- 快召唤伙伴们来围观吧
- 微博 QQ QQ空间 贴吧
- 文档嵌入链接
- 复制
- 微信扫一扫分享
- 已成功复制到剪贴板
报表级控制结构
展开查看详情
1 .Chapter 8 Statement-Level Control Structures
2 .Augment Sebesta Material Programming Languages-Cheng (Fall 2004) http://www.cse.msu.edu/~cse452/Fall2004/Lectures/08-control-new Edited.pptx Type Systems and Structures- Bermúdez https://www.cise.ufl.edu/class/cop5556sp16/Lecture_20.ppt https://www.cise.ufl.edu/class/cop5556sp16/Lecture_20.ppt
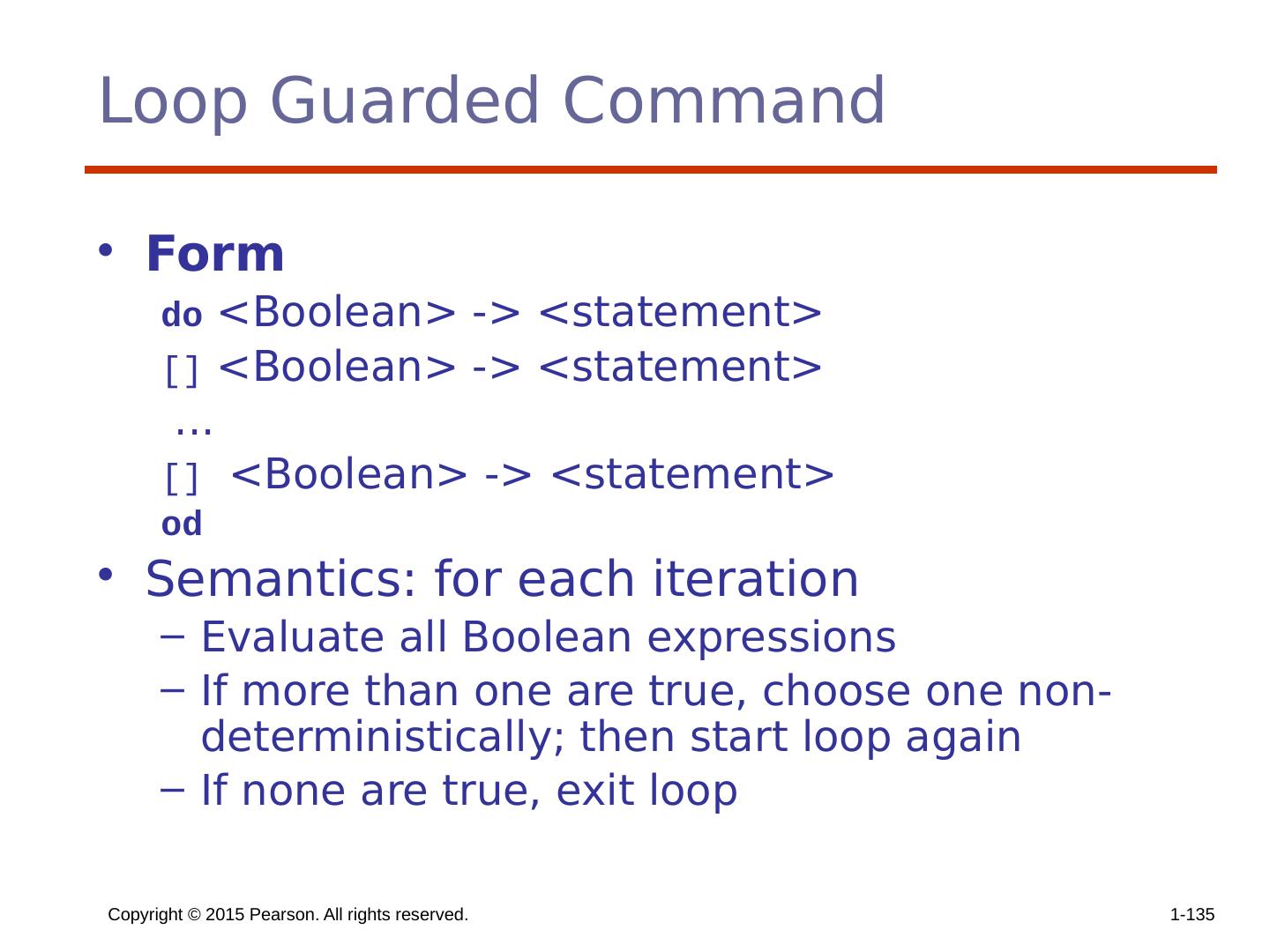
3 .Copyright © 2015 Pearson. All rights reserved. 1- 3 Chapter 8 Topics Introduction Selection Statements Iterative Statements Unconditional Branching Other Selection Statements https://www.cise.ufl.edu/class/cop5556sp16/Lecture_20.ppt Practical PL Level Iteration and Recursion https://www.cise.ufl.edu/class/cop5556sp16/Lecture_21.ppt Guarded Commands Conclusions
4 .Copyright © 2015 Pearson. All rights reserved. 1- 4 Levels of Control Flow Within expressions (Chapter 7) Among program units (Chapter 9) Among program statements (this chapter)
5 .Copyright © 2015 Pearson. All rights reserved. 1- 5 Control Statements: Evolution FORTRAN I control statements were based directly on IBM 704 hardware Much research and argument in the 1960s about the issue One important result: It was proven that all algorithms represented by flowcharts can be coded with only two-way selection and pretest logical loops
6 .Copyright © 2015 Pearson. All rights reserved. 1- 6 Control Structure A control structure is a control statement and the statements whose execution it controls Design question Should a control structure have multiple entries?
7 .Copyright © 2015 Pearson. All rights reserved. 1- 7 Selection Statements A selection statement provides the means of choosing between two or more paths of execution Three general categories: One-way selection statements Two-way selectors statements Multiple-way selectors statements Nested selection statements?
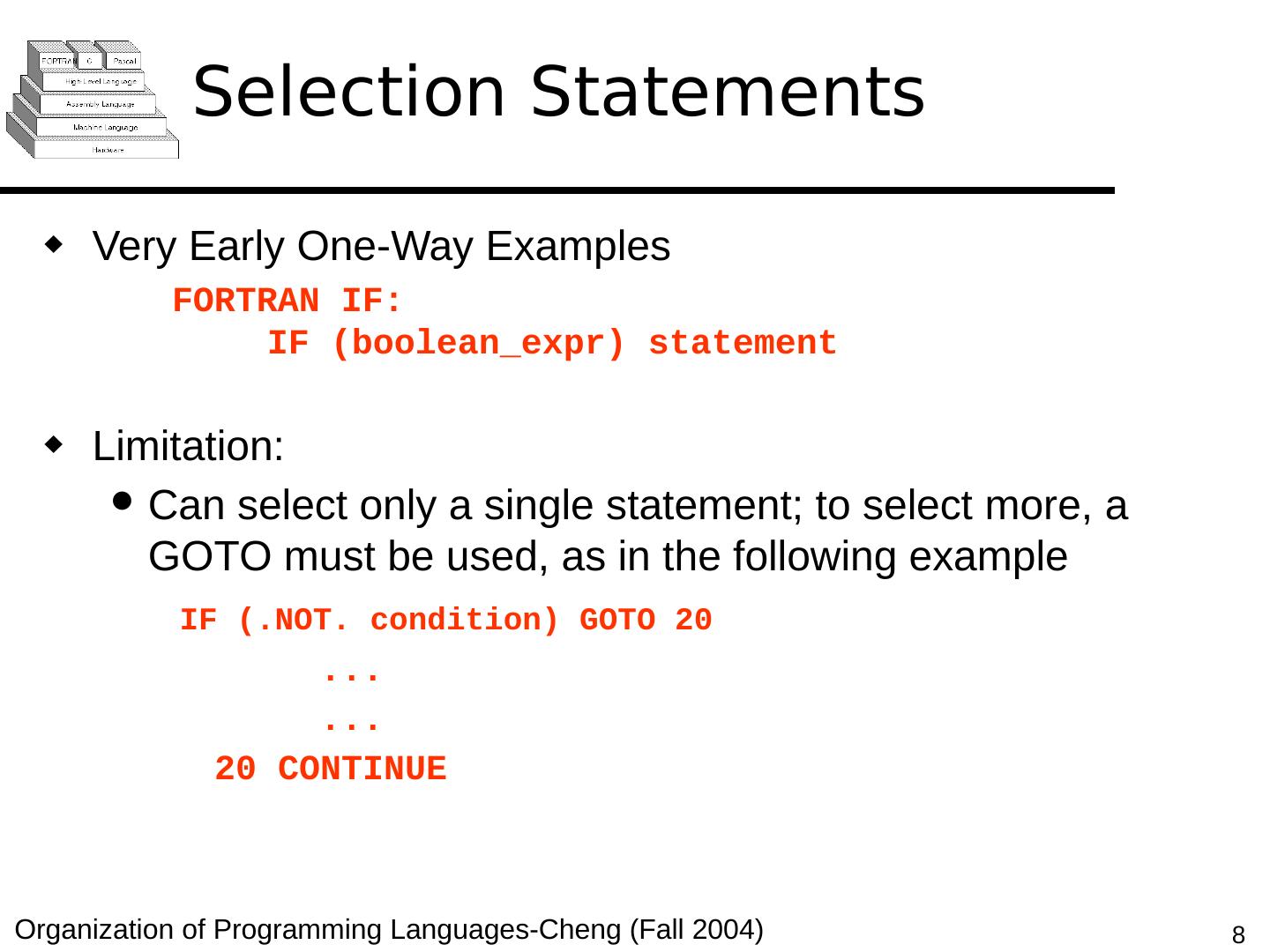
8 .Selection Statements Very Early One-Way Examples FORTRAN IF: IF ( boolean_expr ) statement Limitation: C an select only a single statement; to select more, a GOTO must be used, as in the following example IF (.NOT. condition) GOTO 20 ... ... 20 CONTINUE
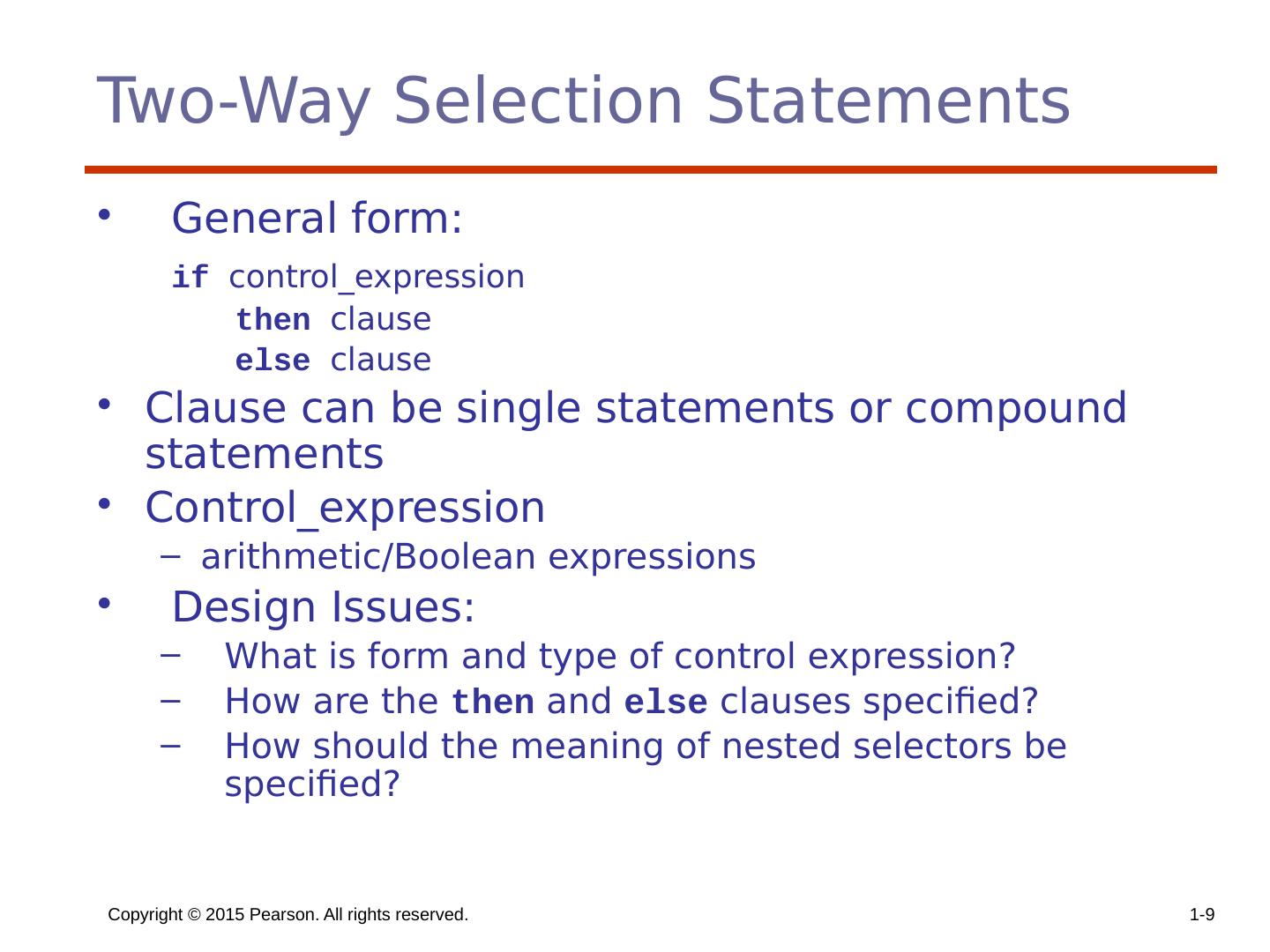
9 .Copyright © 2015 Pearson. All rights reserved. 1- 9 Two-Way Selection Statements General form: if control_expression then clause else clause Clause can be single statements or compound statements Control_expression arithmetic/Boolean expressions Design Issues: What is form and type of control expression? How are the then and else clauses specified? How should the meaning of nested selectors be specified?
