- 快召唤伙伴们来围观吧
- 微博 QQ QQ空间 贴吧
- 文档嵌入链接
- 复制
- 微信扫一扫分享
- 已成功复制到剪贴板
01-Introduction
展开查看详情
1 .CSC2/458 Parallel and Distributed Systems Introduction Sreepathi Pai January 18, 2018 URCS
2 .Outline Administrivia Parallel Computing Distributed Computing
3 .Outline Administrivia Parallel Computing Distributed Computing
4 .People • Instructor: Dr. Sreepathi Pai • E-mail: sree@cs.rochester.edu • Office: Wegmans 3409 • Office Hours: By appointment, but I have an open door policy (10AM–5PM) • TA: Haichuan Yang • Will join us early February.
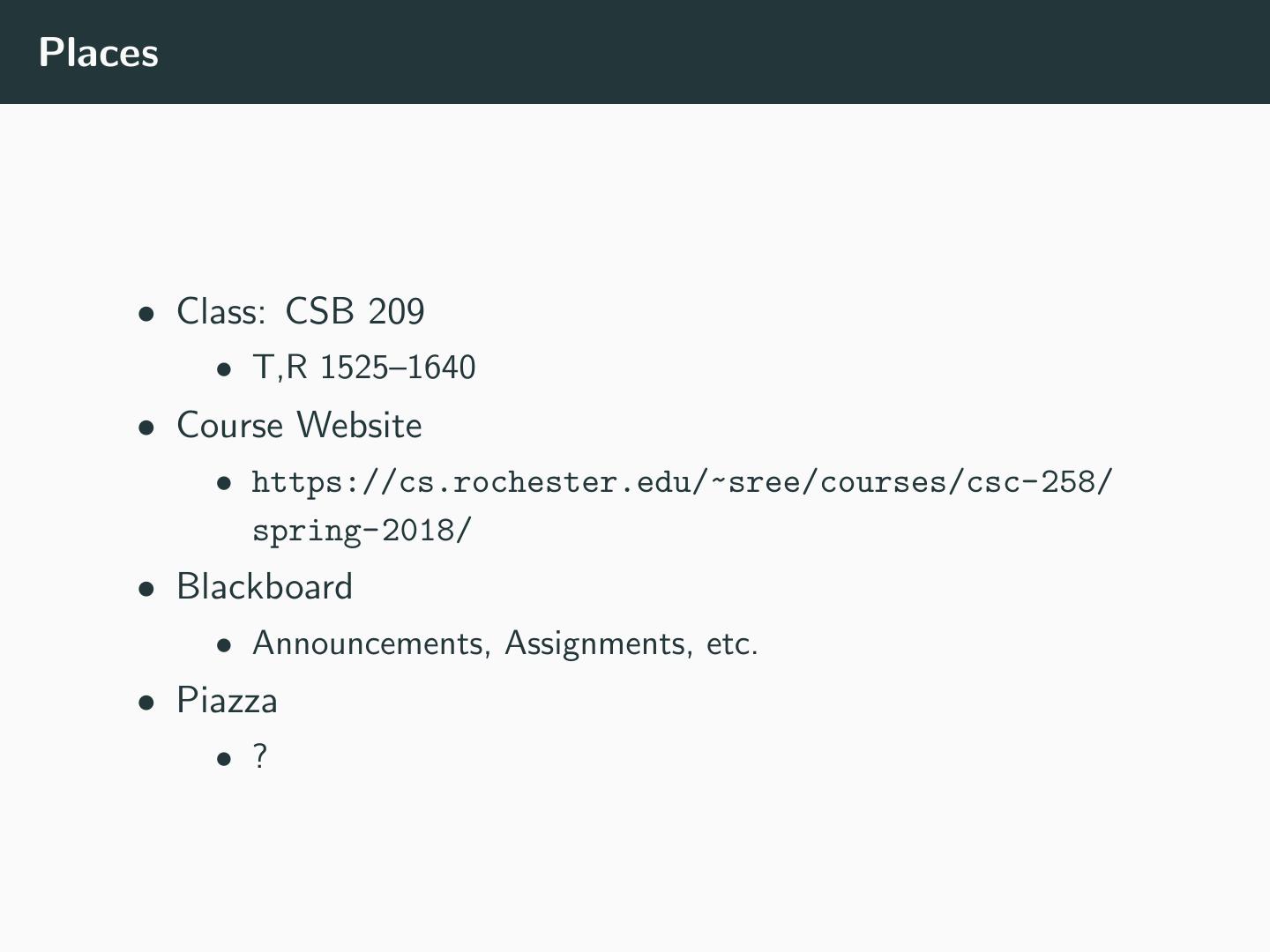
5 .Places • Class: CSB 209 • T,R 1525–1640 • Course Website • https://cs.rochester.edu/~sree/courses/csc-258/ spring-2018/ • Blackboard • Announcements, Assignments, etc. • Piazza • ?
