- 快召唤伙伴们来围观吧
- 微博 QQ QQ空间 贴吧
- 文档嵌入链接
- 复制
- 微信扫一扫分享
- 已成功复制到剪贴板
firewalls 1125 2013
展开查看详情
1 .Firewall Technologies 黃能富 教授 國立清華大學資訊工程系 nfhuang@cs.nthu.edu.tw
2 .Contents Firewall Introduction Firewall Hardware Types Firewall Technologies Firewall Architecture Firewall Deployment VPN (Virtual Private Network) Firewall Labs : Iptables
3 .What is a Firewall ? A firewall isolates organization’s internal net from larger Internet, allowing some packets to pass, blocking others. privately administered 222.22/16 Internet
4 .What is a Firewall ? A firewall acts as a security gateway between two networks Usually between trusted and untrusted networks (such as between a corporate network and the Internet) Internet Corporate Site Corporate Network Gateway
5 .What is a Firewall ? A firewall tracks and controls network communications Decides whether to pass, reject, encrypt, or log communications (Access Control) Corporate Site “ Allow Traffic to Internet” Internet “ Block traffic from Internet”
6 .What is a Firewall? A firewall is a security policy enforcement point that regulates access between computer networks Filters are inherently insecure services Controls TCP protocols http, smtp , ftp, telnet etc Only one of many different security tool’s to control and regulate network traffic
7 .Why Firewalls are Needed Prevent attacks from untrusted networks Protect data integrity of critical information Preserve customer and partner confidence
8 .Firewall goals: All traffic from outside to inside and vice-versa passes through the firewall. Only authorized traffic, as defined by local security policy, will be allowed to pass. The firewall itself is immune to penetration.
9 .What do Firewalls Protect? Data Proprietary corporate information Financial information Sensitive employee or customer data Resources Computing resources Time resources Bandwidth resources Reputation Loss of confidence in an organization Intruder uses an organization’s network to attack other sites
10 .Common Internet Threats Denial of service attacks Specific attacks that can cause a server crash Flooding the server with traffic to disrupt or deny service Intrusion threats Attacks on services/exploits The backend server may not be hardened enough for adequate protection, but the firewall can block external attacks Information threats
11 .How Vulnerable are Internet Services? E-mail or smtp – Simple Mail Transfer Protocol TCP/IP based port 25 (POP 110) Risks Include E-mail bombing (stalking) Anonymous harassment Large amounts of e-mail to a single user address Spamming Messages sent to numerous different users from a host Virus download mechanism Code Red Nimda Not always traceable POP and IMAP can be very insecure
12 .FTP - File Transfer Protocol TCP/IP based port 20/21 Risks Include Unencrypted authentication and data transfers Usernames and passwords can be”sniffed ” Unencrypted data transfers Data can be viewed Often part of default installations Anonymous ftp is possible How Vulnerable are Internet Services?