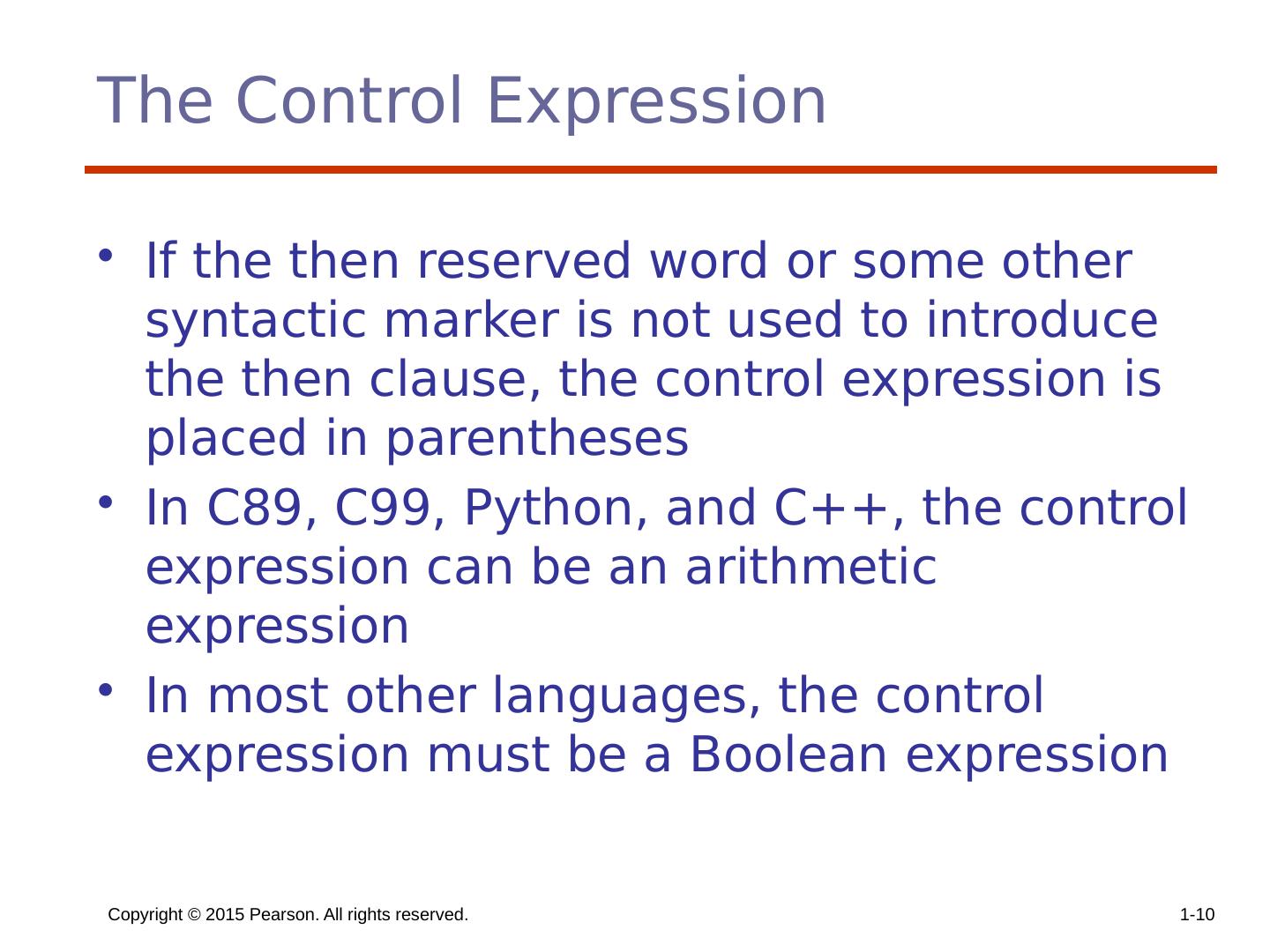
10 .Copyright © 2015 Pearson. All rights reserved. 1- 10 The Control Expression If the then reserved word or some other syntactic marker is not used to introduce the then clause, the control expression is placed in parentheses In C89, C99, Python, and C++, the control expression can be an arithmetic expression In most other languages, the control expression must be a Boolean expression
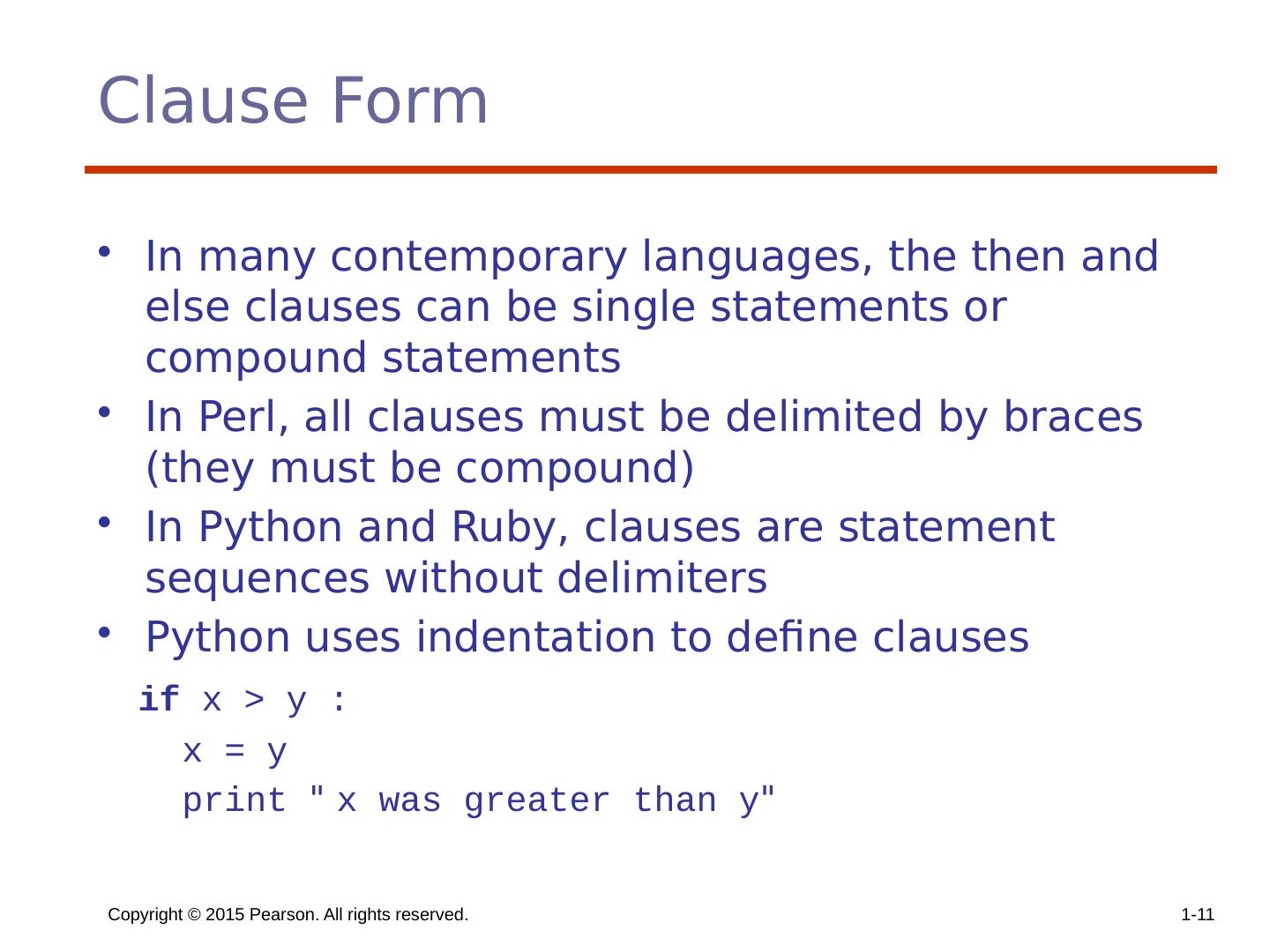
11 .Copyright © 2015 Pearson. All rights reserved. 1- 11 Clause Form In many contemporary languages, the then and else clauses can be single statements or compound statements In Perl, all clauses must be delimited by braces (they must be compound) In Python and Ruby, clauses are statement sequences without delimiters Python uses indentation to define clauses if x > y : x = y print " x was greater than y "
12 .Copyright © 2015 Pearson. All rights reserved. 1- 11 Clause Form In many contemporary languages, the then and else clauses can be single statements or compound statements In Perl, all clauses must be delimited by braces (they must be compound) In Python and Ruby, clauses are statement sequences without delimiters Python uses indentation to define clauses if x > y : x = y print " x was greater than y "