6 .Pre-requisites • CSC 256: Operating Systems • Processes, Threads, Scheduling • Synchronization: Mutexes, Semaphores • Interprocess Communication • CSC 254: Programming Language Design and Implementation • Parallel Programming Constructs • Concurrency This is a non-exhaustive list.
7 .References • No required textbooks for this class • But a lot of reading! • Books and materials have been placed on reserve • Some online, some in Carlson Library • See Blackboard for information on accessing Reserves
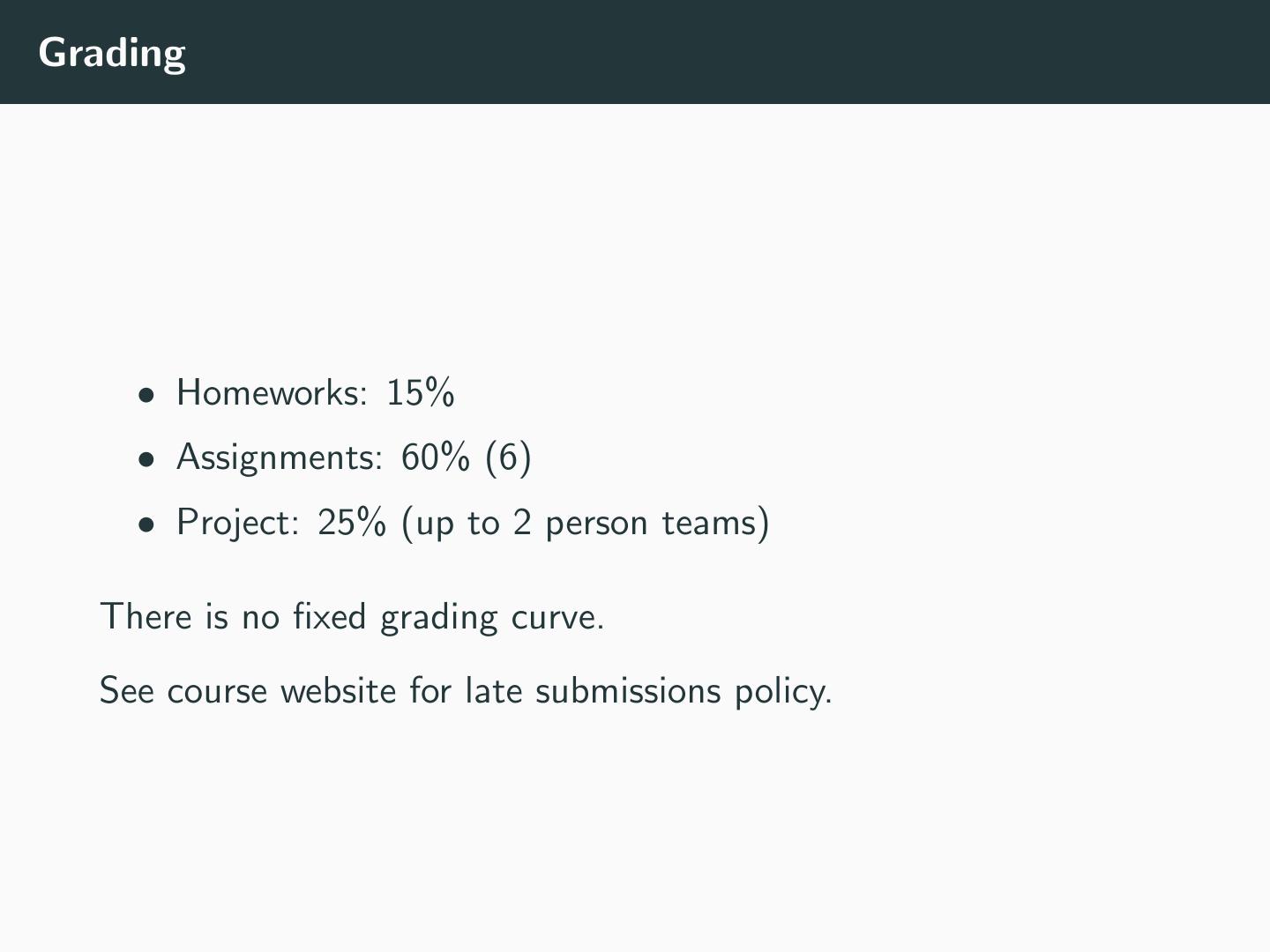
8 .Grading • Homeworks: 15% • Assignments: 60% (6) • Project: 25% (up to 2 person teams) There is no fixed grading curve. See course website for late submissions policy.
9 .Project Expectations • Depends on number of people in team • May put up a list of projects as suggestions • You’re free to do your own project • Project report • Project presentation