13 .How Vulnerable are Internet Services? Telnet TCP/IP based port 23 Risks include Unencrypted authentication Unencrypted interactive session Session hijacking Included in default installations Can allow remote root login
14 .How Vulnerable are Internet Services? HTTP – Hypertext Transfer Protocol TCP/IP based port 80 Risks Include Browsers can be used to run dangerous commands Difficult to secure Remote execution of commands and execution (server side) Non-secure add-on applications Java Cookies
15 .How Vulnerable are Internet Services? HTTPS – Secure Hypertext Transfer Protocol TCP/IP based port 443 Risks Include Browsers can be used to run dangerous commands Remote execution of commands and execution (server side) Becomes a tunnel for any data Can be used to subvert firewall/security controls
16 .How Vulnerable are Internet Services? DNS TCP and UDP based ports 53 and 1024 Risks include DNS cache poisoning Bad data to redirect valid connections to the wrong server DNS spoofing Bad data to redirect valid connections to the wrong server Absolutely needed for network services
17 .How Vulnerable are Internet Services? SNMP – Simple Network Management Protocol UDP based Risks include Unencrypted data transfers Poor authentication through “community relationships” Transfer of highly sensitive data Does use access lists
18 .How Vulnerable are Internet Services? NFS – Network File System NFS is a shared file structure Based on a trust model of network machines Certain machines can access shared file systems Risks include No “user ” authentication IP Spoofing to gain access Most secure NFS is still very insecure
19 .How Vulnerable are Internet Services? NFS – Network File System NFS is a shared file structure Based on a trust model of network machines Certain machines can access shared file systems Risks include No “user ” authentication IP Spoofing to gain access Most secure NFS is still very insecure
20 .Firewall Hardware Types Three basic hardware types Appliance based systems Purpose built Simple Highly integrated 3 rd Party servers General use systems Additional support channel Greater flexibility Hybrid servers Purpose built for a limited product line Often closely integrated with software offerings May have separate support channel Most have highly integrated components
21 .Firewall Hardware Types Appliance based system problems OS and Kernel hardening and security may be done by vendor only Tightly coupled software and hardware may have insecure code unknown to user Hard to inspect or verify All security controls are determined through a single vendor Appliances are used to simplify implementation and support efforts causing some loss of administrative control