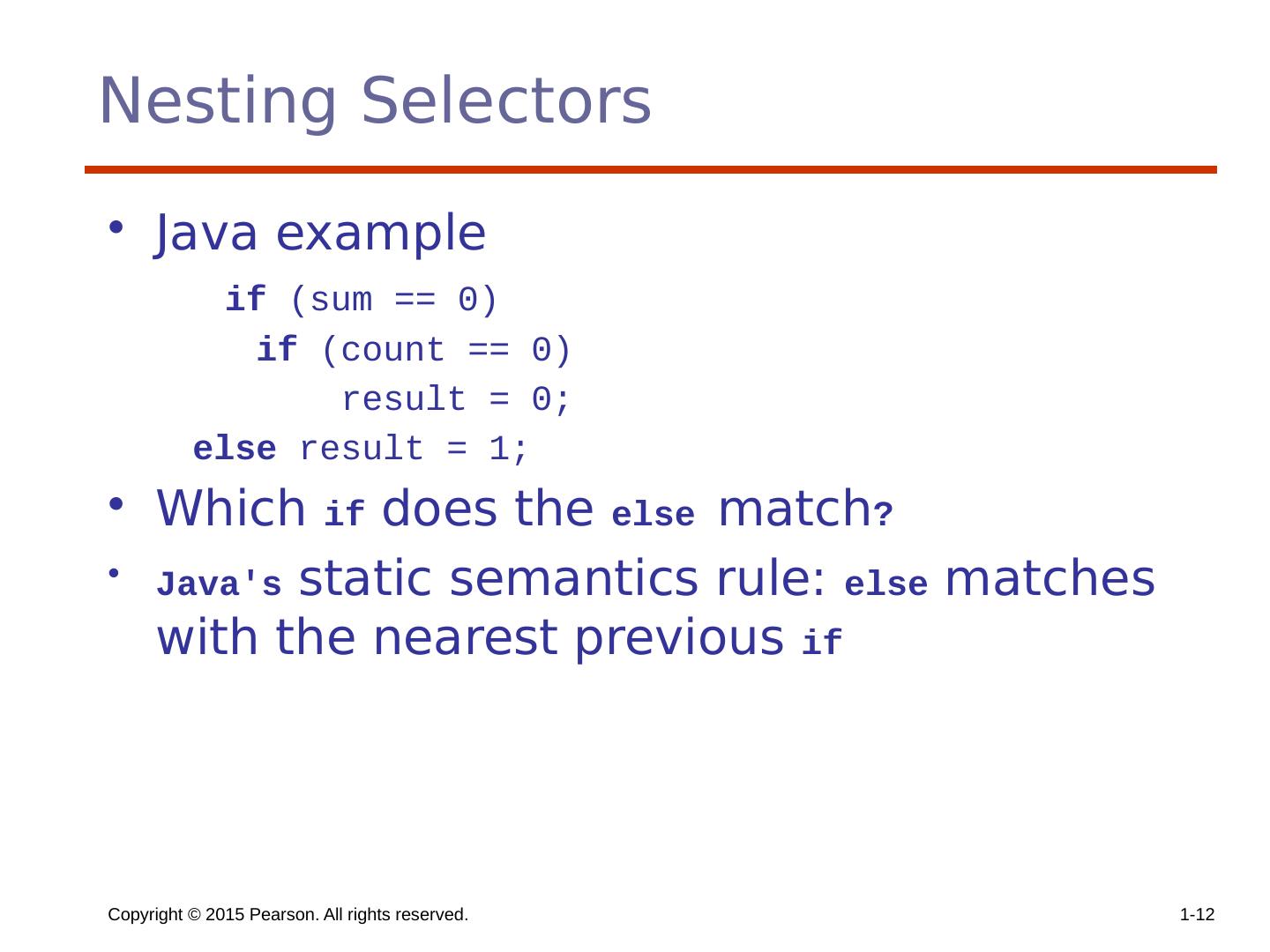
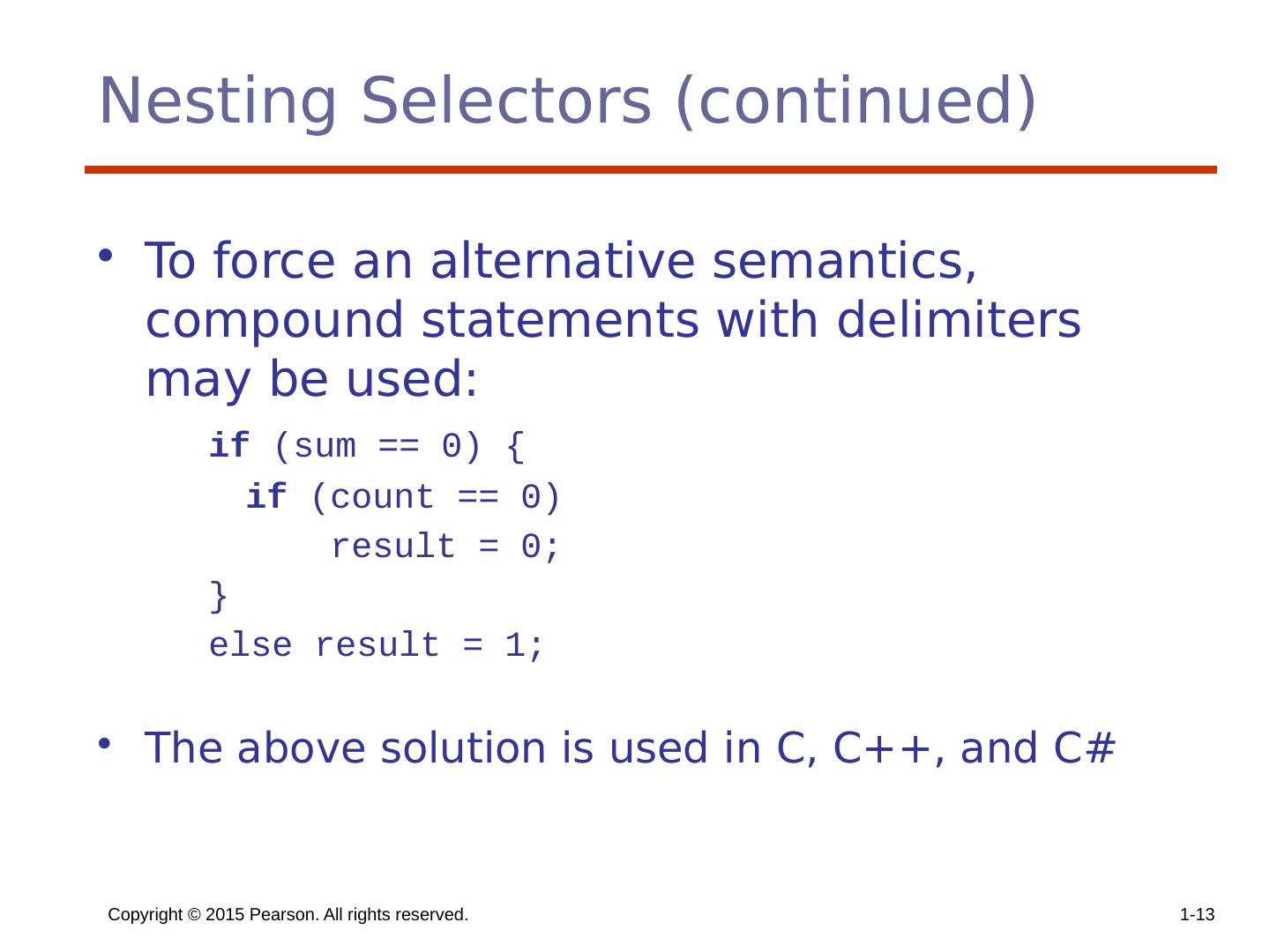
13 .Copyright © 2015 Pearson. All rights reserved. 1- 13 Nesting Selectors (continued) To force an alternative semantics, compound statements with delimiters may be used: if (sum == 0) { if (count == 0) result = 0; } else result = 1; The above solution is used in C, C++, and C#
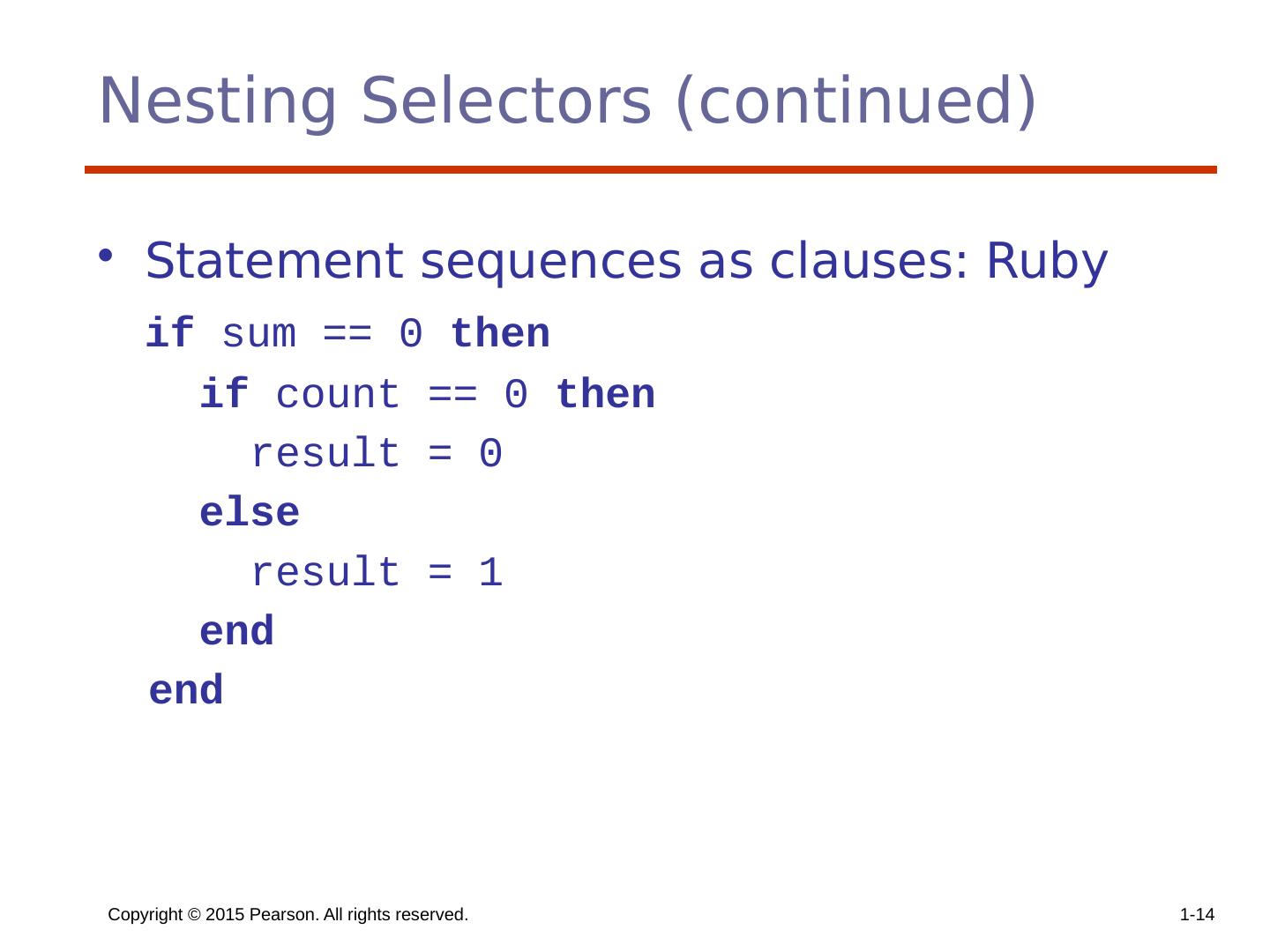
14 .Copyright © 2015 Pearson. All rights reserved. 1- 14 Nesting Selectors (continued) Statement sequences as clauses: Ruby if sum == 0 then if count == 0 then result = 0 else result = 1 end end
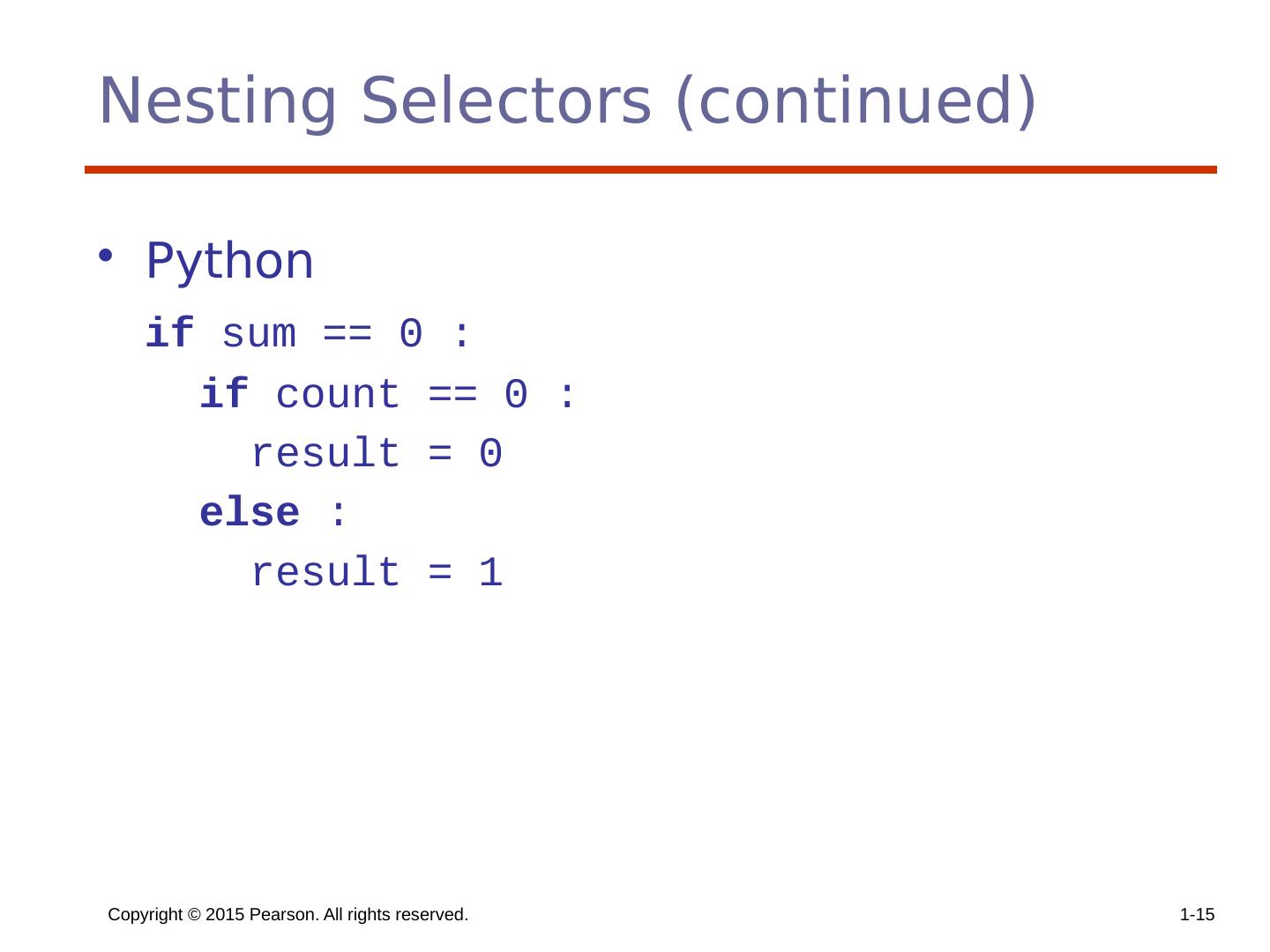
15 .Copyright © 2015 Pearson. All rights reserved. 1- 15 Nesting Selectors (continued) Python if sum == 0 : if count == 0 : result = 0 else : result = 1
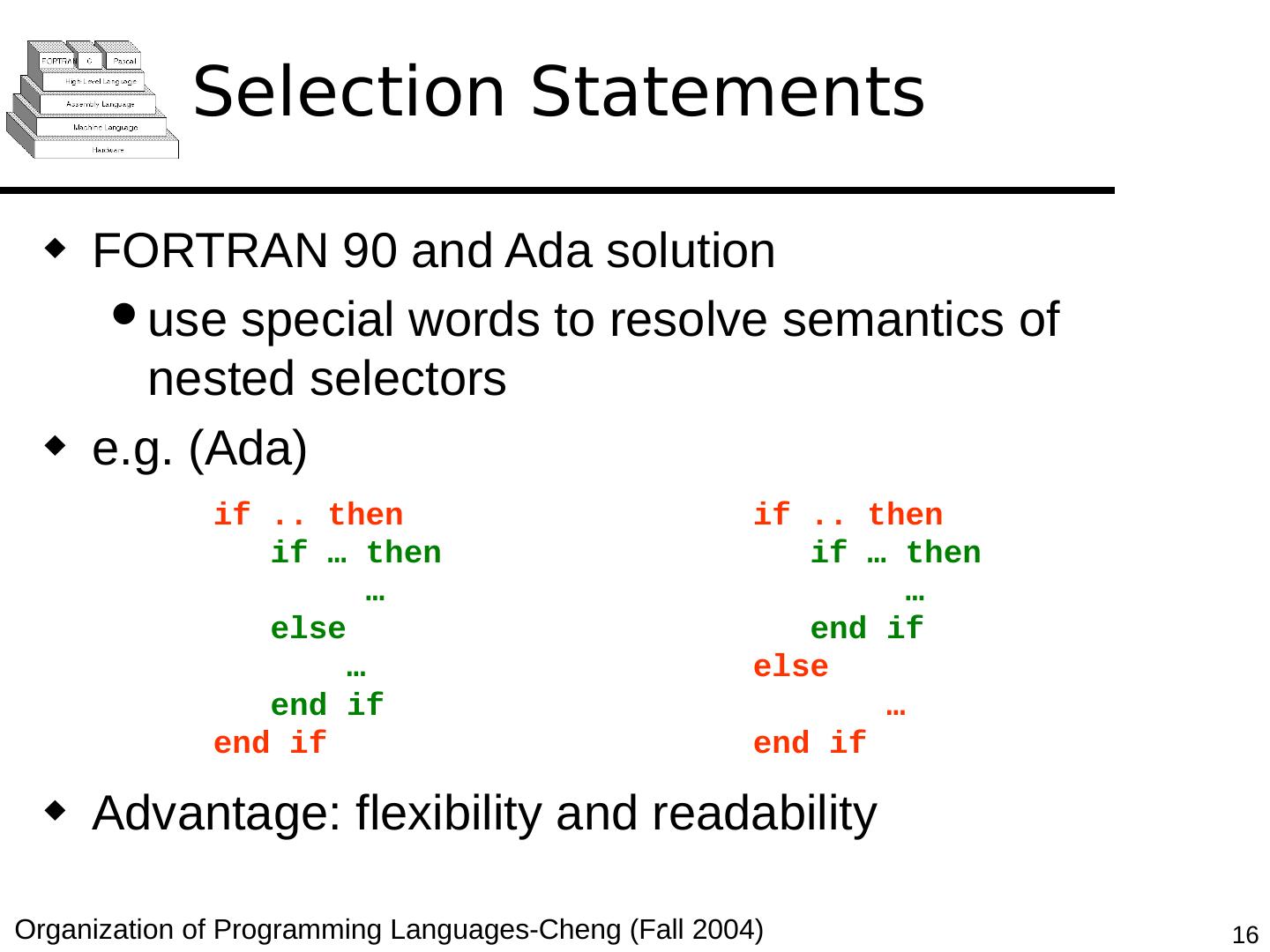
16 .Selection Statements FORTRAN 90 and Ada solution use special words to resolve semantics of nested selectors e.g. (Ada) Advantage: flexibility and readability if .. then if … then … end if else … end if if .. then if … then … else … end if end if
