- 快召唤伙伴们来围观吧
- 微博 QQ QQ空间 贴吧
- 文档嵌入链接
- 复制
- 微信扫一扫分享
- 已成功复制到剪贴板
PowerPoint Presentation
展开查看详情
1 .• node https://store.theartofservice.com/itil-2011-foundation-complete-certification-kit-fourth-edition-study-guide-ebook-and-online-course.html
2 . IPv6 address Solicited-node multicast address 1 The least significant 24 bits of the solicited- node multicast address group ID are filled with the least significant 24 bits of the interface's unicast or anycast address. These addresses allow link-layer address resolution via Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) on the link without disturbing all nodes on the local network. A host is required to join a Solicited-Node multicast group for each of its configured unicast or anycast addresses. https://store.theartofservice.com/itil-2011-foundation-complete-certification-kit-fourth-edition-study-guide-ebook-and-online-course.html
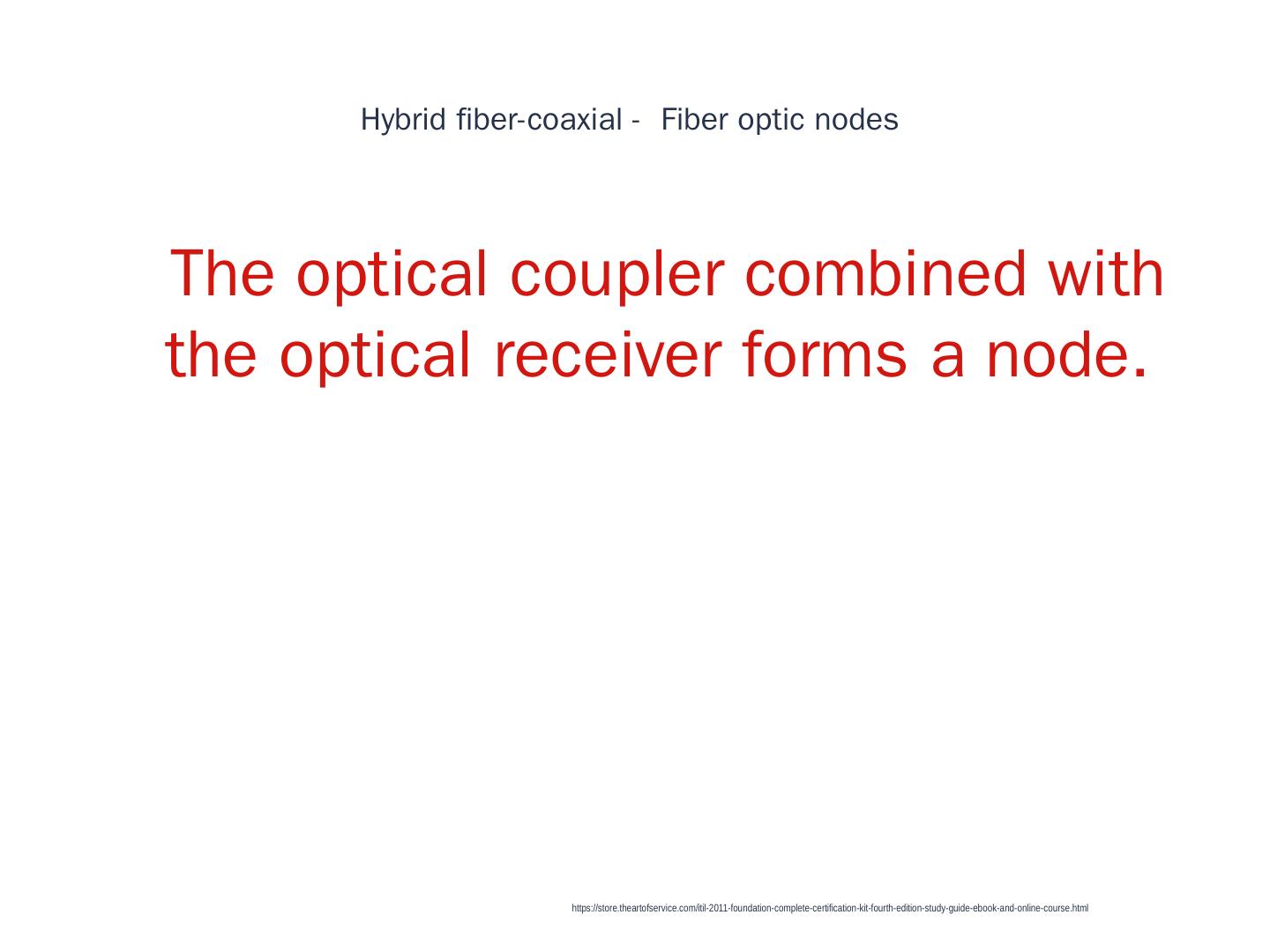
3 . Hybrid fibre-coaxial Fiber optic nodes 1 The optical coupler combined with the optical receiver forms a node. https://store.theartofservice.com/itil-2011-foundation-complete-certification-kit-fourth-edition-study-guide-ebook-and-online-course.html
4 . Hybrid fibre-coaxial Fiber optic nodes 1 The optical portion of the network provides a large amount of flexibility. If there are not many fiber-optic cables to the node, wavelength division multiplexing can be used to combine multiple optical signals onto the same fiber. Optical