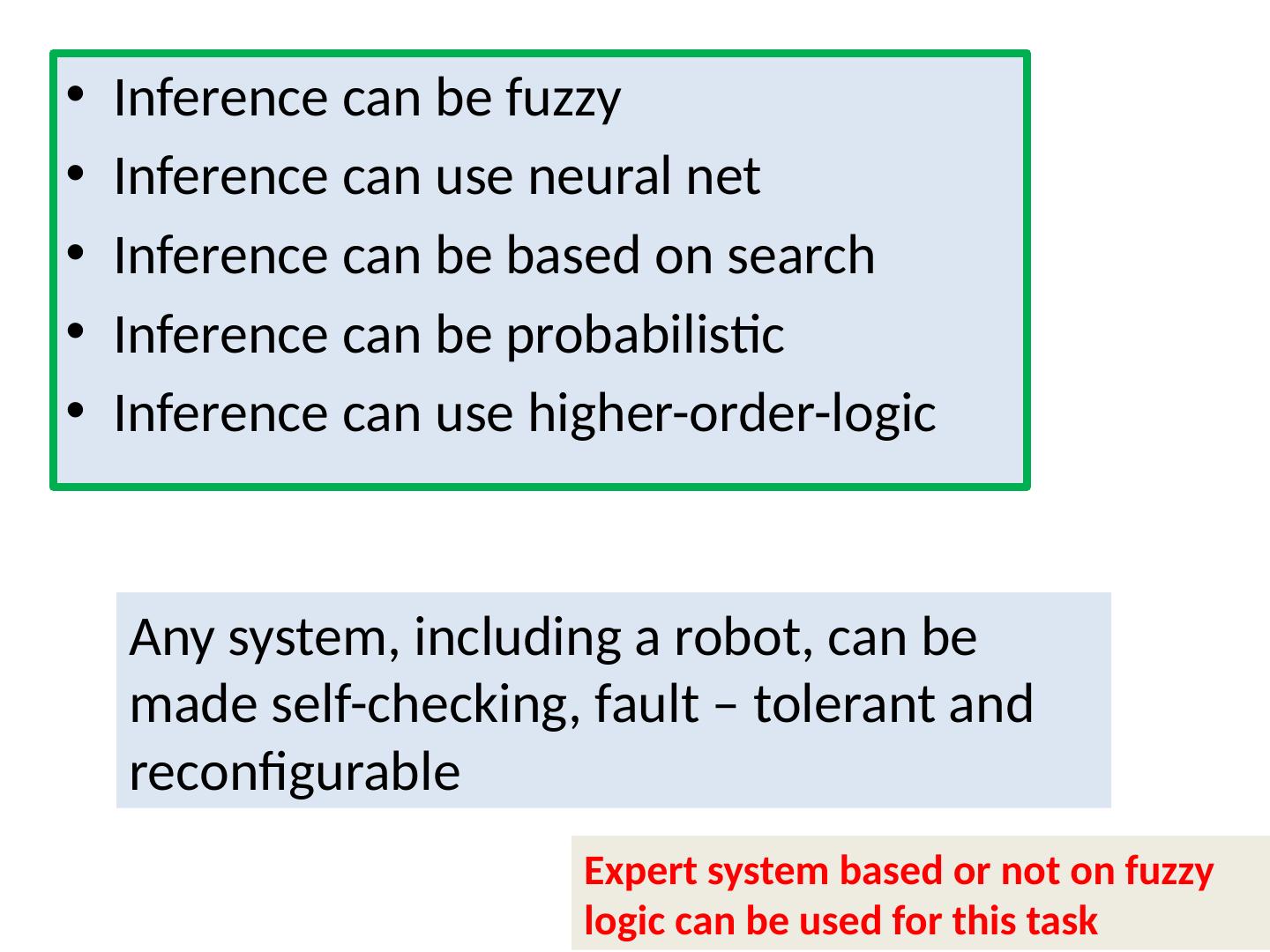
19 .Inference can be fuzzy Inference can use neural net Inference can be based on search Inference can be probabilistic Inference can use higher-order-logic Any system, including a robot, can be made self-checking, fault – tolerant and reconfigurable Expert system based or not on fuzzy logic can be used for this task