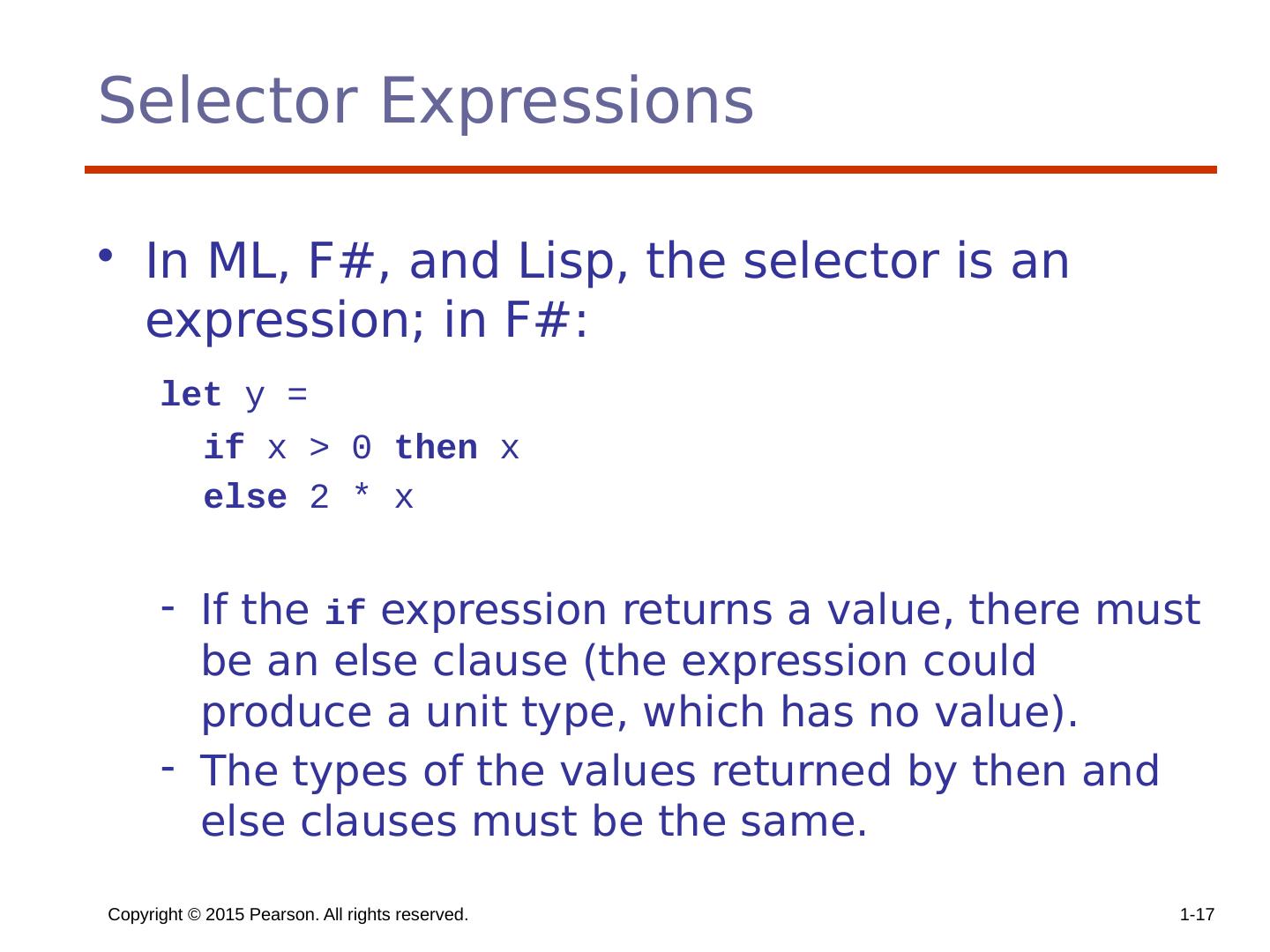
17 .Selector Expressions In ML, F#, and Lisp, the selector is an expression; in F#: let y = if x > 0 then x else 2 * x If the if expression returns a value, there must be an else clause (the expression could produce a unit type, which has no value). The types of the values returned by then and else clauses must be the same. Copyright © 2015 Pearson. All rights reserved. 1- 17
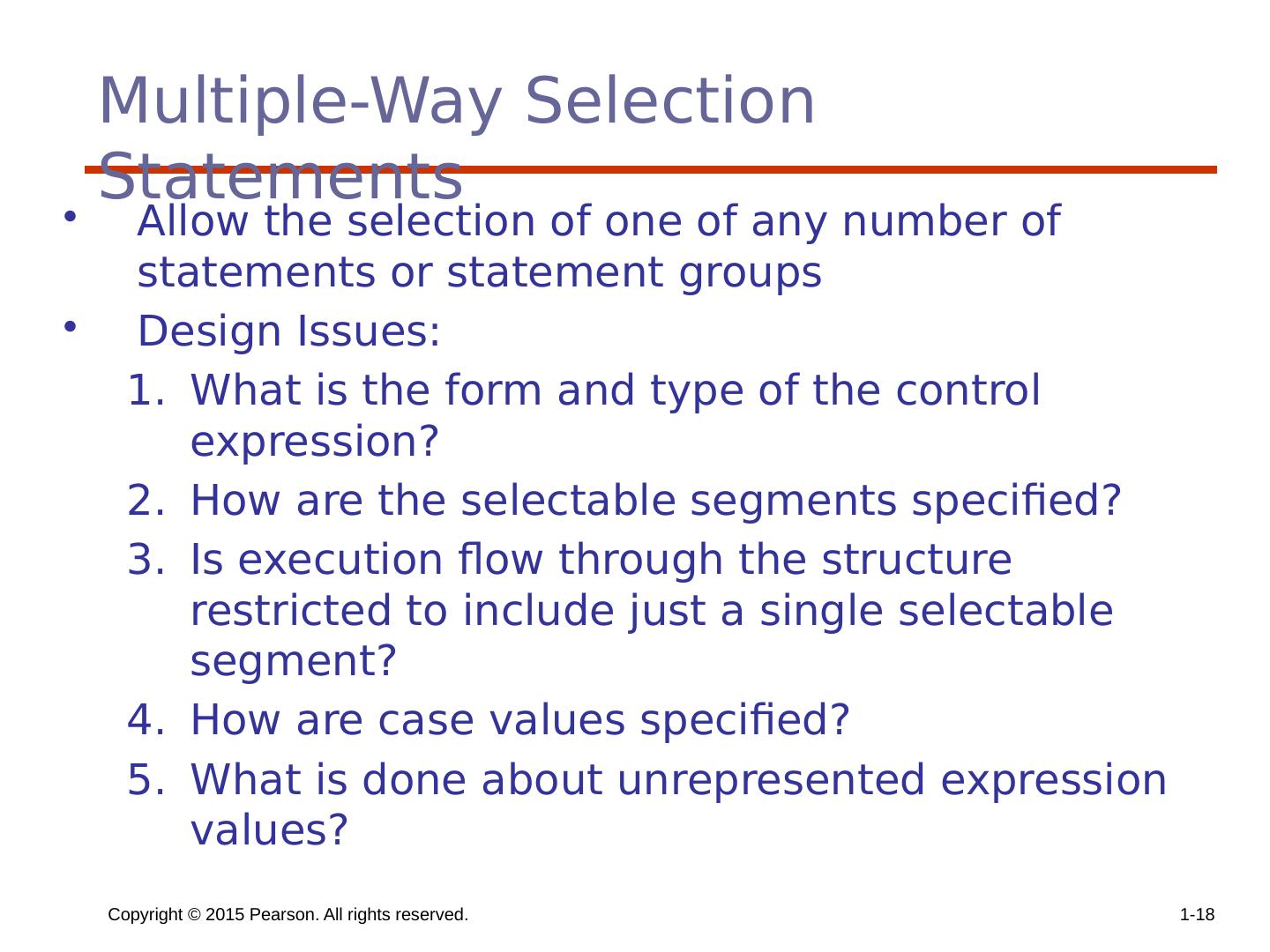
18 .Copyright © 2015 Pearson. All rights reserved. 1- 18 Multiple-Way Selection Statements Allow the selection of one of any number of statements or statement groups Design Issues: What is the form and type of the control expression? How are the selectable segments specified? Is execution flow through the structure restricted to include just a single selectable segment? How are case values specified? What is done about unrepresented expression values?
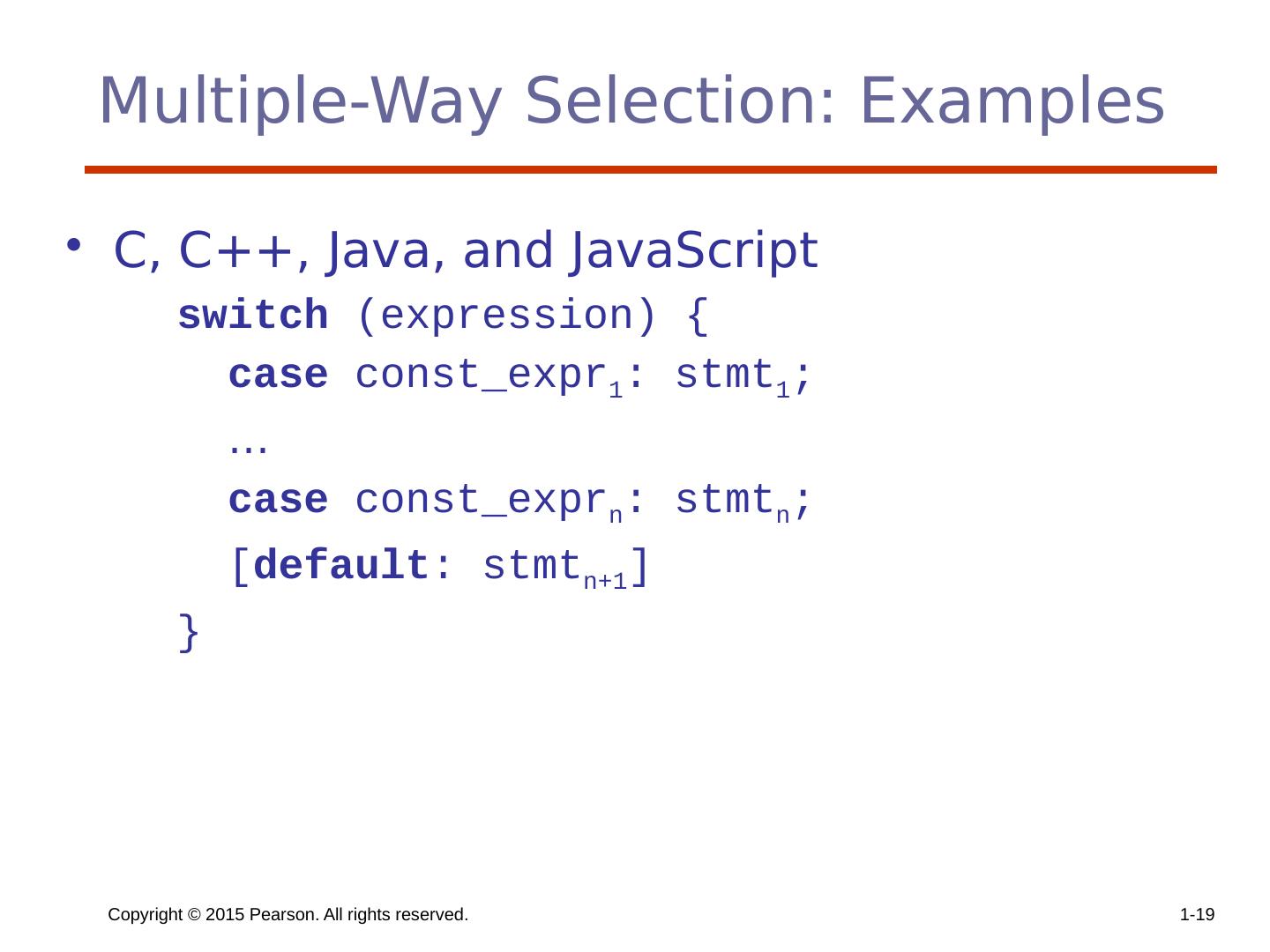
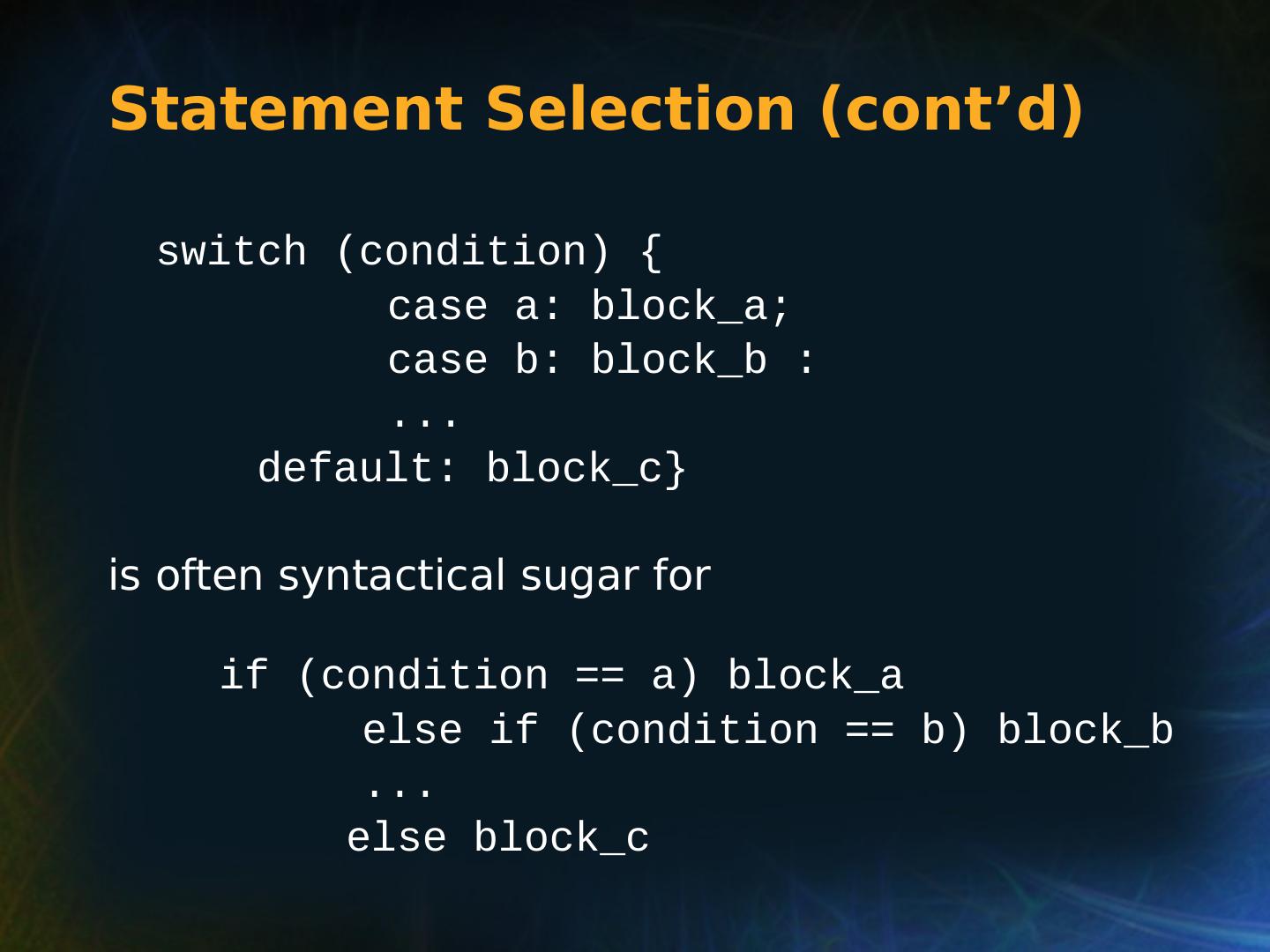
19 .Copyright © 2015 Pearson. All rights reserved. 1- 19 Multiple-Way Selection: Examples C, C++, Java, and JavaScript switch (expression) { case const_expr 1 : stmt 1 ; … case const_expr n : stmt n ; [ default : stmt n+1 ] }