10 .Academic Honesty • Unless otherwise stated, you may not show your code to other students • You may discuss, brainstorm, etc. with your fellow students but all submitted work must be your own • All help received must be acknowledged in writing when submitting your assignments and homeworks • All external code you use must be clearly marked as such in your submission • Use a comment and provide URL if appropriate • If in doubt, ask the instructor All violations of academic honesty will be dealt with strictly as per UR’s Academic Honesty Policy.
11 .Outline Administrivia Parallel Computing Distributed Computing
12 .Parallel Machines are Everywhere • Starting 2004, all desktop CPUs have multiple “cores” • Even most mobile phones have multiple CPUs! • Why?
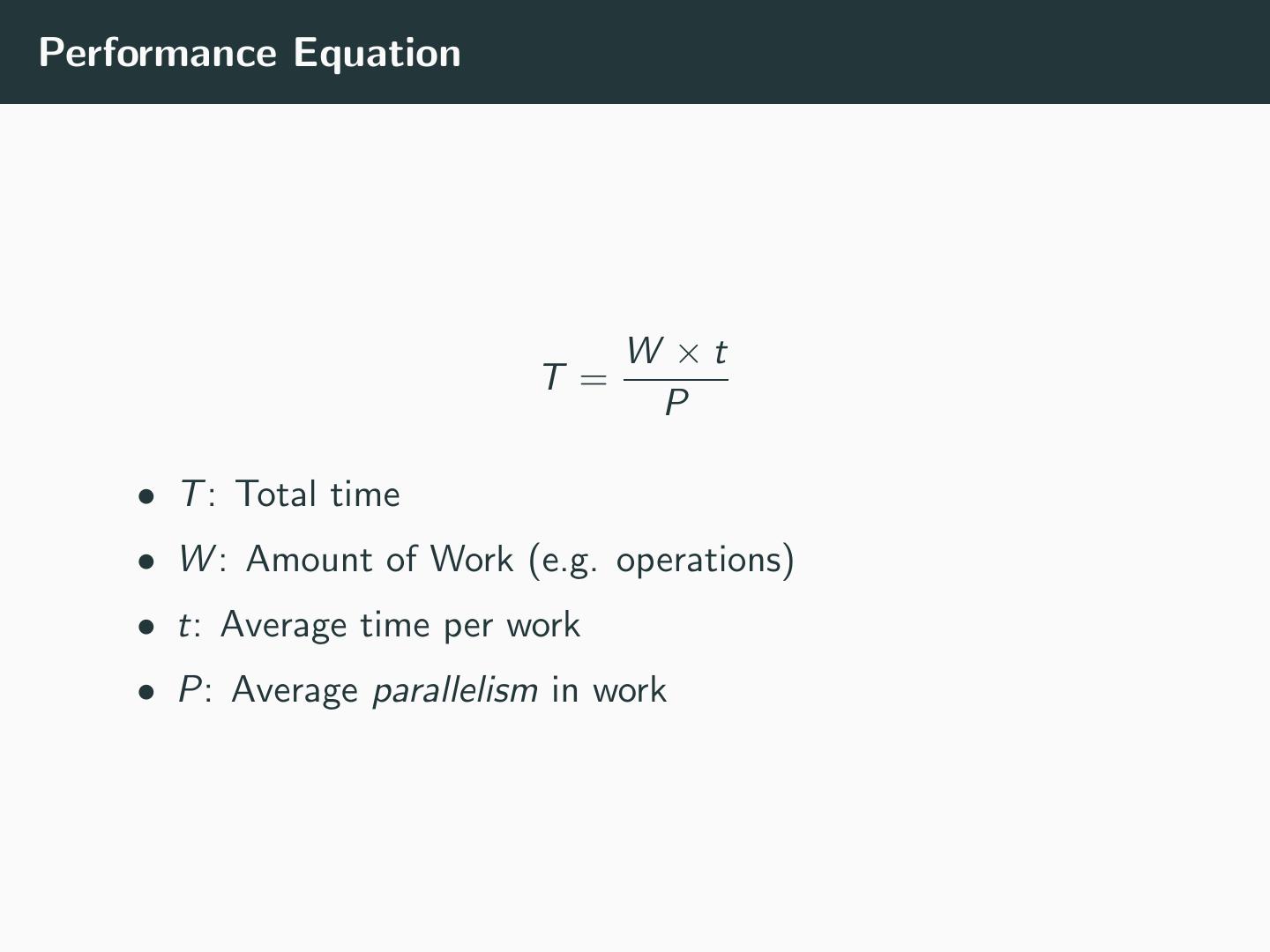