20 .Concepts of Knowledge Representation: DATA
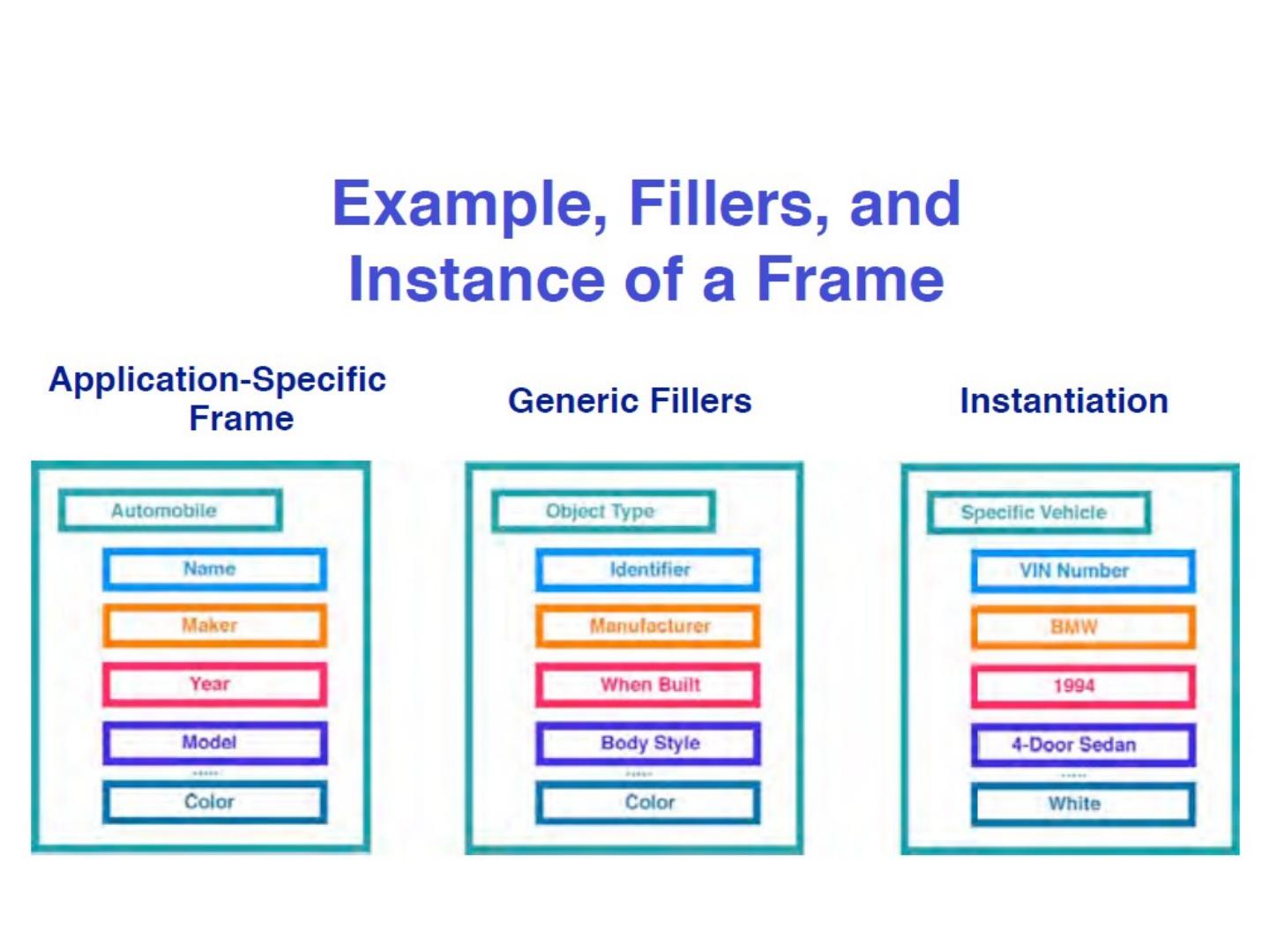
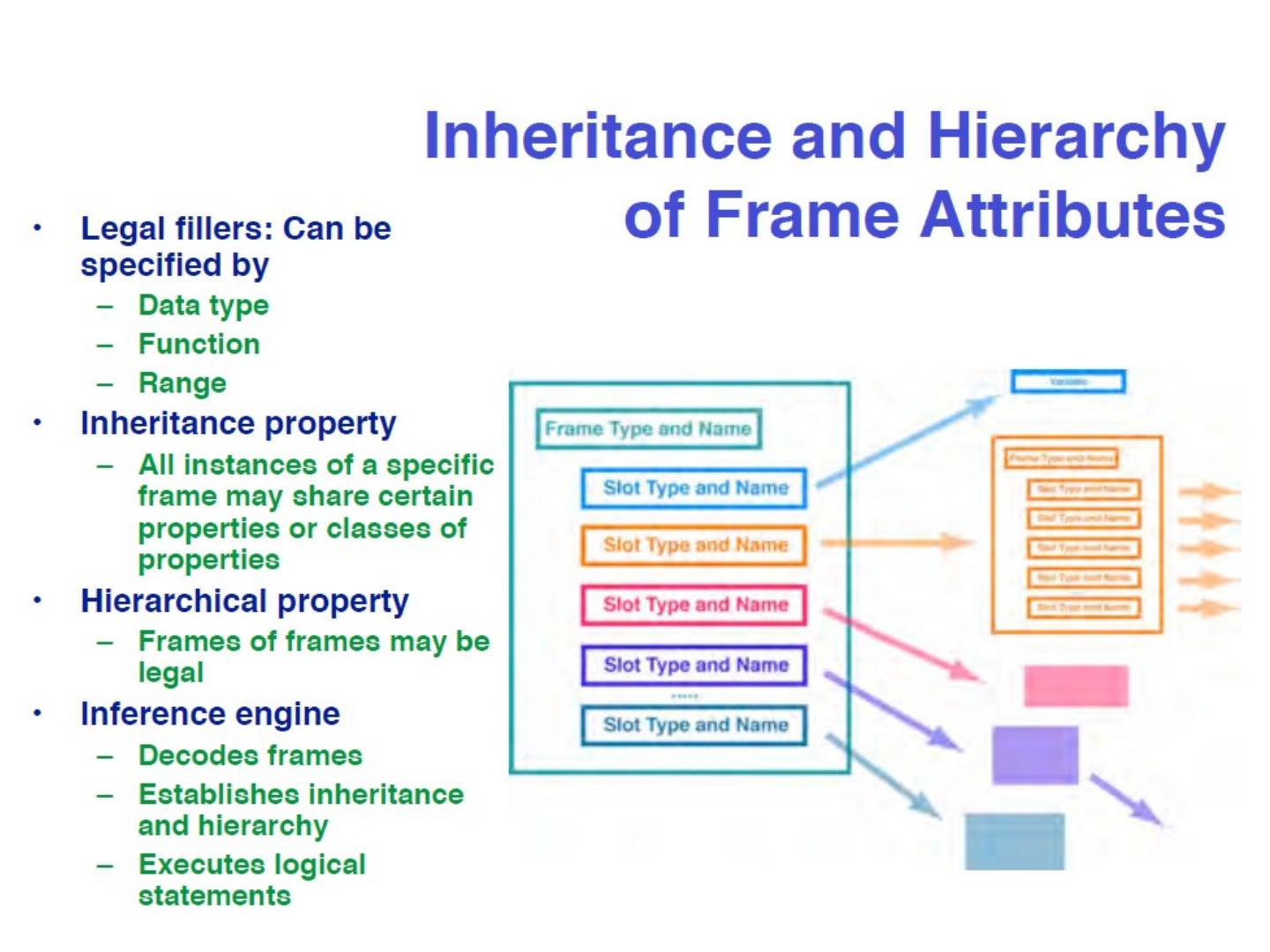
21 .Often used are: sets, schemes, frames and databases
22 .Often used are: sets, schemes, frames and databases
23 .Often used are: sets, schemes, frames and databases