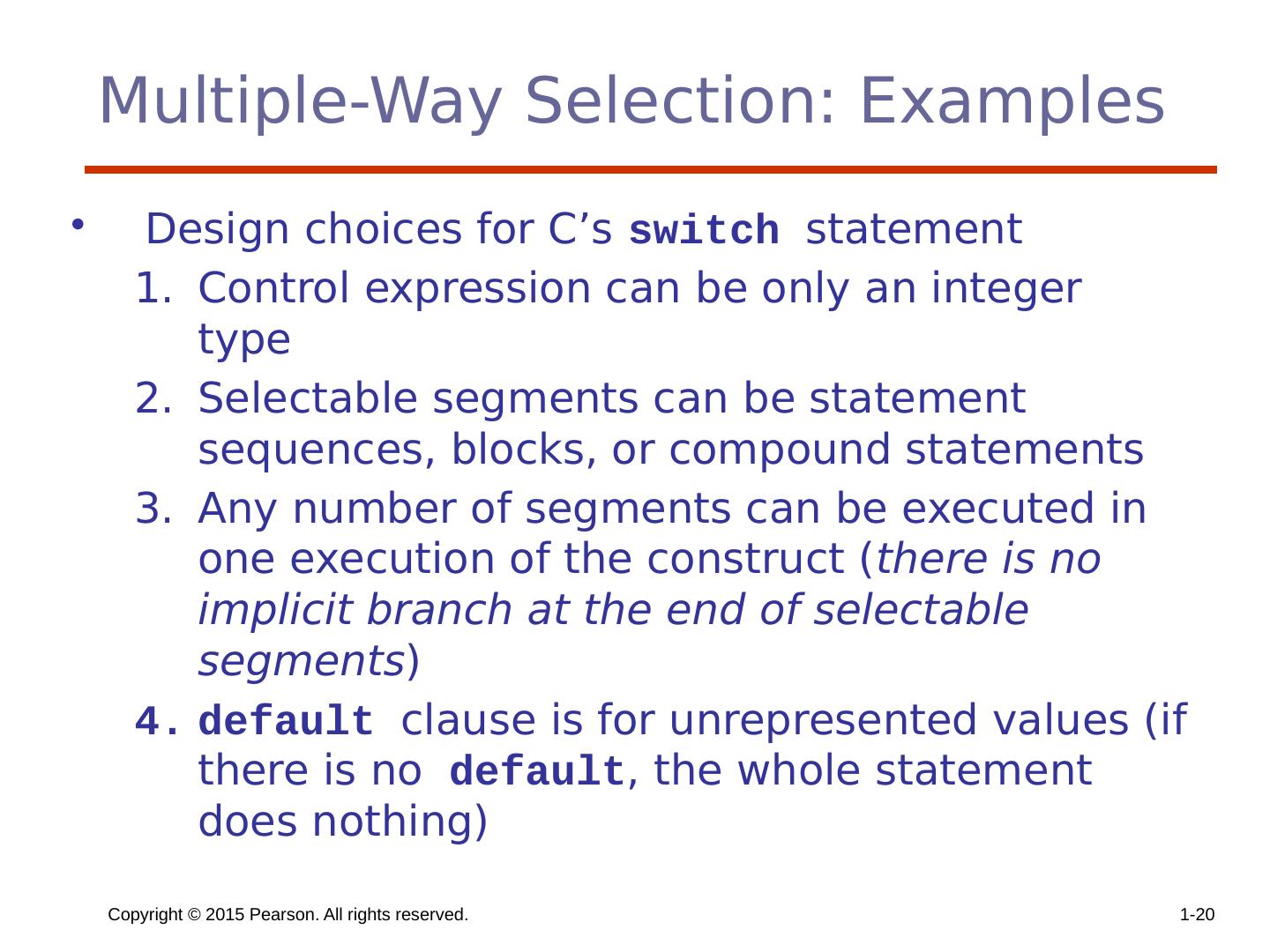
20 .Copyright © 2015 Pearson. All rights reserved. 1- 20 Multiple-Way Selection: Examples Design choices for C’s switch statement Control expression can be only an integer type Selectable segments can be statement sequences, blocks, or compound statements Any number of segments can be executed in one execution of the construct ( there is no implicit branch at the end of selectable segments ) default clause is for unrepresented values (if there is no default , the whole statement does nothing)
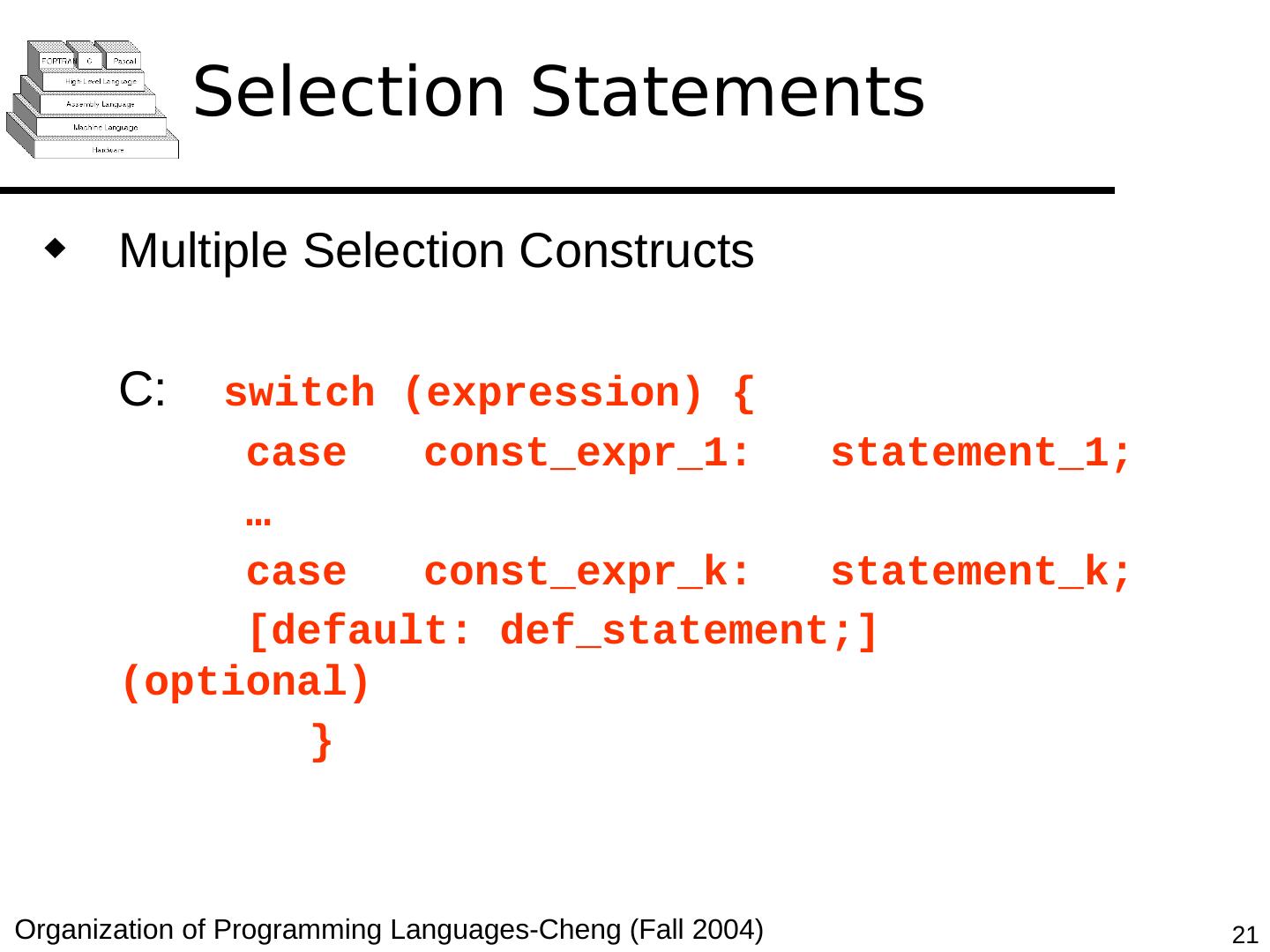
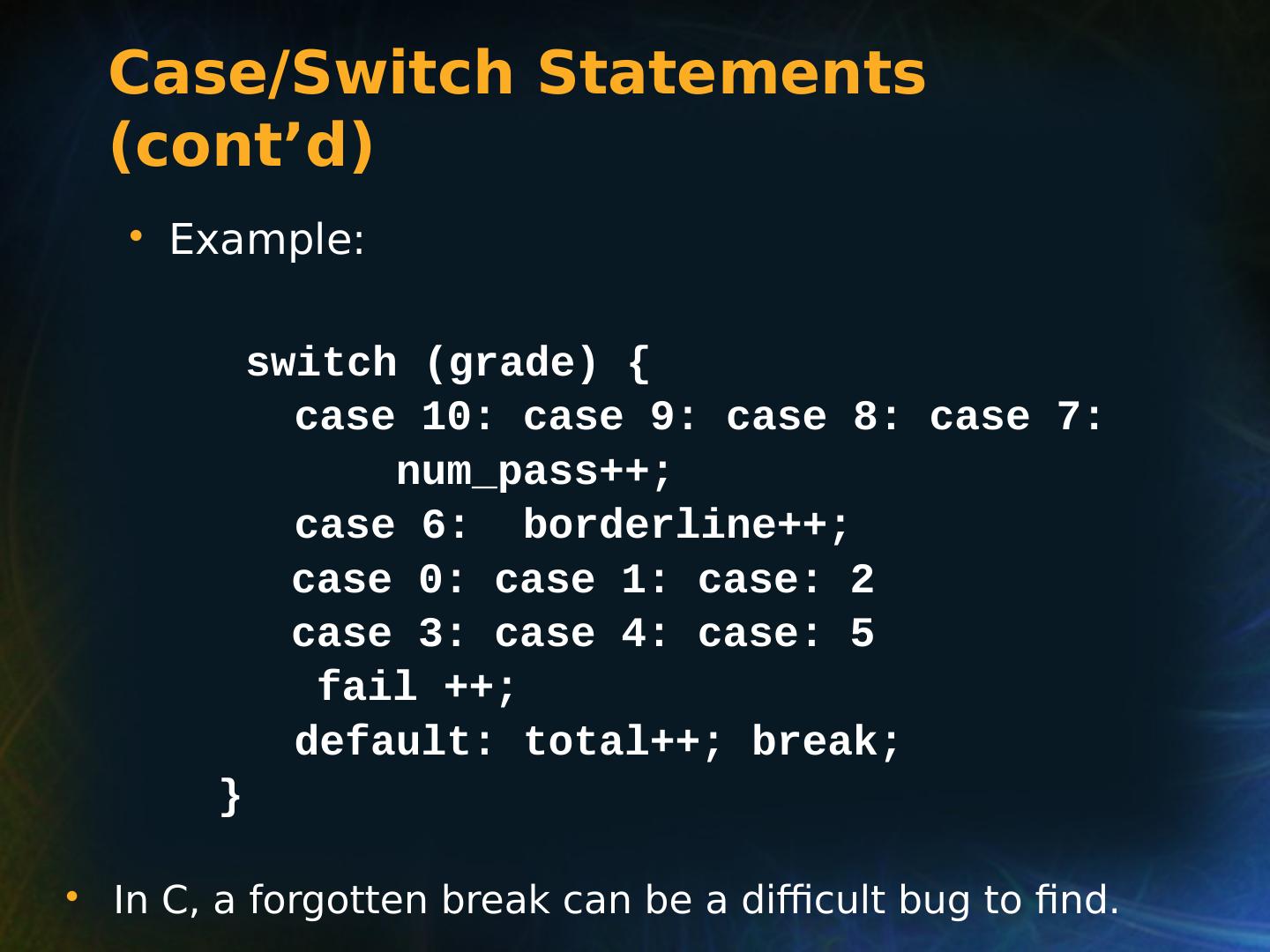
21 .Selection Statements Multiple Selection Constructs C: switch (expression) { case const_expr_1: statement_1; … case const_expr_k: statement_k; [default: def_statement;] (optional) }
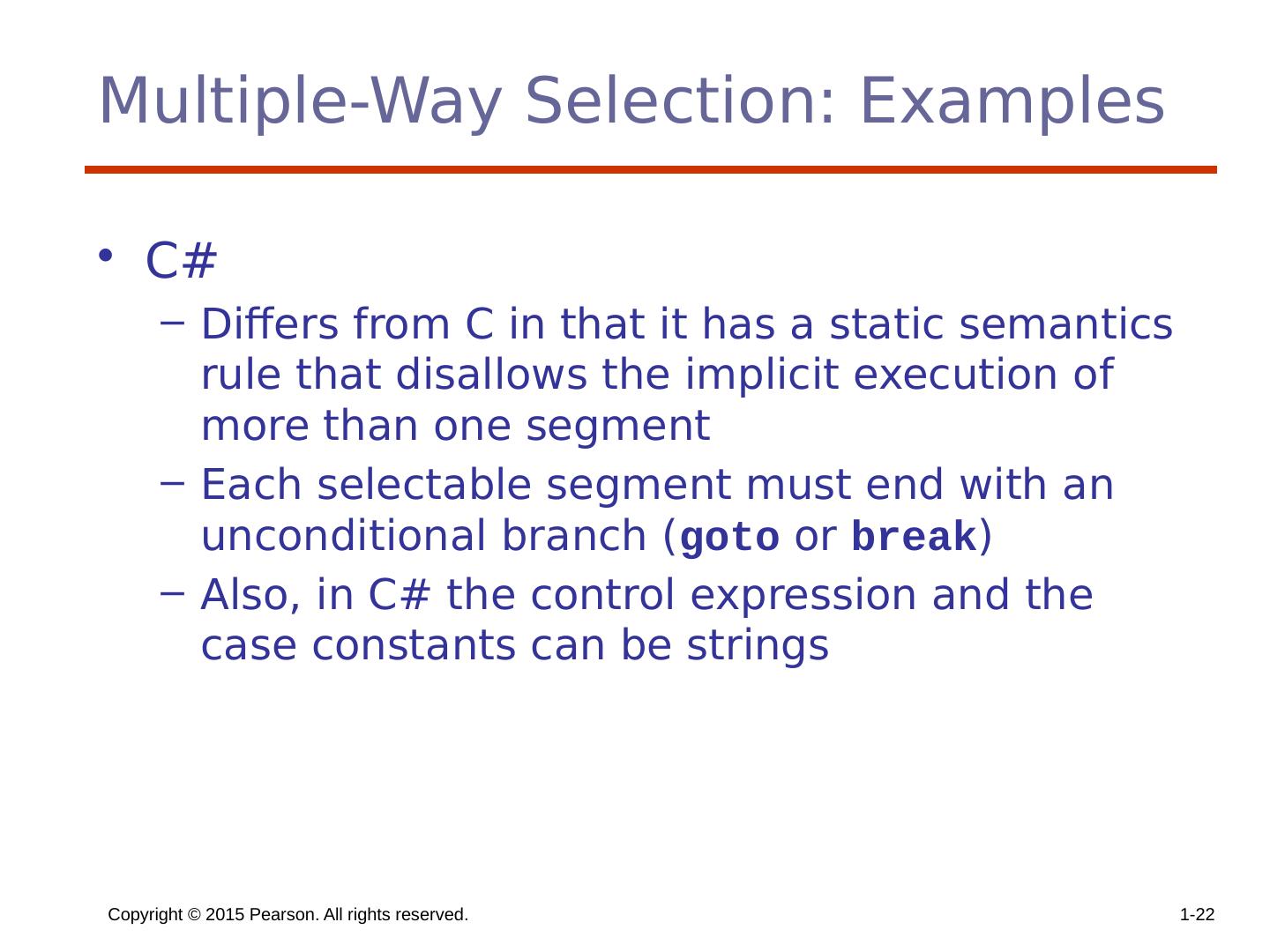
22 .Copyright © 2015 Pearson. All rights reserved. 1- 22 Multiple-Way Selection: Examples C# Differs from C in that it has a static semantics rule that disallows the implicit execution of more than one segment Each selectable segment must end with an unconditional branch ( goto or break ) Also, in C# the control expression and the case constants can be strings