13 .Performance Equation W ×t T = P • T : Total time • W : Amount of Work (e.g. operations) • t: Average time per work • P: Average parallelism in work
14 .Exercise 10 34 342 20 71 123 101 589
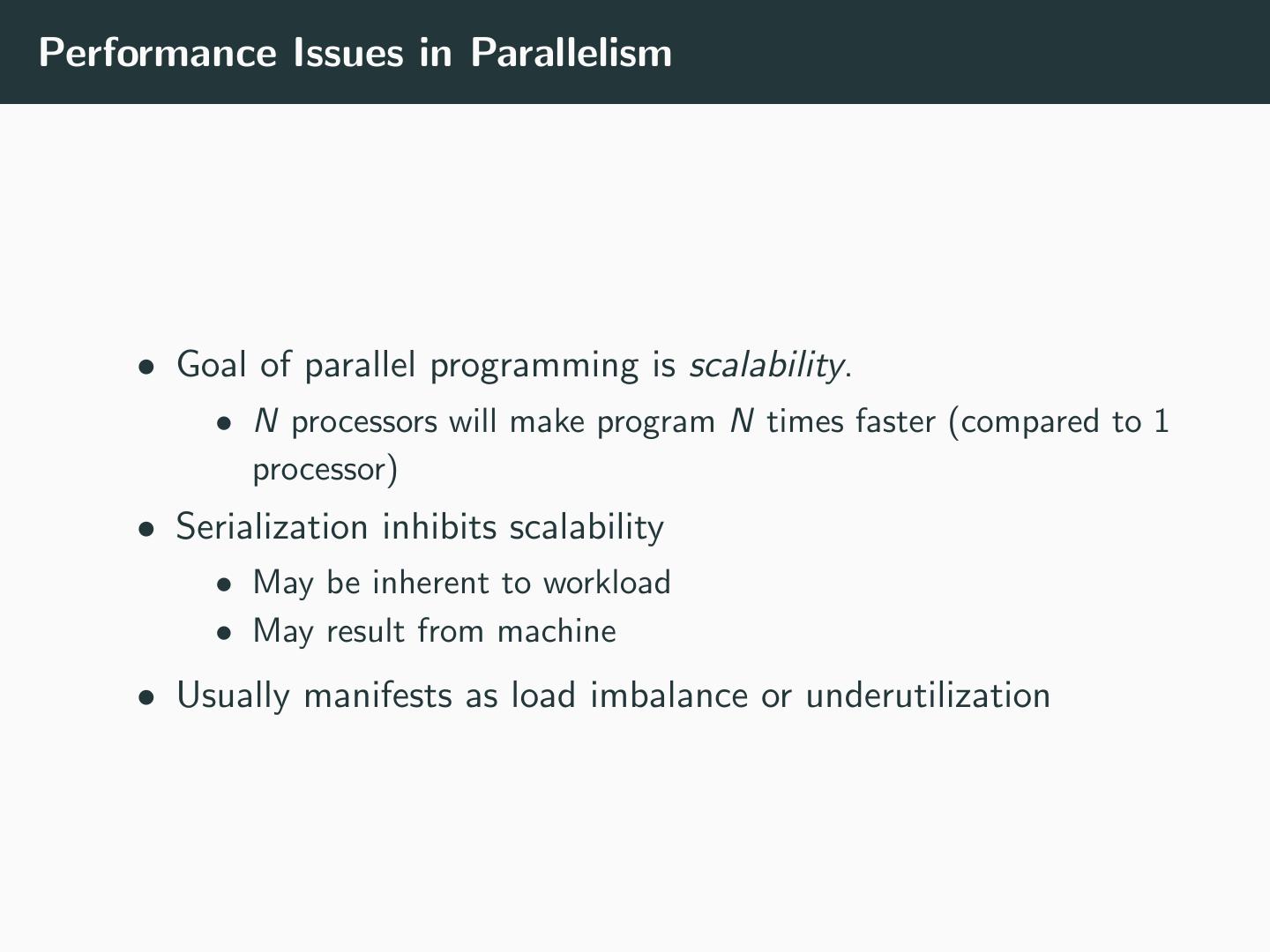
15 .Performance Issues in Parallelism • Goal of parallel programming is scalability. • N processors will make program N times faster (compared to 1 processor) • Serialization inhibits scalability • May be inherent to workload • May result from machine • Usually manifests as load imbalance or underutilization
16 .Correctness Issues in Parallelism • Why can we do the addition in parallel?
17 .Correctness Issues in Parallelism • Ordering in Serial programs • How do you debug serial programs? • Ordering in Parallel programs • How do you debug parallel programs?
18 .Outline Administrivia Parallel Computing Distributed Computing
19 .Distributed Computation Can we break up a program so its parts run on different computers? Each part communicates with the others using messages.
20 .Why distribute? • To parallelize • Problem can be solved by one computer, but you want it faster • To scale • Problem can be solved by one computer, but there are lots of problem instances to be solved • Too big a problem for one computer • Inherently distributed
21 .Implications of Distribution • Location • Distributed State
22 .Distributed Systems in Real Life
23 .Distributed Systems in Real Life: Somewhat obvious • The telephone system • The Internet • The banking system • The traffic system • ...
24 .Distributed Systems in Real Life: Not so obvious • Cellular systems • Plants • Animals • Fungi
25 .Challenges in Distributed Systems • Correctness • Termination In the presence of: • Delays • Failures