24 .Often used are: sets, schemes, frames and databases
25 .Animal Decision Tree: Example Now we will illustrate some of these concepts on examples We will discuss forward chaining and backward chaining
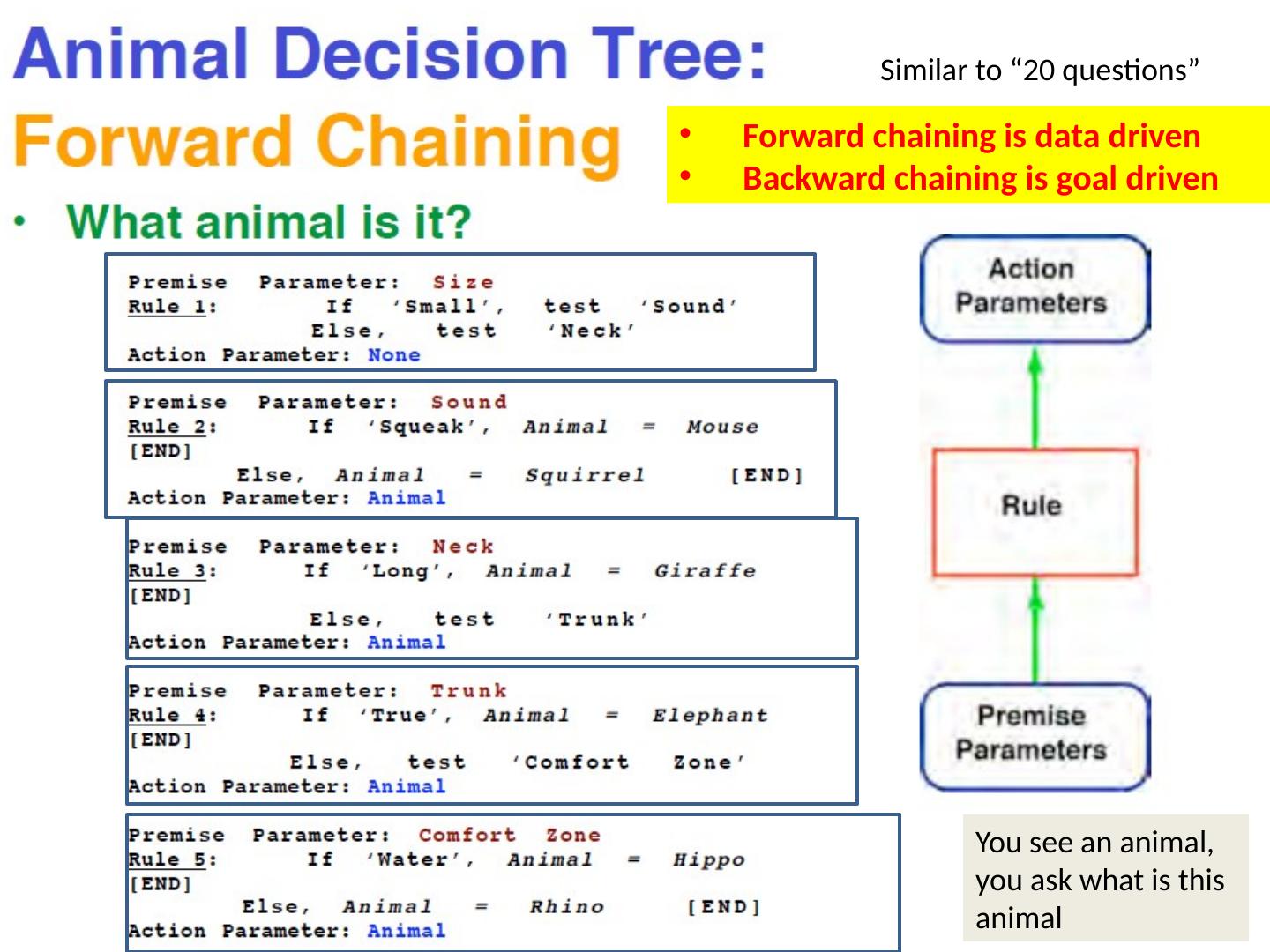
26 .Similar to “20 questions” Forward chaining is data driven Backward chaining is goal driven You see an animal, you ask what is this animal
27 .Forward chaining is data driven Backward chaining is goal driven You know animal name, you ask why this is the specified by name animal, what attributes testify to this decision. Keep in mind, apply.
28 .Animal Decision Tree Parameters Rules Programs
29 .Animal Decision Tree Parameters Rules Programs