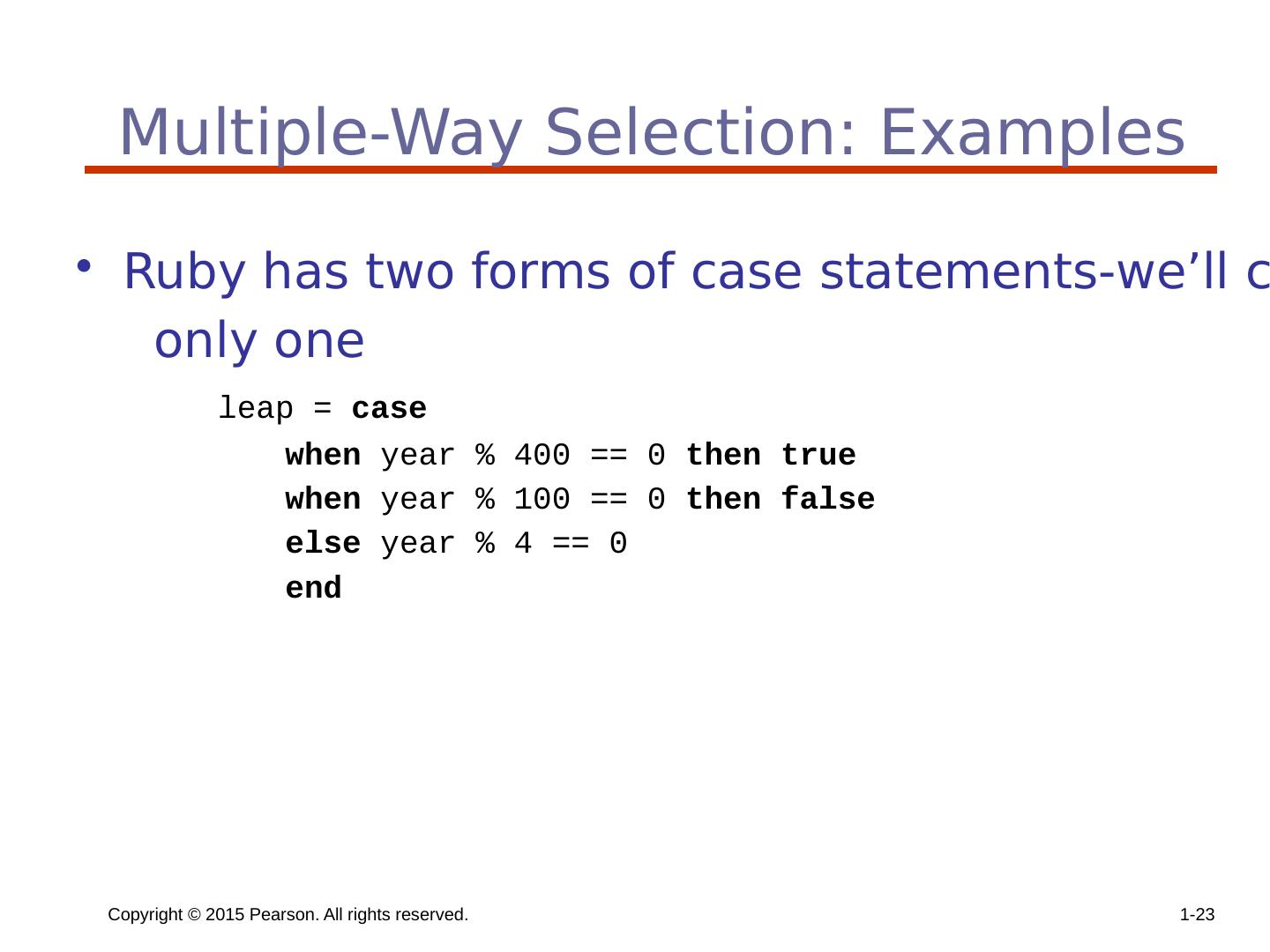
23 .Copyright © 2015 Pearson. All rights reserved. 1- 23 Multiple-Way Selection: Examples Ruby has two forms of case statements-we’ll cover only one leap = case when year % 400 == 0 then true when year % 100 == 0 then false else year % 4 == 0 end
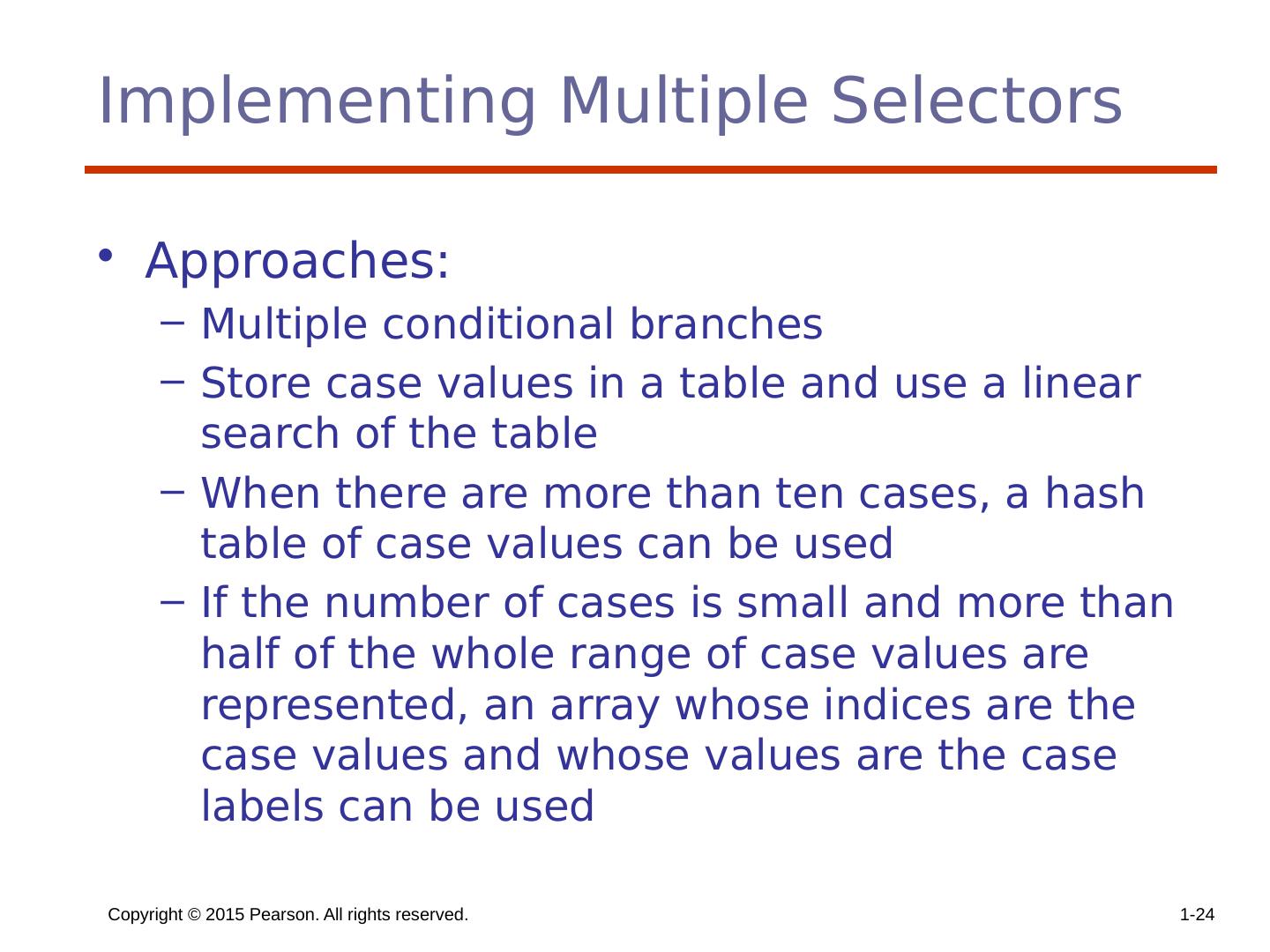
24 .Implementing Multiple Selectors Approaches: Multiple conditional branches Store case values in a table and use a linear search of the table When there are more than ten cases, a hash table of case values can be used If the number of cases is small and more than half of the whole range of case values are represented, an array whose indices are the case values and whose values are the case labels can be used Copyright © 2015 Pearson. All rights reserved. 1- 24
25 .Copyright © 2015 Pearson. All rights reserved. 1- 25 Multiple-Way Selection Using if Multiple Selectors can appear as direct extensions to two-way selectors, using else-if clauses, for example in Python: if count < 10 : bag1 = True elif count < 100 : bag2 = True elif count < 1000 : bag3 = True