filters are used to combine and split optical wavelengths onto the single fiber. For example, the downstream signal could be on a wavelength at 1310 nm and the return signal could be on a wavelength at 1550 nm. https://store.theartofservice.com/itil-2011-foundation-complete-certification-kit-fourth-edition-study-guide-ebook-and-online-course.html
5 . Device file Node creation 1 Nodes are created by the mknod system call. The command-line program for creating nodes is also called mknod. Nodes can be moved or deleted by the usual filesystem system calls (rename, unlink) and commands (mv, rm). When passed the option -R or -a while copying a device node, the cp -l command creates a new device node with the same attributes of the original. https://store.theartofservice.com/itil-2011-foundation-complete-certification-kit-fourth-edition-study-guide-ebook-and-online-course.html
6 . Device file Node creation 1 Some Unix versions include a script named makedev or MAKEDEV to create all necessary devices in the directory /dev. It only makes sense on systems whose devices are statically assigned major numbers (e.g. by means of hardcoding it in their kernel module). https://store.theartofservice.com/itil-2011-foundation-complete-certification-kit-fourth-edition-study-guide-ebook-and-online-course.html
7 . Anycast Local and global nodes 1 the AS is added a few more times) to make the path longer so that a local node announcement is preferred over a global node announcement. https://store.theartofservice.com/itil-2011-foundation-complete-certification-kit-fourth-edition-study-guide-ebook-and-online-course.html
8 . Computer network Network nodes 1 Apart from the physical communications media described above, networks comprise additional basic hardware building blocks, such as network interface controller cards (NICs), repeaters, hubs, bridges, switches, routers, and firewalls. https://store.theartofservice.com/itil-2011-foundation-complete-certification-kit-fourth-edition-study-guide-ebook-and-online-course.html
9 . Mono (software) - MonoDevelop 1 MonoDevelop is a free GNOME integrated development environment primarily designed for C# and other .NET languages such as Nemerle, Boo, and Java (via IKVM.NET), although it also supports languages such as C, C++, Python, Java, and Vala. MonoDevelop was originally a port of SharpDevelop to Gtk#, but it has since evolved to meet the needs of Mono developers. The IDE includes class management, built-in help, code completion, Stetic (a GUI designer), project support, and an integrated debugger. https://store.theartofservice.com/itil-2011-foundation-complete-certification-kit-fourth-edition-study-guide-ebook-and-online-course.html
10 . Mono (software) - MonoDevelop 1 The MonoDoc browser provides access to API documentation and code samples. The documentation browser uses wiki-style content management, allowing developers to edit and improve the documentation. https://store.theartofservice.com/itil-2011-foundation-complete-certification-kit-fourth-edition-study-guide-ebook-and-online-course.html