22 .Firewall Hardware Types 3 rd Party server problems OS and Kernel hardening and security must be done by implementation staff Expertise procedures OS software may have many known vulnerabilities / security holes Each must be plugged All security controls are determined through corporate policy 3rd party systems require a larger degree of administration and procedure
23 .Firewall Hardware Types Hybrid servers OS and Kernel hardening is started by vendor and completed by end user security staff —can help to make it more robust Packaged software and hardware are generally reviewed for security All security controls are determined through a more partnered structure Hybrid servers are also used to simplify implementation and support efforts without giving away administrative control
24 .Firewall Hardware Types Hybrid servers OS and Kernel hardening is started by vendor and completed by end user security staff —can help to make it more robust Packaged software and hardware are generally reviewed for security All security controls are determined through a more partnered structure Hybrid servers are also used to simplify implementation and support efforts without giving away administrative control
25 .Firewalls Technologies Traditional packet filters filters often combined with router, creating a firewall widely available in routers, linux Application gateways often implemented with SOCKS today Stateful Inspection filters maintains connection state
26 .Evolution of Firewalls Packet Filter Stateful Inspection Stage of Evolution Application Proxy
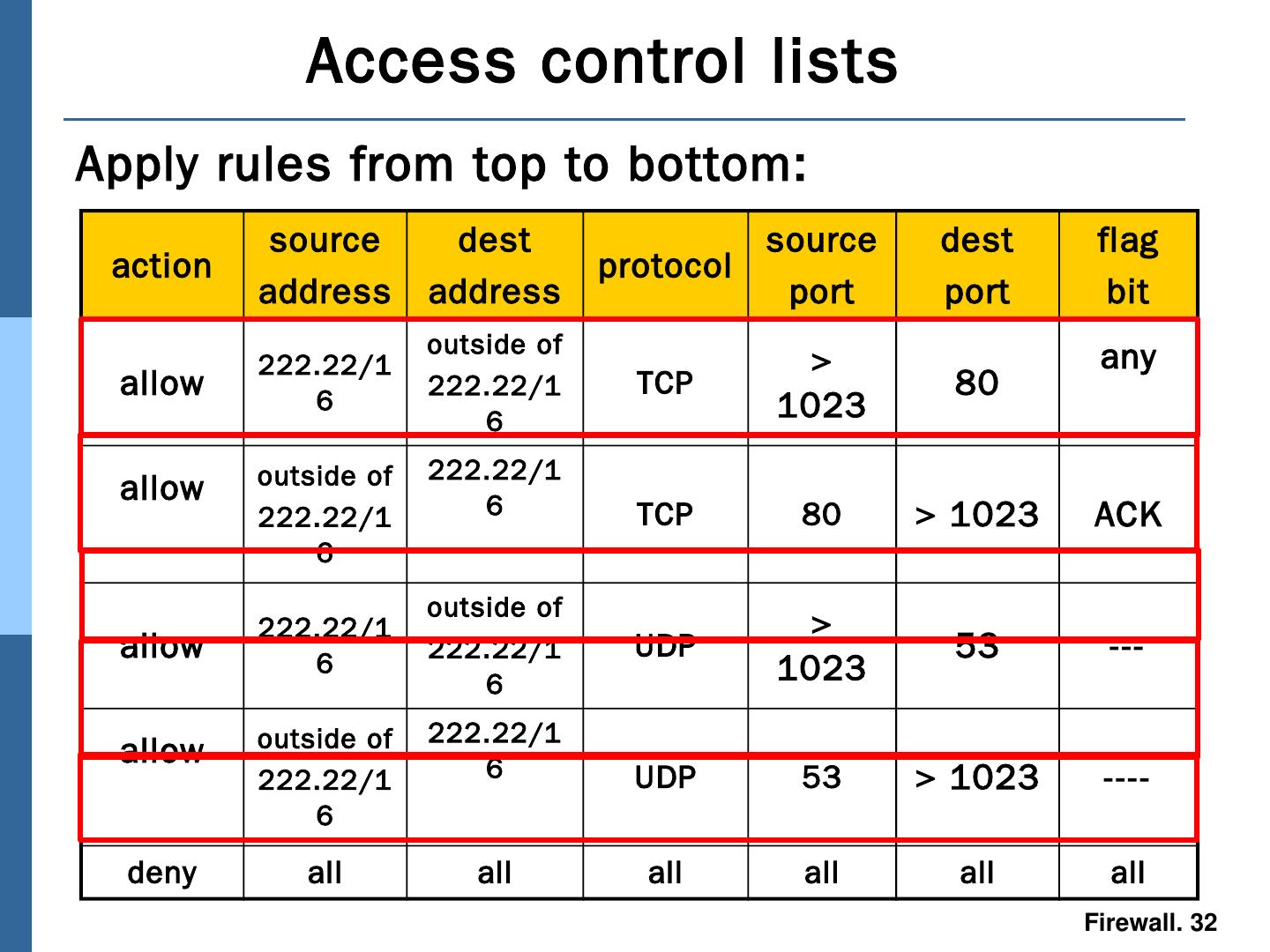
27 .Traditional packet filters source IP address destination IP address source port destination port TCP flag bits SYN bit set: datagram for connection initiation ACK bit set: part of established connection TCP or UDP or ICMP Firewalls often configured to block all UDP direction Is the datagram leaving or entering the internal network? router interface decisions can be different for different interfaces Analyzes each datagram going through it; makes drop decision based on:
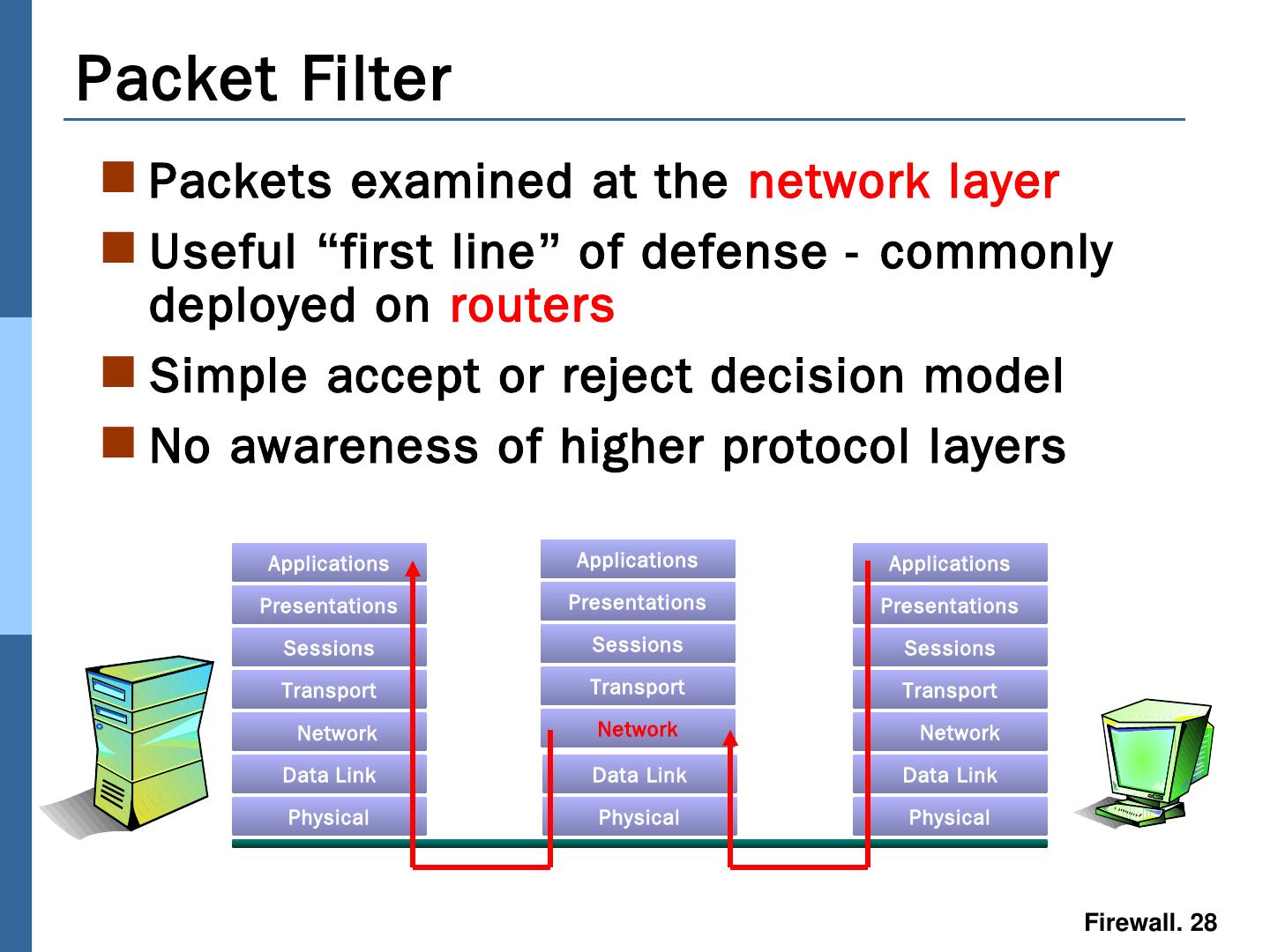
28 .Packets examined at the network layer Useful “ first line ” of defense - commonly deployed on routers Simple accept or reject decision model No awareness of higher protocol layers Packet Filter Applications Presentations Sessions Transport Data Link Physical Data Link Physical Applications Presentations Sessions Transport Data Link Physical Network Presentations Sessions Transport Applications Network Network
29 .Packets examined at the network layer Useful “ first line ” of defense - commonly deployed on routers Simple accept or reject decision model No awareness of higher protocol layers Packet Filter Applications Presentations Sessions Transport Data Link Physical Data Link Physical Applications Presentations Sessions Transport Data Link Physical Network Presentations Sessions Transport Applications Network Network