26 .Copyright © 2015 Pearson. All rights reserved. 1- 26 Multiple-Way Selection Using if The Python example can be written as a Ruby case case when count < 10 then bag1 = true when count < 100 then bag2 = true when count < 1000 then bag3 = true end
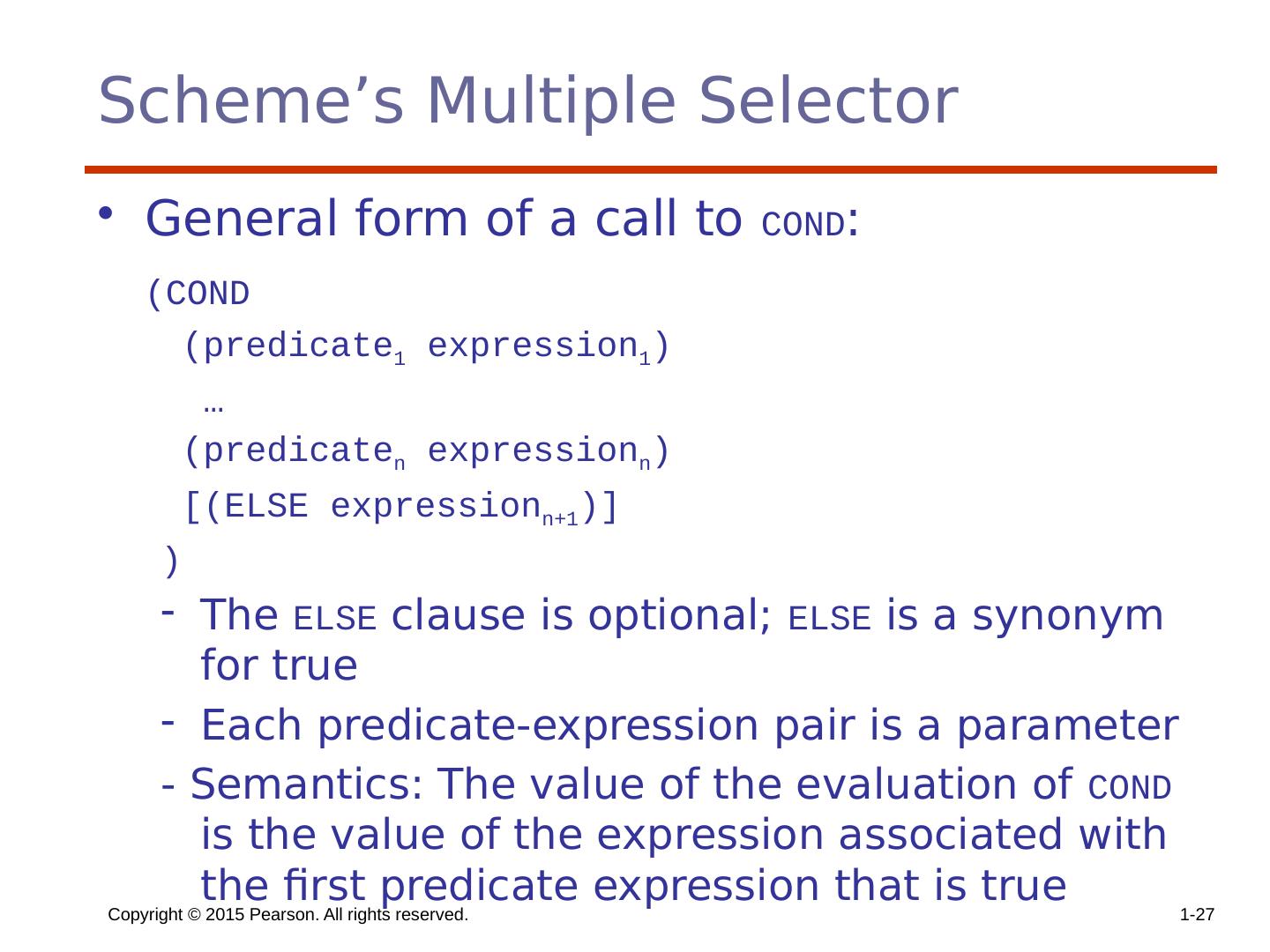
27 .Scheme’s Multiple Selector General form of a call to COND : (COND (predicate 1 expression 1 ) … (predicate n expression n ) [(ELSE expression n+1 )] ) The ELSE clause is optional; ELSE is a synonym for true Each predicate-expression pair is a parameter - Semantics: The value of the evaluation of COND is the value of the expression associated with the first predicate expression that is true Copyright © 2015 Pearson. All rights reserved. 1- 27
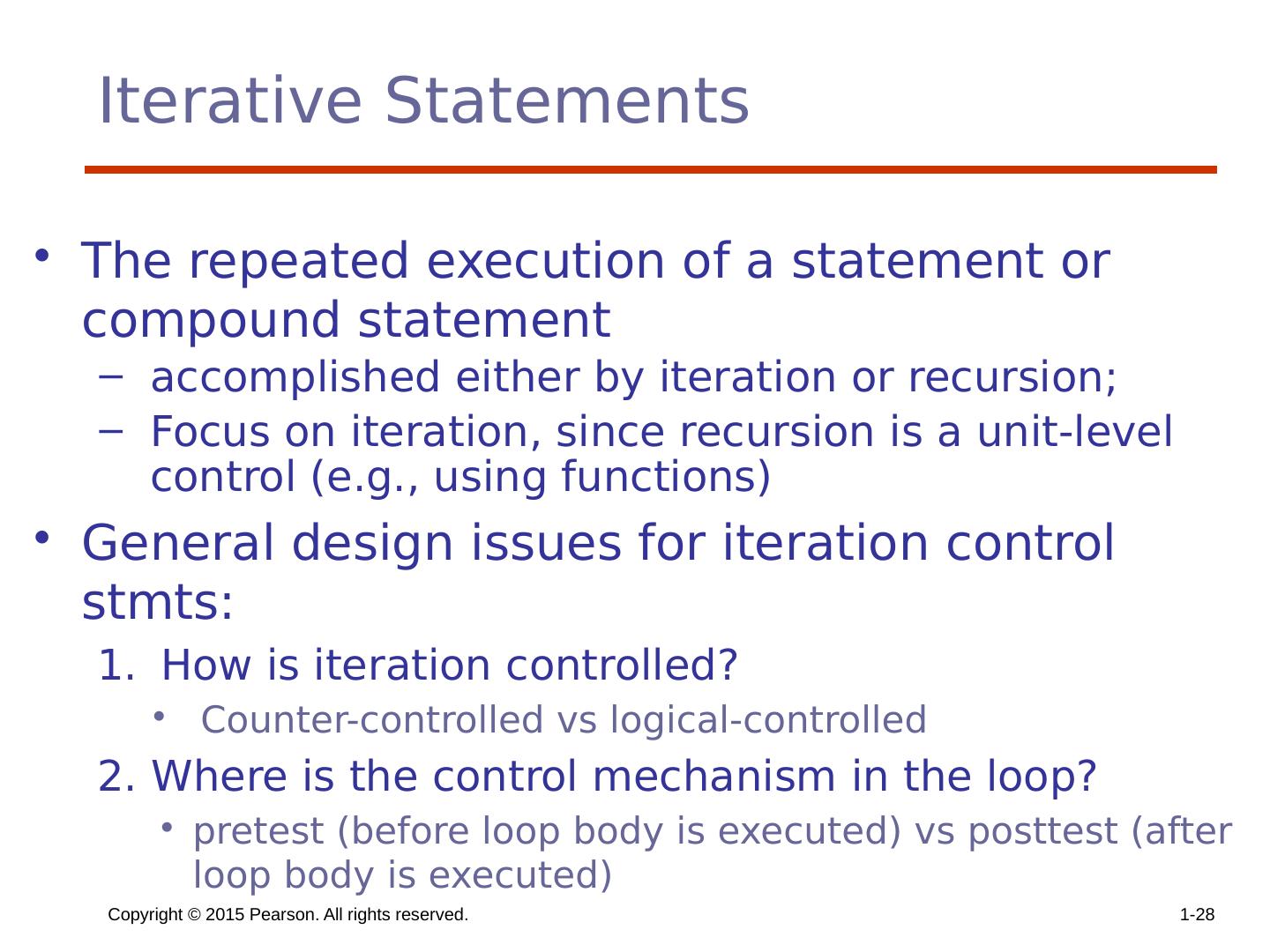
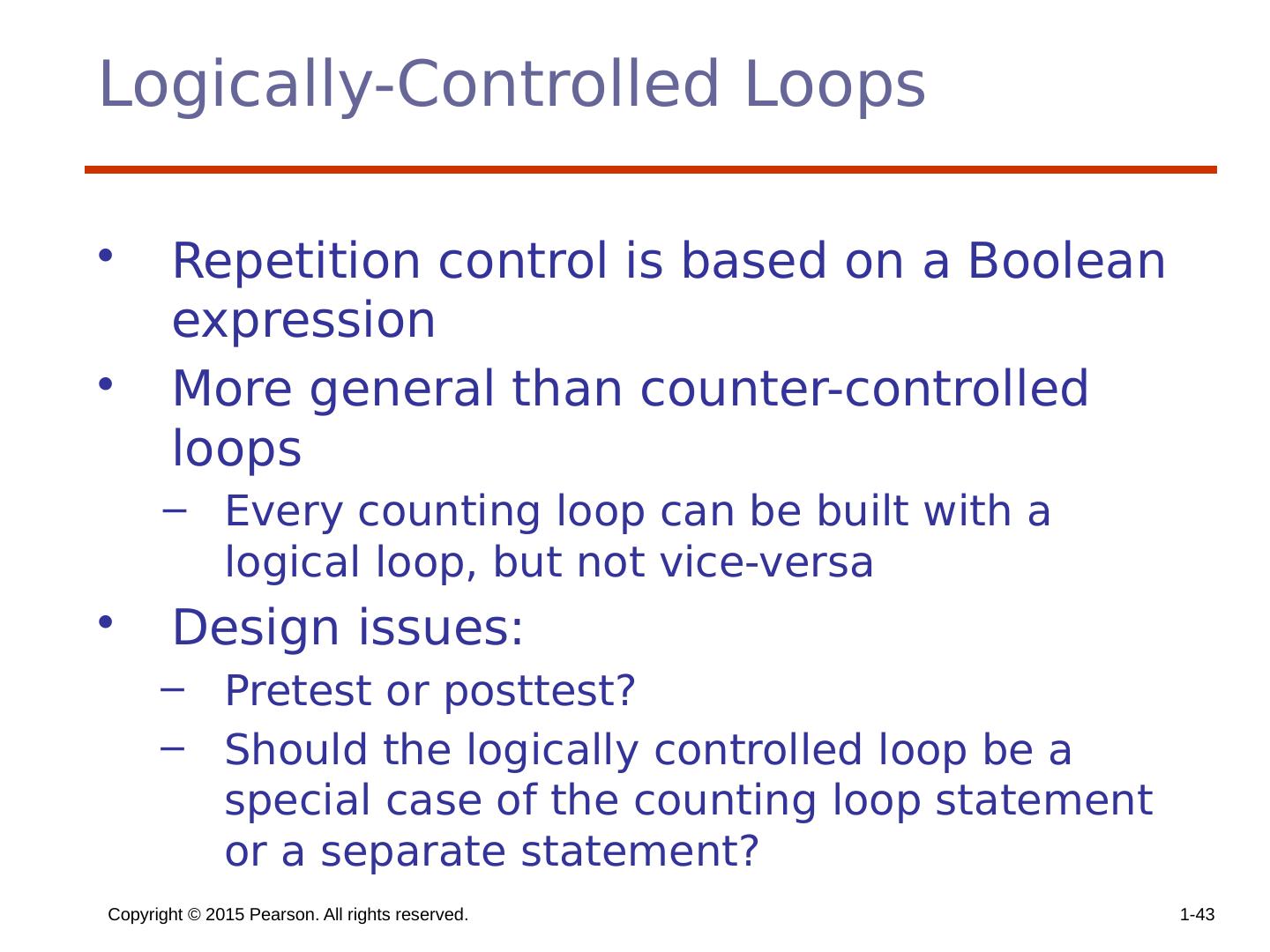
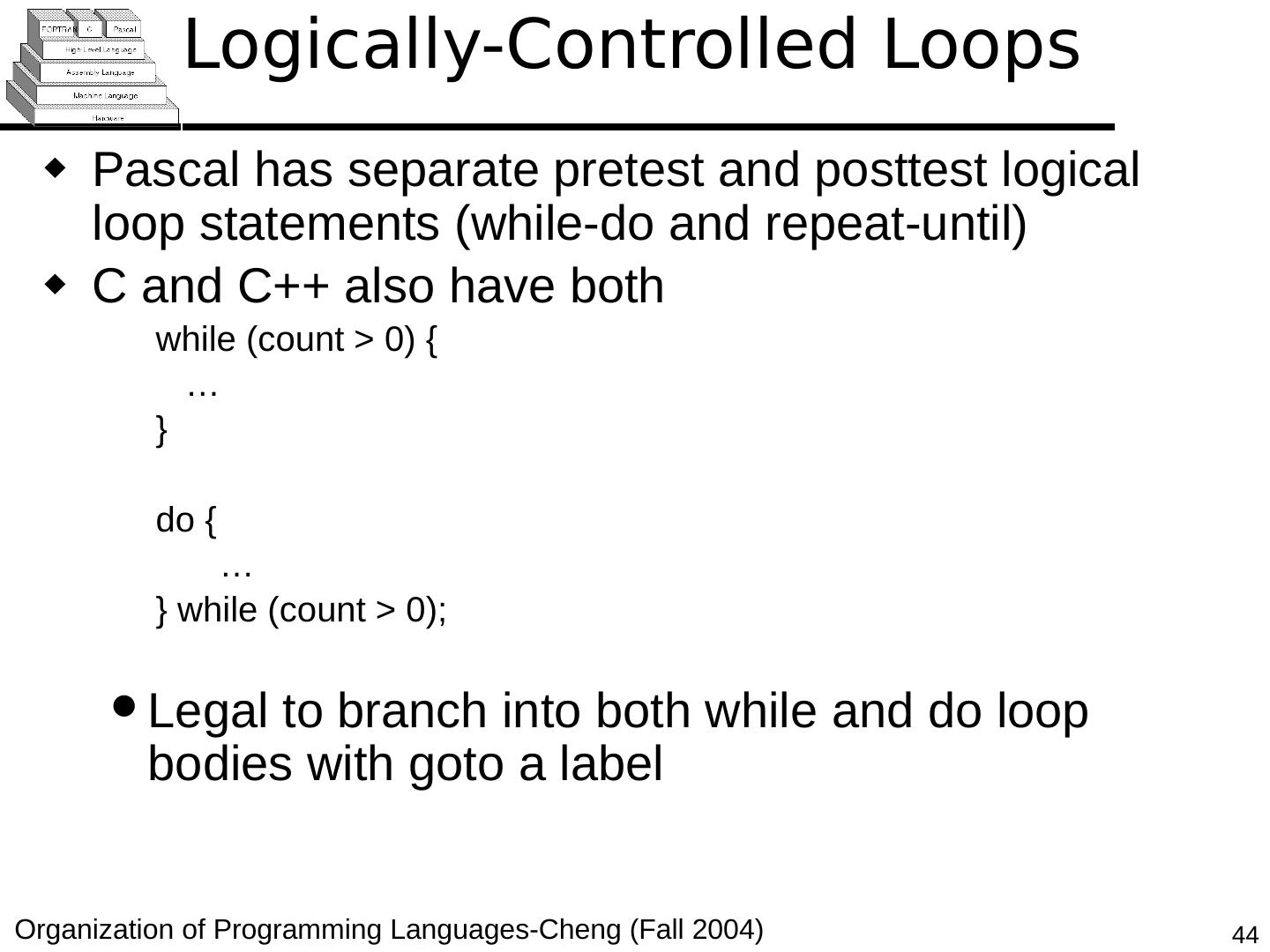
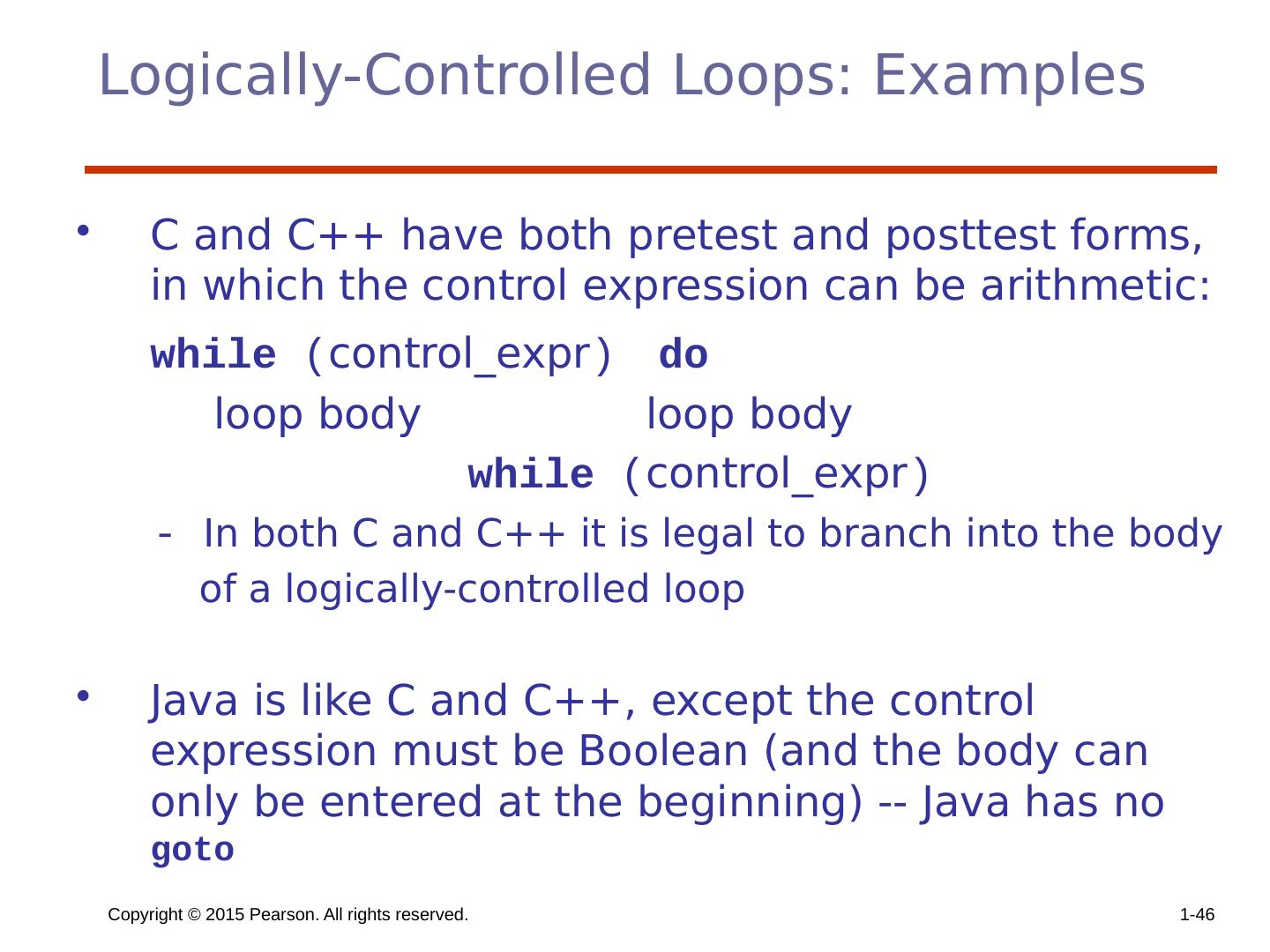
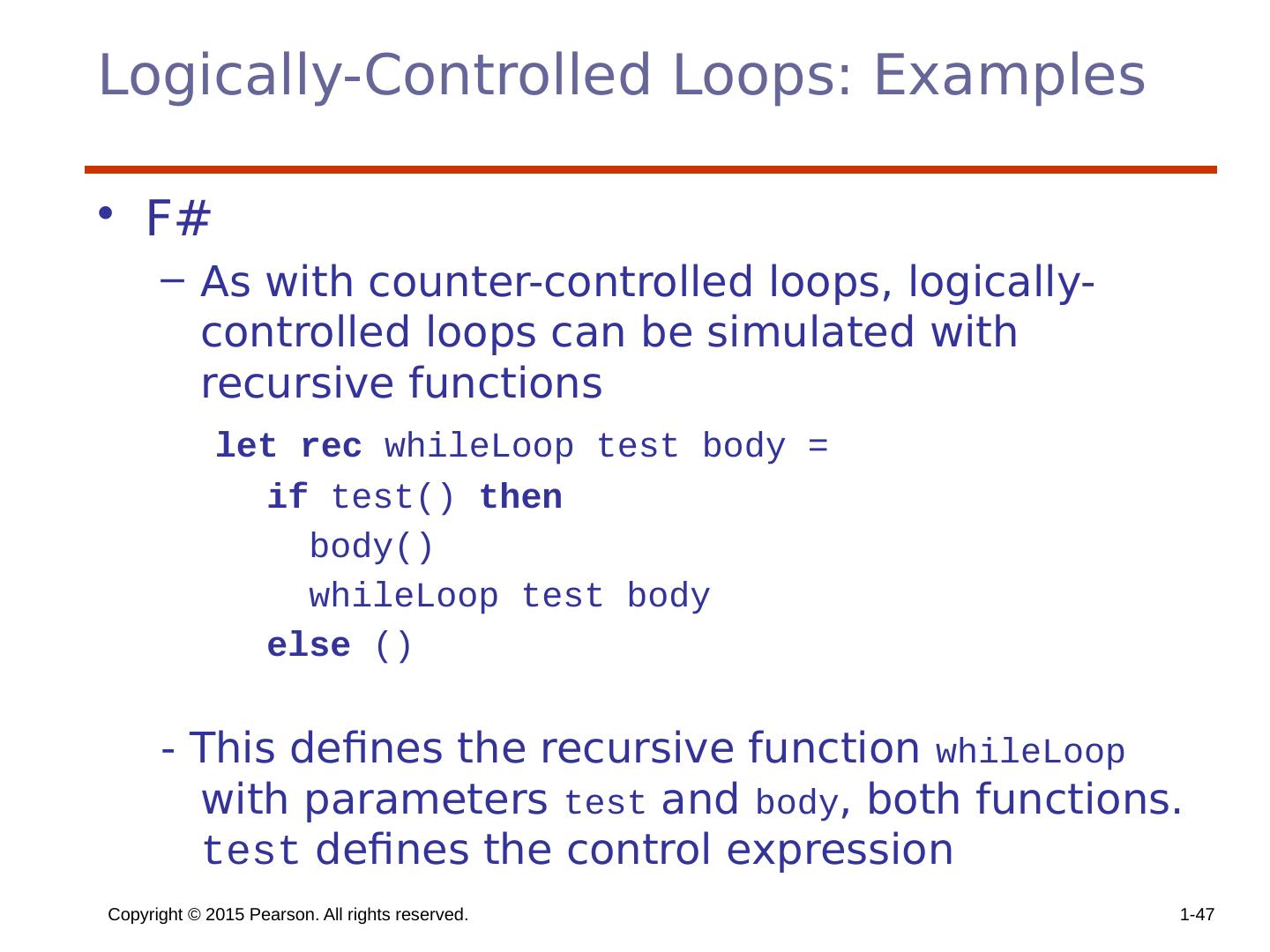
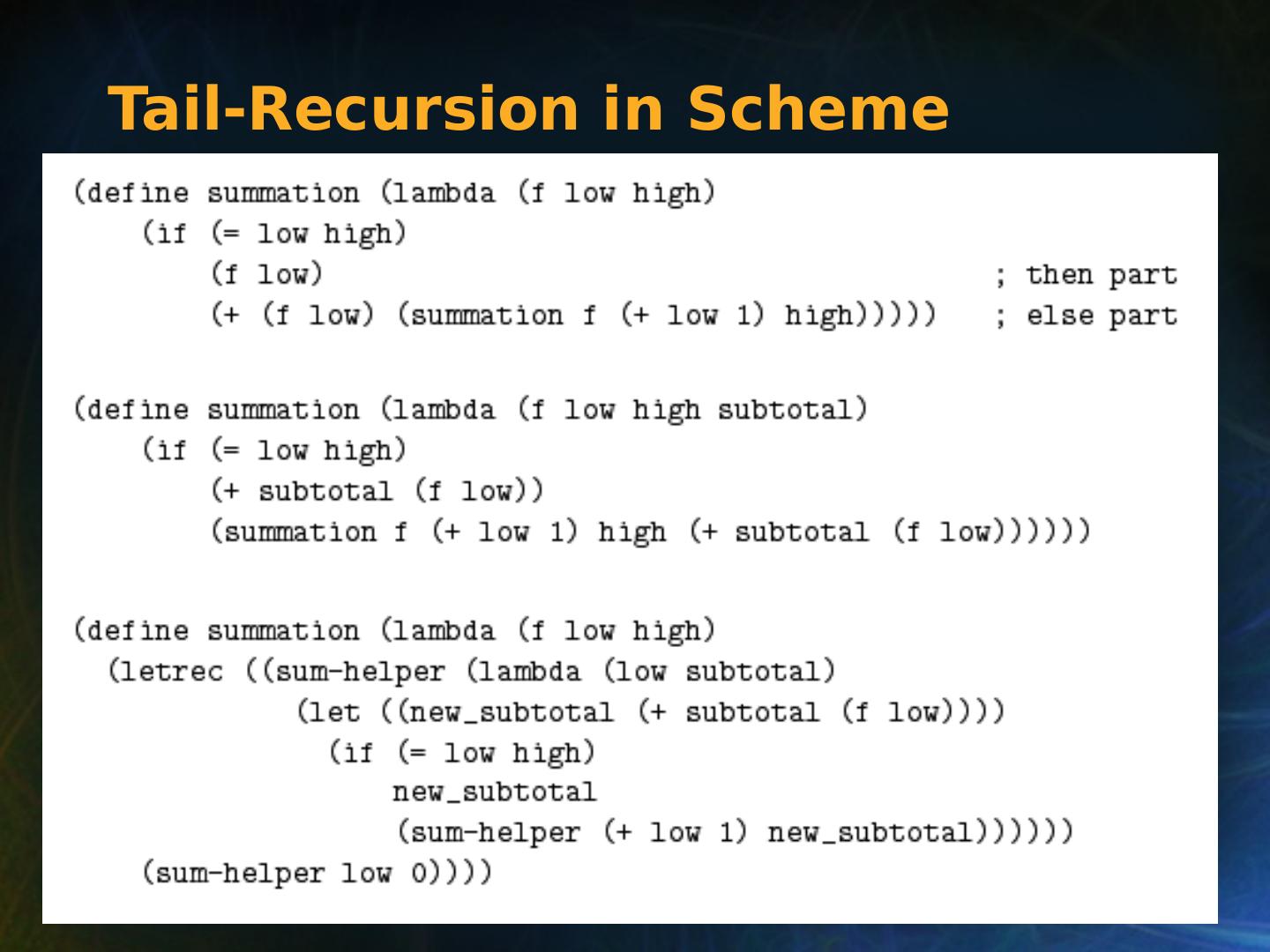
28 .Copyright © 2015 Pearson. All rights reserved. 1- 28 Iterative Statements The repeated execution of a statement or compound statement accomplished either by iteration or recursion; Focus on iteration, since recursion is a unit-level control (e.g., using functions) General