11 . Persistent data structure - Fat Node 1 In order to navigate through the structure, each original field value in a node has a version stamp of zero. https://store.theartofservice.com/itil-2011-foundation-complete-certification-kit-fourth-edition-study-guide-ebook-and-online-course.html
12 . Persistent data structure - Complexity of Fat Node 1 For access time, we must find the right version at each node as we traverse the structure https://store.theartofservice.com/itil-2011-foundation-complete-certification-kit-fourth-edition-study-guide-ebook-and-online-course.html
13 . IBM Sequoia - Node architecture 1 Sequoia is a Blue Gene/Q design, building off previous Blue Gene designs. It consists of 96 racks containing 98,304 compute nodes [1024/rack]. The compute nodes are 16-core PowerPC A2 processor chips with 16 GB of DDR3 memory each. Thus the system contains in total 1,572,864 processor cores [96*1024*16] with 1.5 PiB memory. It covers an area of about 3,000 square feet (280 m2). The computer nodes are interconnected in a 5-dimensional torus topology. https://store.theartofservice.com/itil-2011-foundation-complete-certification-kit-fourth-edition-study-guide-ebook-and-online-course.html
14 . inode 1 In computing, an inode (index node) is a data structure found in many Unix file systems. Each inode stores all the information about a file system object (file, device node, socket, pipe, etc.). It does not store the file's data content and file name except for certain cases in modern file systems. https://store.theartofservice.com/itil-2011-foundation-complete-certification-kit-fourth-edition-study-guide-ebook-and-online-course.html
15 . inode - Etymology 1 The reason for designating these as "i" nodes is unknown. When asked, Unix pioneer Dennis Ritchie replied: https://store.theartofservice.com/itil-2011-foundation-complete-certification-kit-fourth-edition-study-guide-ebook-and-online-course.html
16 . inode - Etymology 1 In truth, I don't know either. It was just a term that we started to use. "Index" is my best guess, because of the slightly unusual file system structure that stored the access information of files as a flat array on the disk, with all the hierarchical directory information living aside from this. Thus the i-number is an index in this array, the i-node is the selected element of the array. (The "i-" notation was used in the 1st edition manual; its hyphen was gradually dropped.) https://store.theartofservice.com/itil-2011-foundation-complete-certification-kit-fourth-edition-study-guide-ebook-and-online-course.html
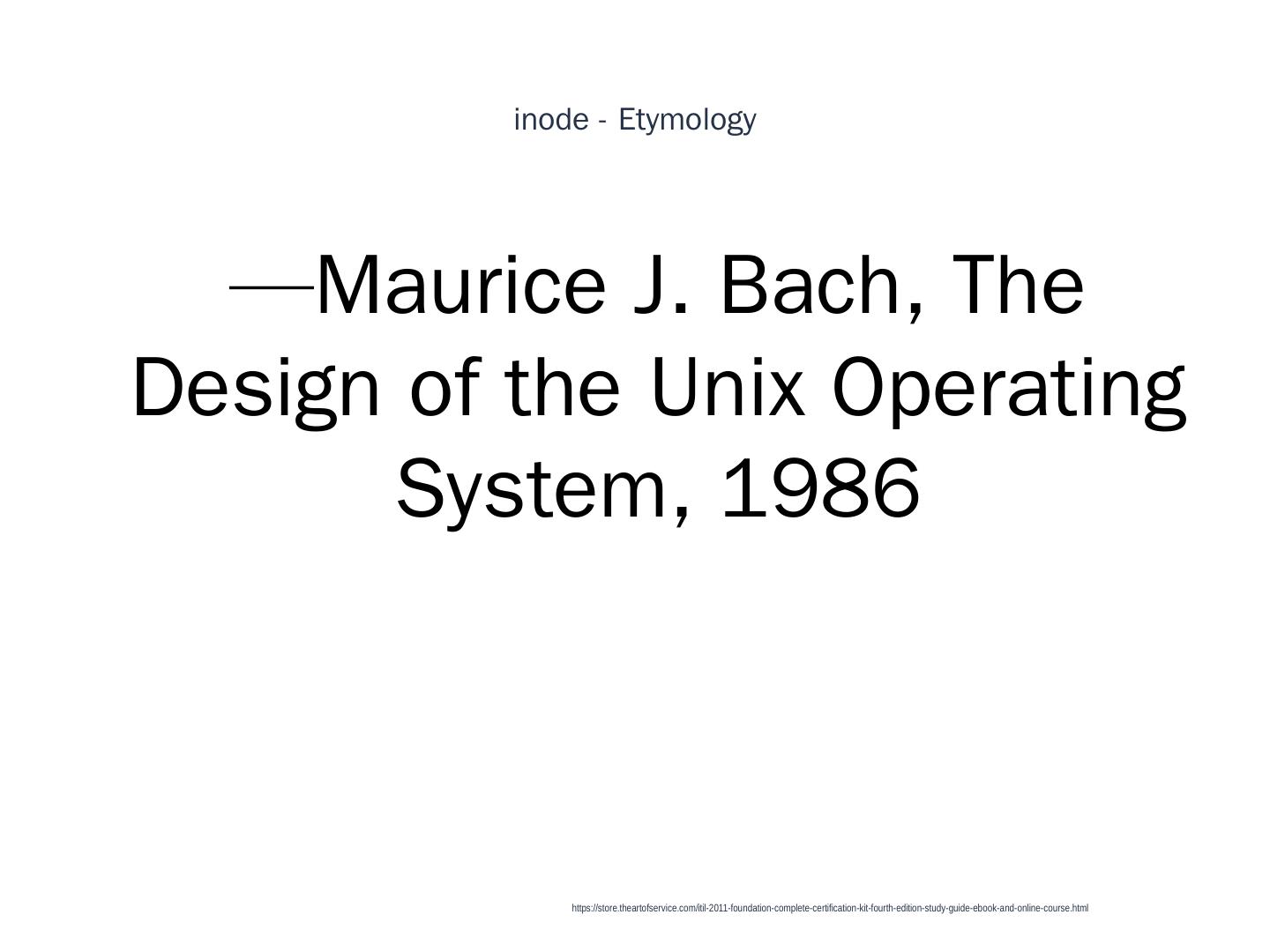
17 . inode - Etymology 1 Also Maurice J. Bach writes: https://store.theartofservice.com/itil-2011-foundation-complete-certification-kit-fourth-edition-study-guide-ebook-and-online-course.html
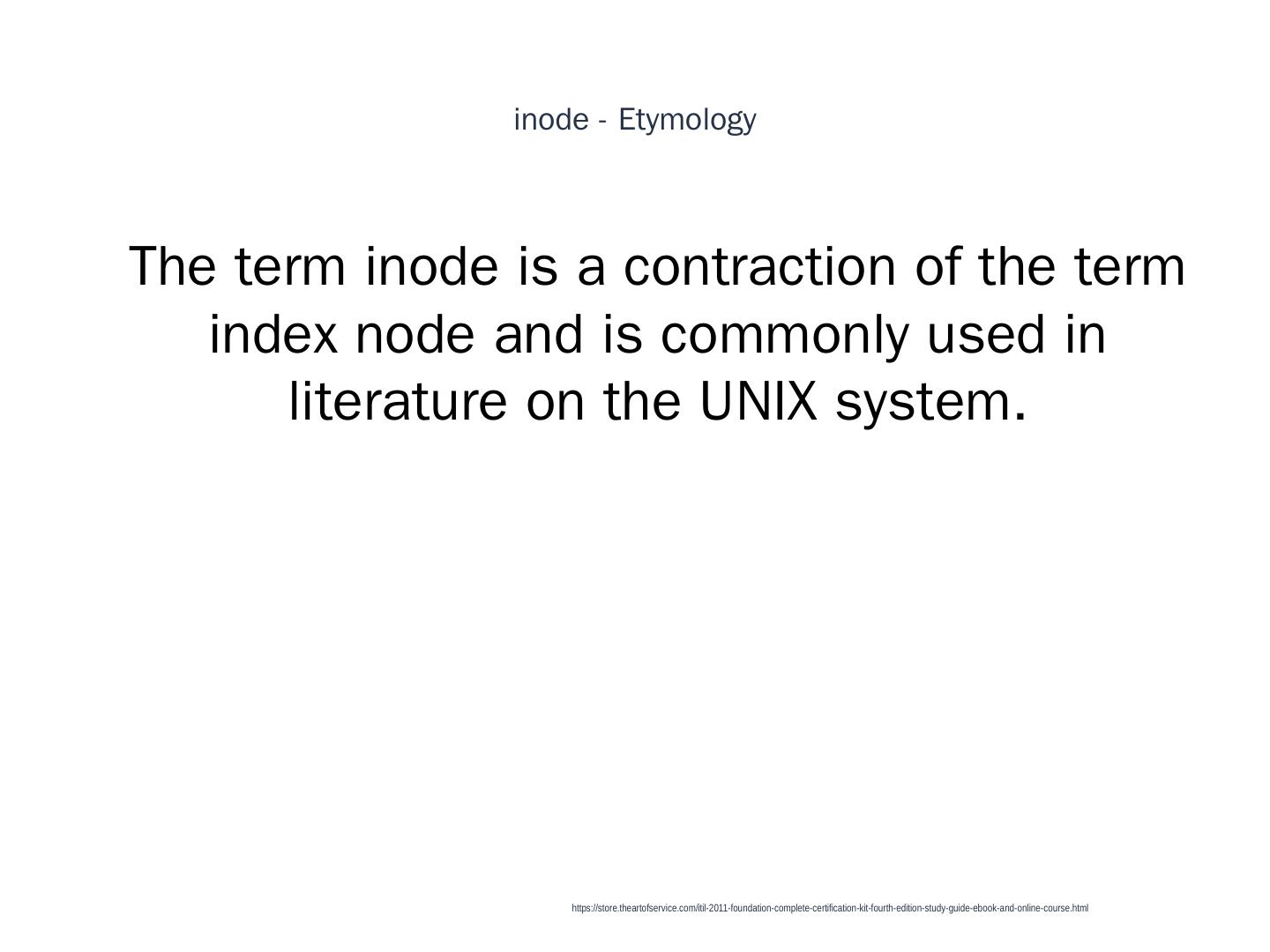
18 . inode - Etymology 1 The term inode is a contraction of the term index node and is commonly used in literature on the UNIX system. https://store.theartofservice.com/itil-2011-foundation-complete-certification-kit-fourth-edition-study-guide-ebook-and-online-course.html
19 . inode - Etymology 1 —Maurice J. Bach, The Design of the Unix Operating System, 1986 https://store.theartofservice.com/itil-2011-foundation-complete-certification-kit-fourth-edition-study-guide-ebook-and-online-course.html
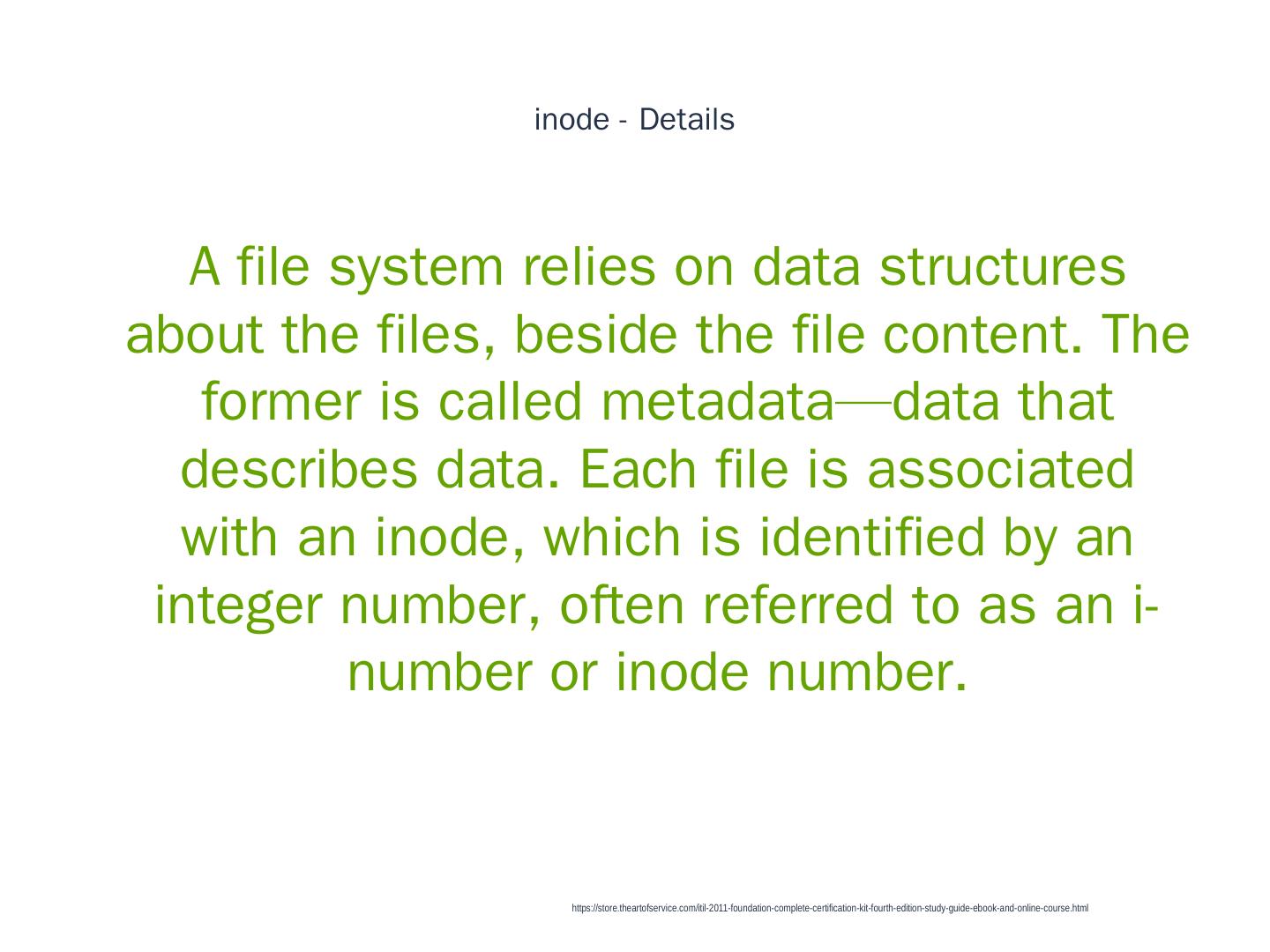
20 . inode - Details 1 A file system relies on data structures about the files, beside the file content. The former is called metadata—data that describes data. Each file is associated with an inode, which is identified by an integer number, often referred to as an i- number or inode number. https://store.theartofservice.com/itil-2011-foundation-complete-certification-kit-fourth-edition-study-guide-ebook-and-online-course.html
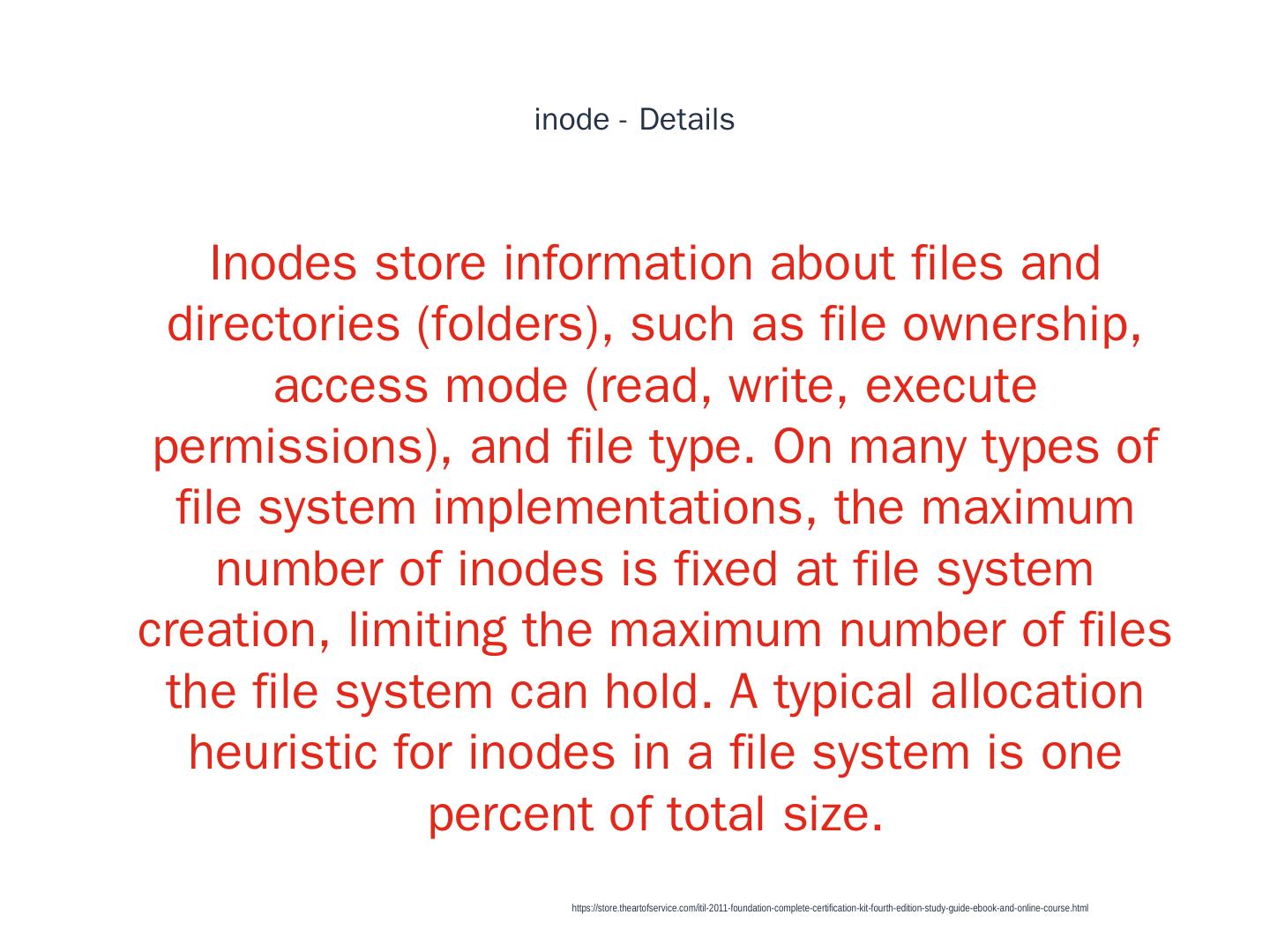
21 . inode - Details 1 Inodes store information about files and directories (folders), such as file ownership, access mode (read, write, execute permissions), and file type. On many types of file system implementations, the maximum number of inodes is fixed at file system creation, limiting the maximum number of files the file system can hold. A typical allocation heuristic for inodes in a file system is one percent of total size. https://store.theartofservice.com/itil-2011-foundation-complete-certification-kit-fourth-edition-study-guide-ebook-and-online-course.html