design issues for iteration control stmts : How is iteration controlled? Counter-controlled vs logical-controlled 2. Where is the control mechanism in the loop? pretest (before loop body is executed) vs posttest (after loop body is executed)
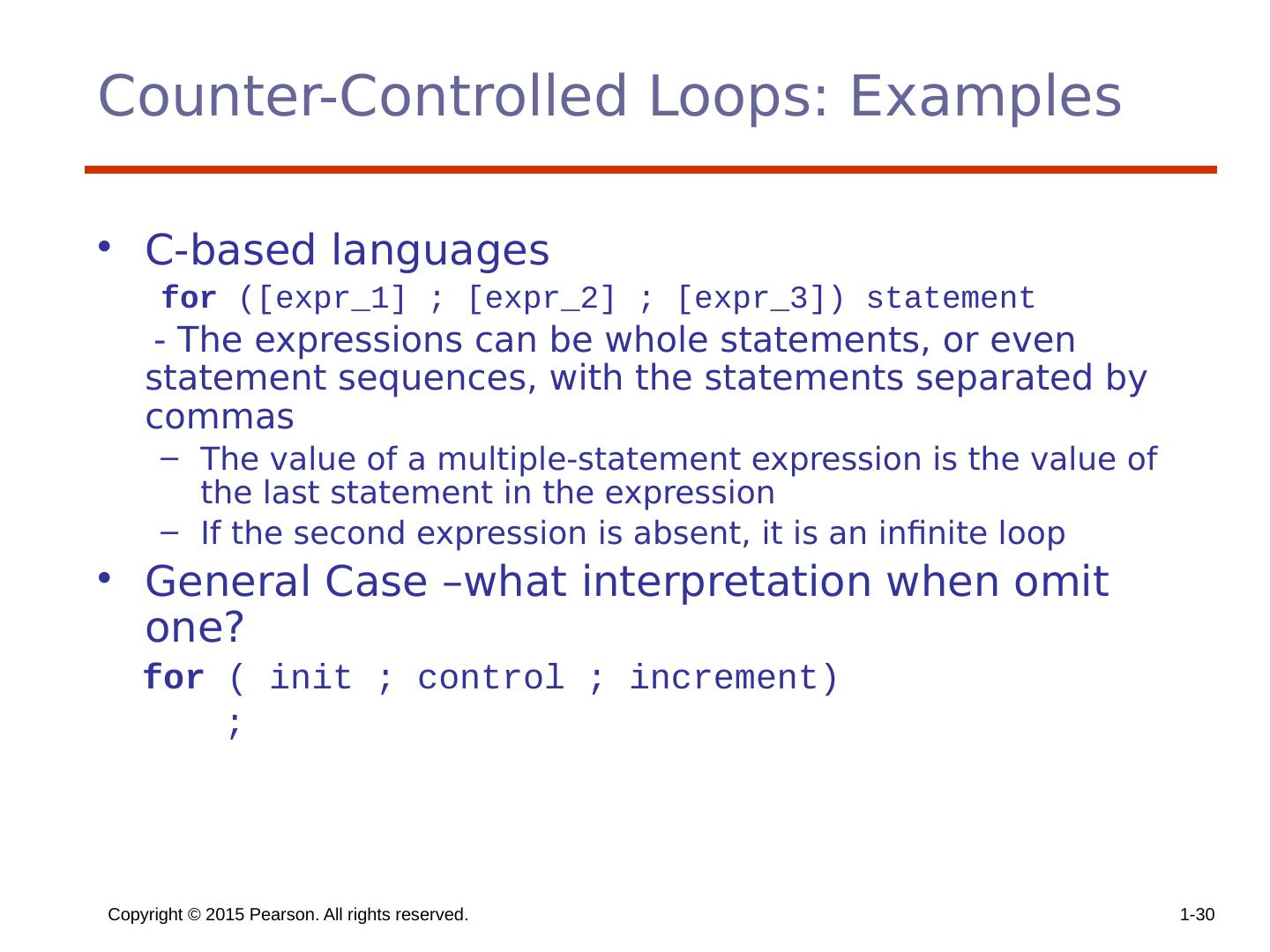
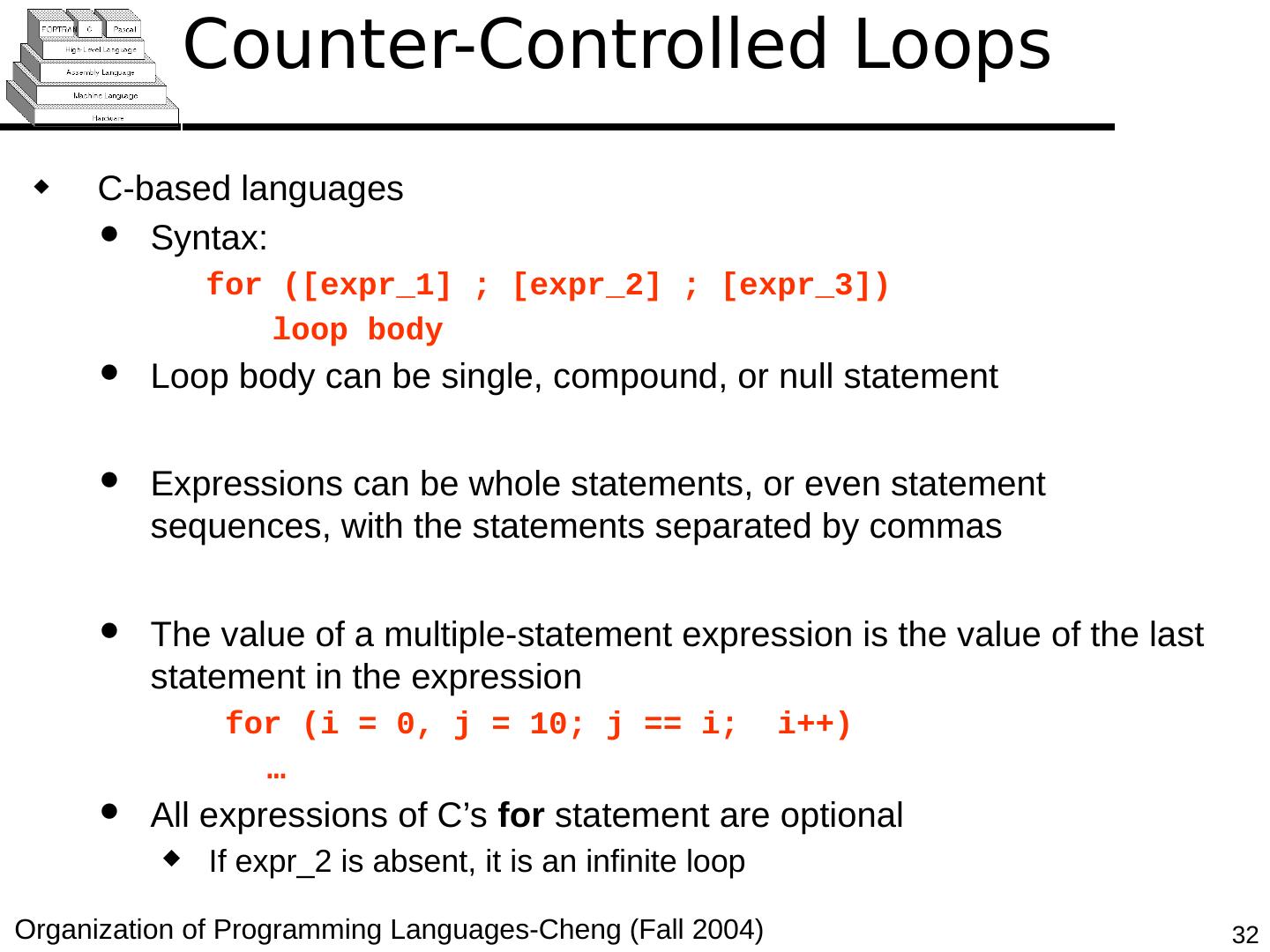
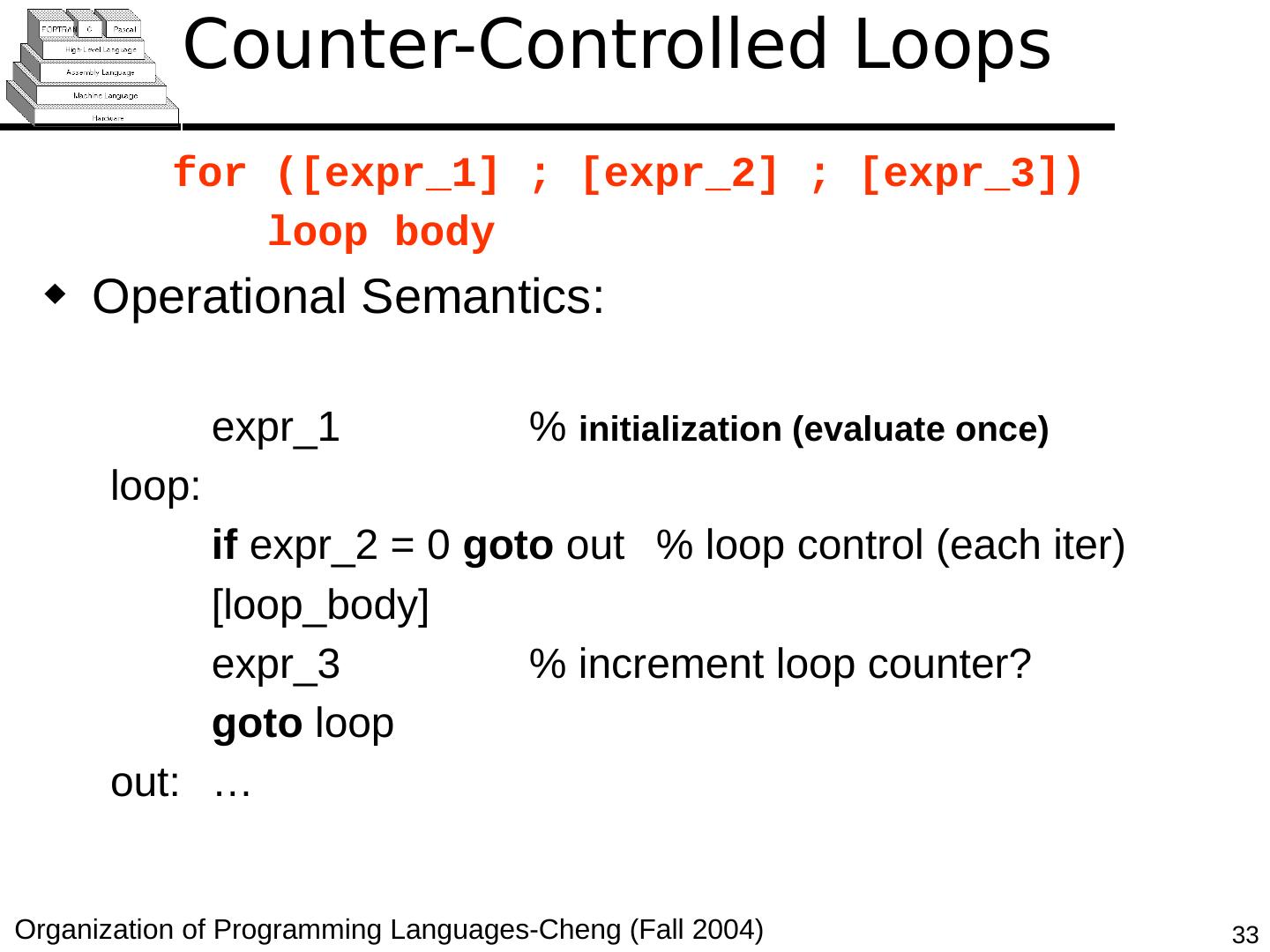
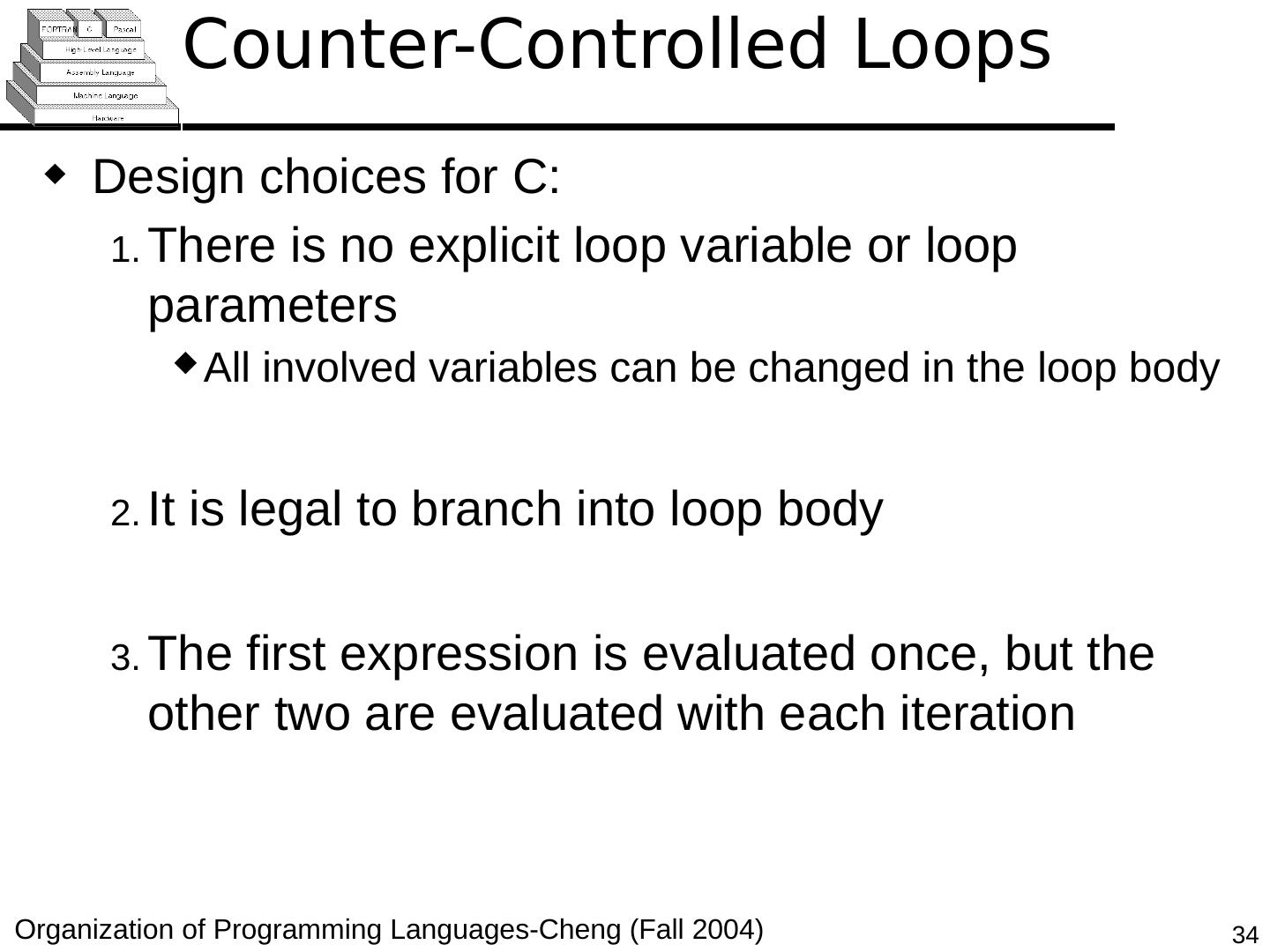
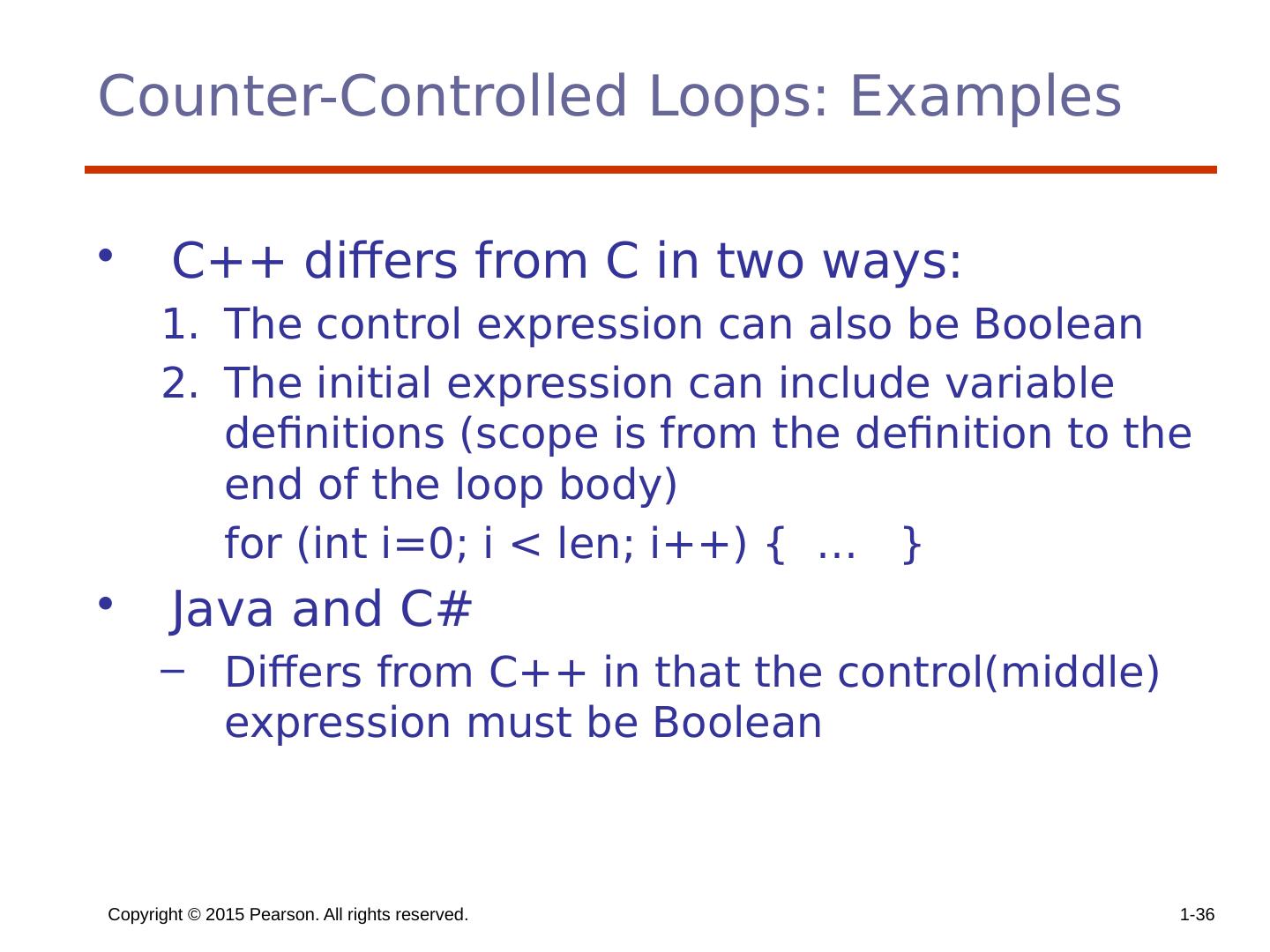
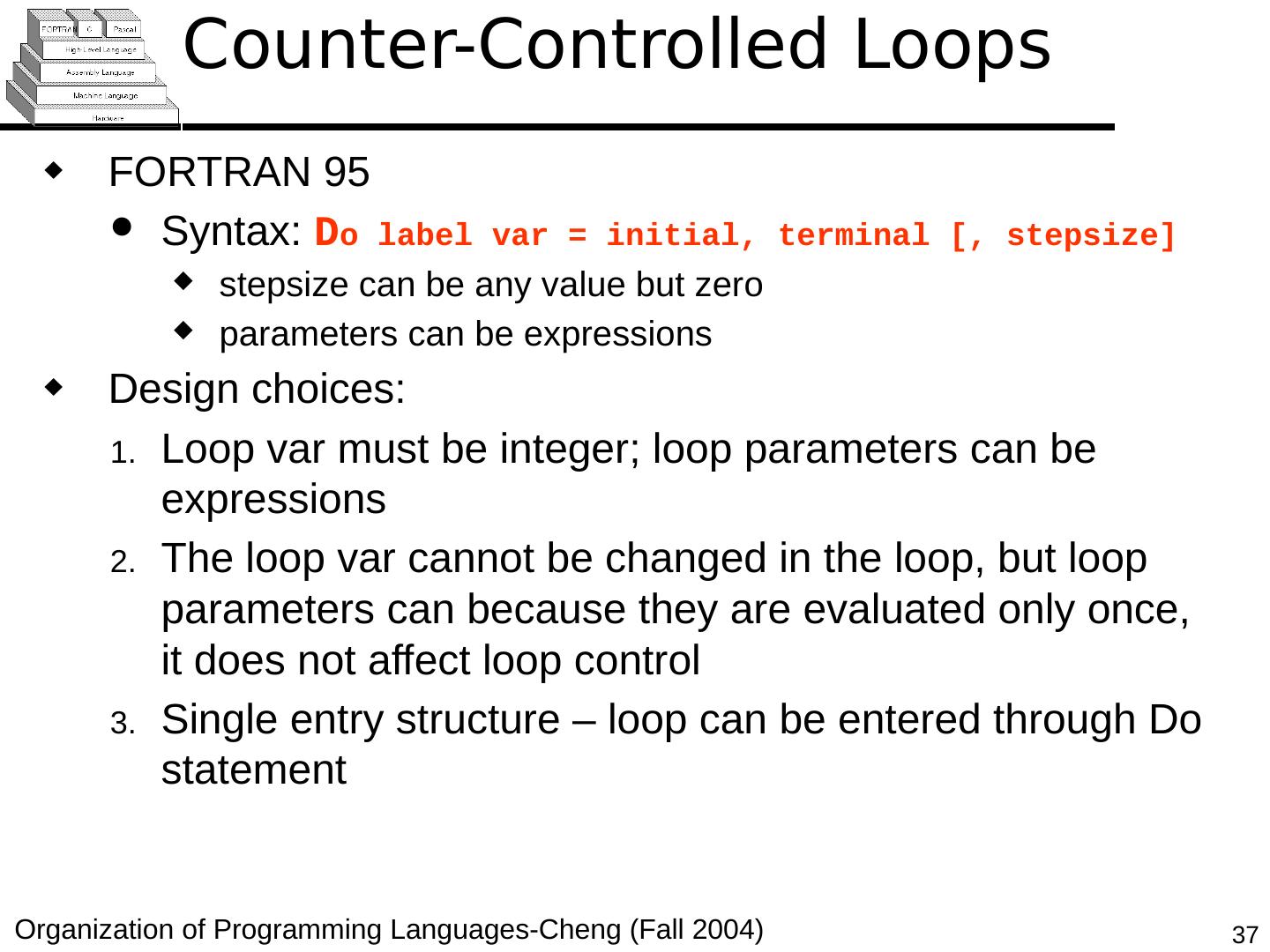
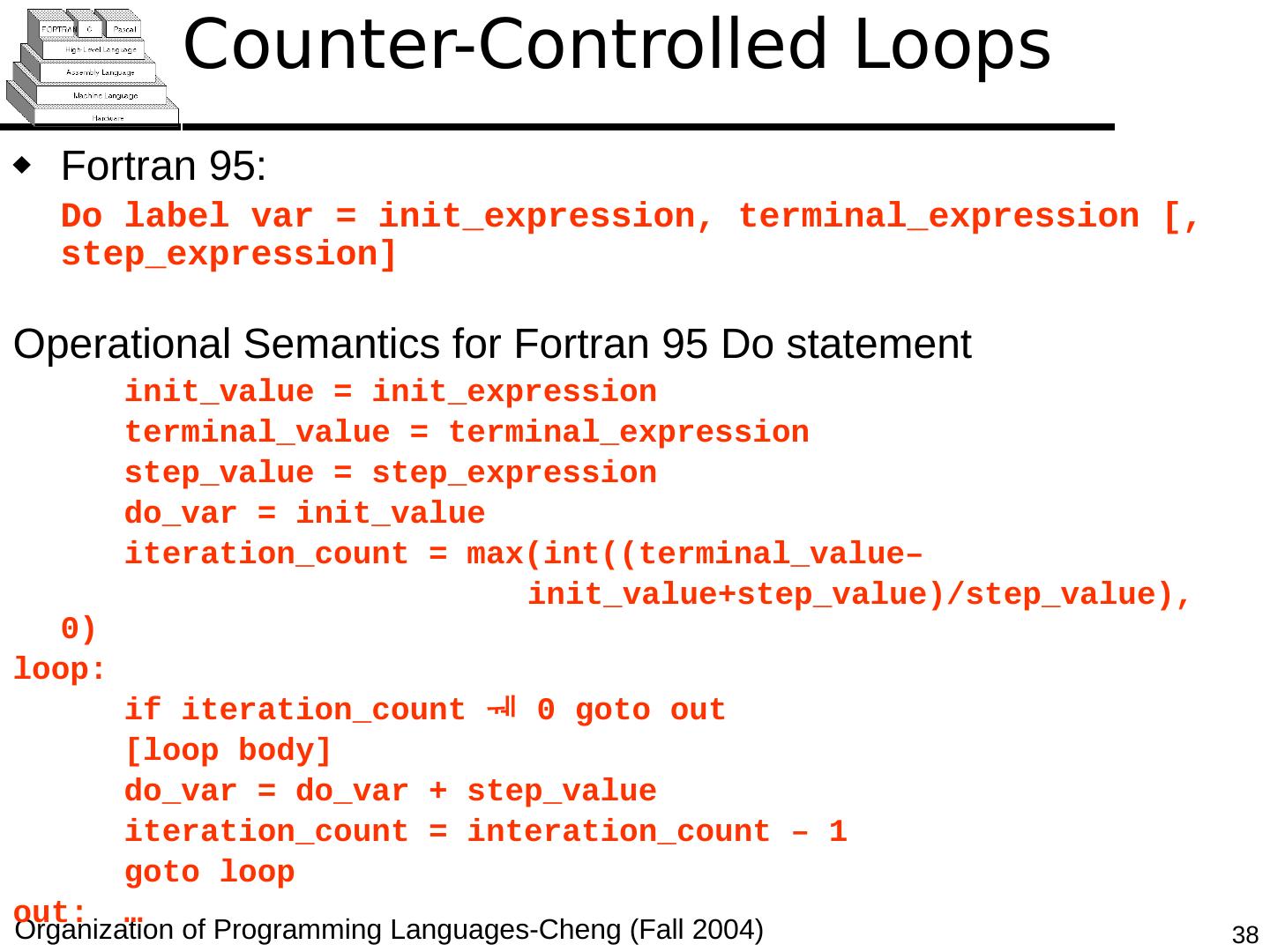
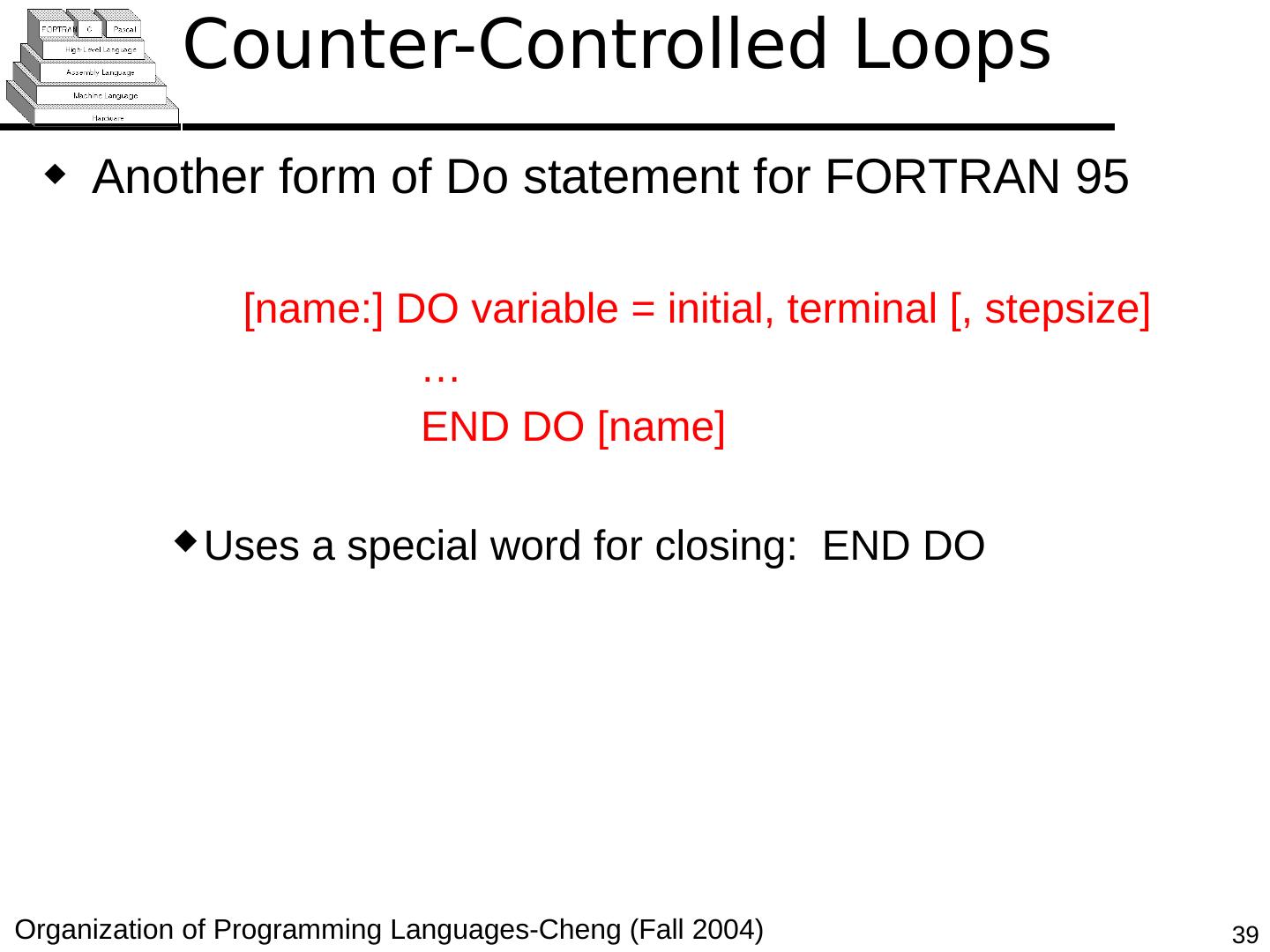
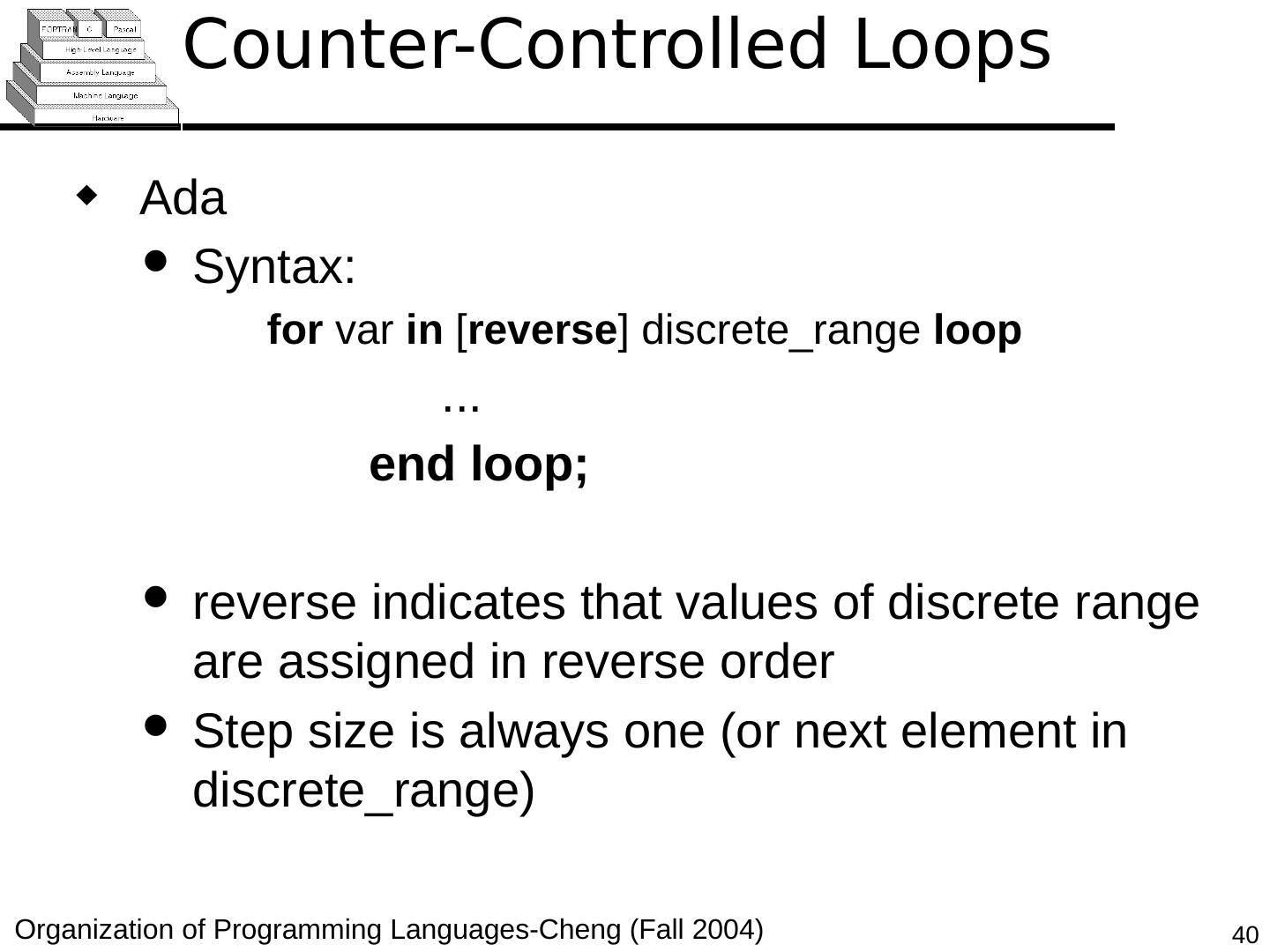
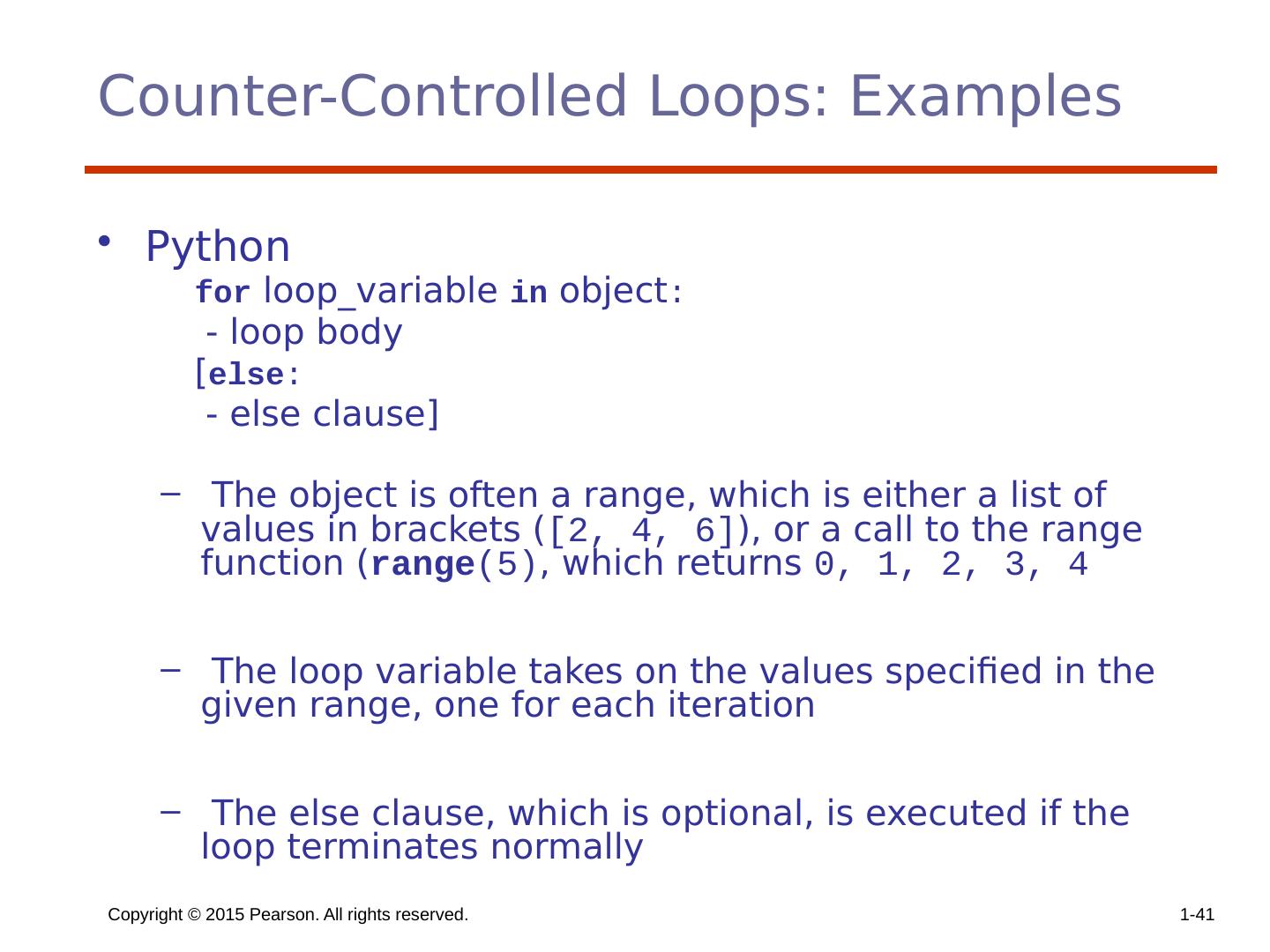
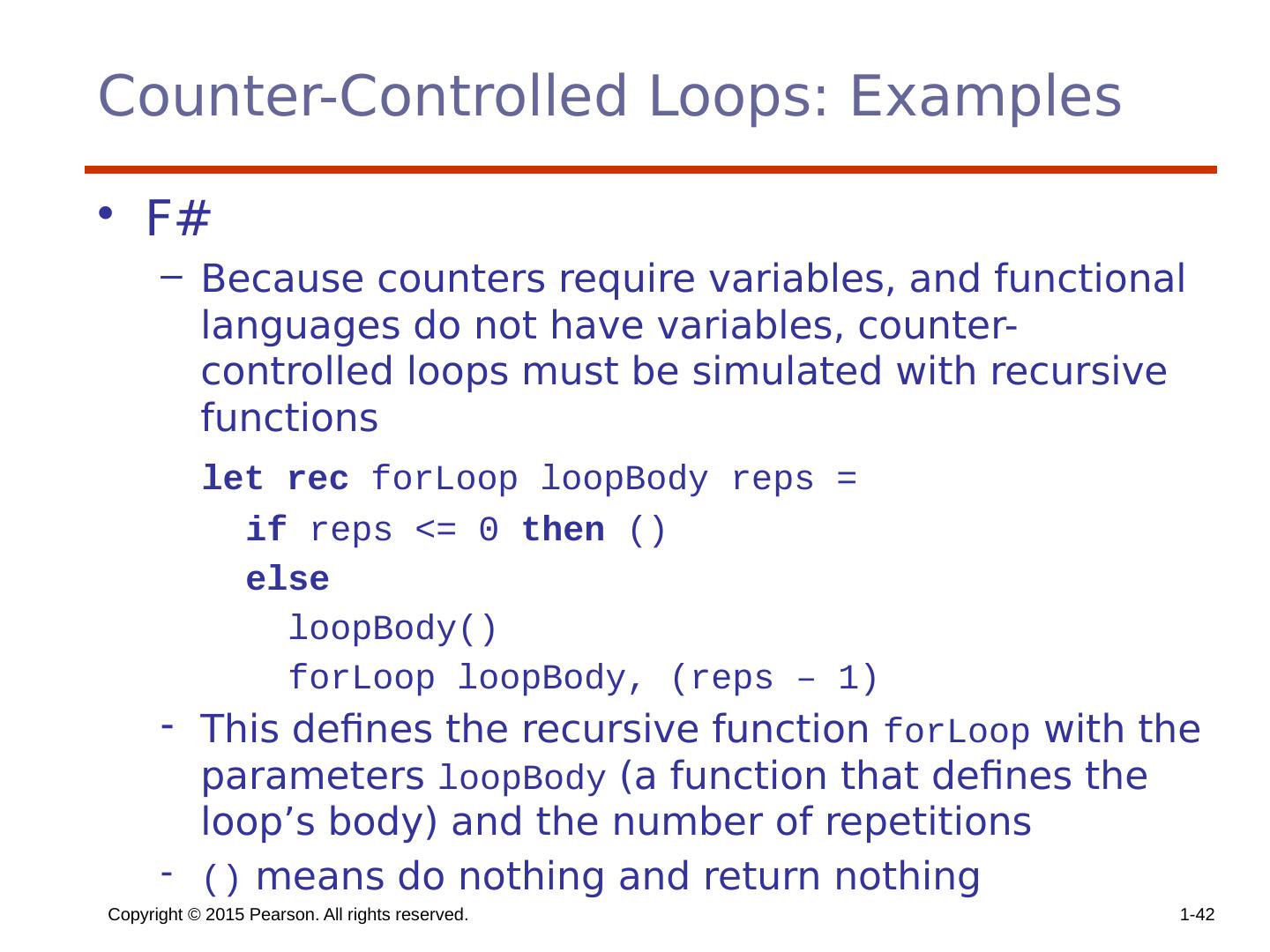
29 .Copyright © 2015 Pearson. All rights reserved. 1- 29 Counter-Controlled Loops A counting iterative statement has a loop variable, and a means of specifying the initial and terminal , and stepsize values Design Issues: What are the type and scope of the loop variable? Should it be legal for the loop variable or loop parameters to be changed in the loop body, and if so, does the change affect loop control? Should the loop parameters be evaluated only once, or once for every iteration?