22 . inode - Details 1 The inode number indexes a table of inodes in a known location on the device; from the inode number, the file system driver portion of the kernel can access the contents of the inode, including the location of the file allowing access to the file. https://store.theartofservice.com/itil-2011-foundation-complete-certification-kit-fourth-edition-study-guide-ebook-and-online-course.html
23 . inode - Details 1 A file's inode number can be found using the ls -i command. The ls -i command prints the i-node number in the first column of the report. https://store.theartofservice.com/itil-2011-foundation-complete-certification-kit-fourth-edition-study-guide-ebook-and-online-course.html
24 . inode - Details 1 Some Unix-style file systems such as ReiserFS omit an inode table, but must store equivalent data in order to provide equivalent capabilities. The data may be called stat data, in reference to the stat system call that provides the data to programs. https://store.theartofservice.com/itil-2011-foundation-complete-certification-kit-fourth-edition-study-guide-ebook-and-online-course.html
25 . inode - Details 1 Unix directories are lists of association structures, each of which contains one filename and one inode number. https://store.theartofservice.com/itil-2011-foundation-complete-certification-kit-fourth-edition-study-guide-ebook-and-online-course.html
26 . inode - Details 1 The file system driver must search a directory looking for a particular filename and then convert the filename to the correct corresponding inode number. https://store.theartofservice.com/itil-2011-foundation-complete-certification-kit-fourth-edition-study-guide-ebook-and-online-course.html
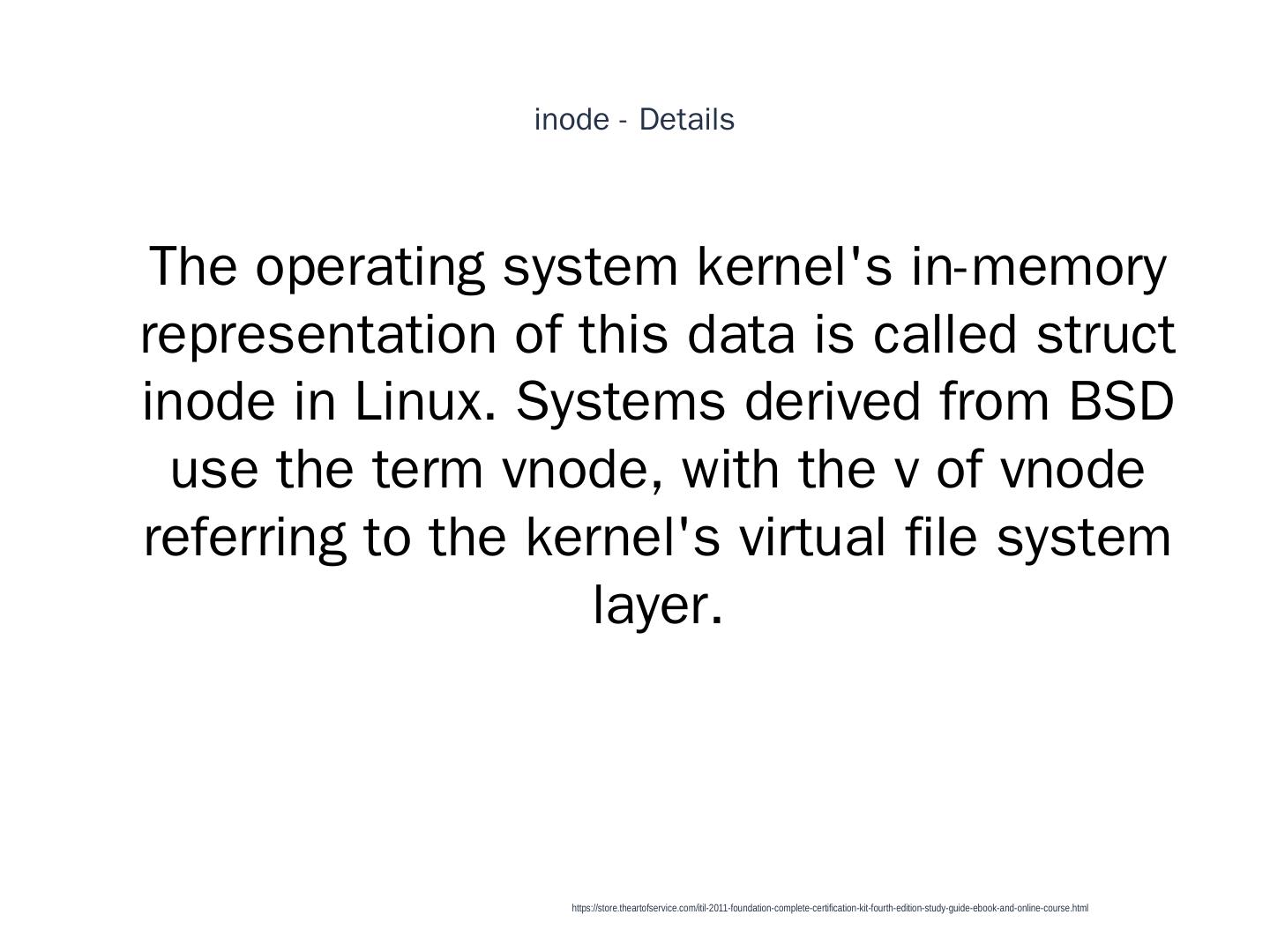
27 . inode - Details 1 The operating system kernel's in-memory representation of this data is called struct inode in Linux. Systems derived from BSD use the term vnode, with the v of vnode referring to the kernel's virtual file system layer. https://store.theartofservice.com/itil-2011-foundation-complete-certification-kit-fourth-edition-study-guide-ebook-and-online-course.html
28 . inode - POSIX inode description 1 The POSIX standard mandates filesystem behavior that is strongly influenced by traditional UNIX filesystems. Regular files must have the following attributes: https://store.theartofservice.com/itil-2011-foundation-complete-certification-kit-fourth-edition-study-guide-ebook-and-online-course.html
29 . inode - POSIX inode description 1 The file mode which determines the file type and how the file's owner, its group, and others can access the file. https://store.theartofservice.com/itil-2011-foundation-complete-certification-kit-fourth-edition-study-guide-ebook-and-online-course.html