- 快召唤伙伴们来围观吧
- 微博 QQ QQ空间 贴吧
- 文档嵌入链接
- 复制
- 微信扫一扫分享
- 已成功复制到剪贴板
相机模型
展开查看详情
1 .Lecture 8 Camera Models Professor Silvio Savarese Computational Vision and Geometry Lab Silvio Savarese Lecture 8 - 15-Oct-14
2 .Lecture 8 Camera Models • Pinhole cameras • Cameras & lenses • The geometry of pinhole cameras • Other camera models Reading: [FP] Chapter 1 “Cameras” [FP] Chapter 2 “Geometric Camera Models” [HZ] Chapter 6 “Camera Models” Some slides in this lecture are courtesy to Profs. J. Ponce, S. Seitz, F-F Li Silvio Savarese Lecture 8 - 15-Oct-14
3 . How do we see the world? • Let’s design a camera – Idea 1: put a piece of film in front of an object – Do we get a reasonable image?
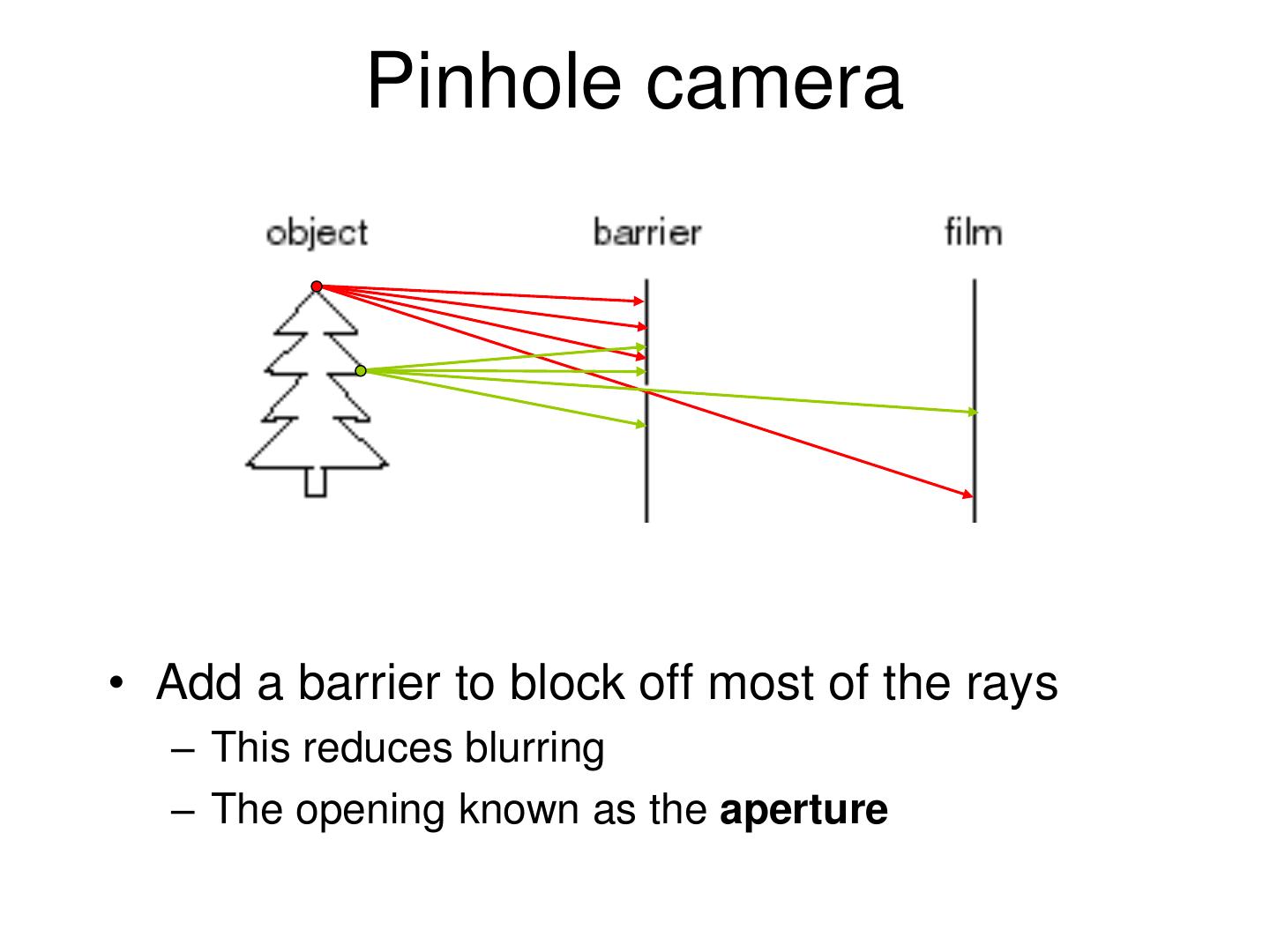
4 . Pinhole camera • Add a barrier to block off most of the rays – This reduces blurring – The opening known as the aperture
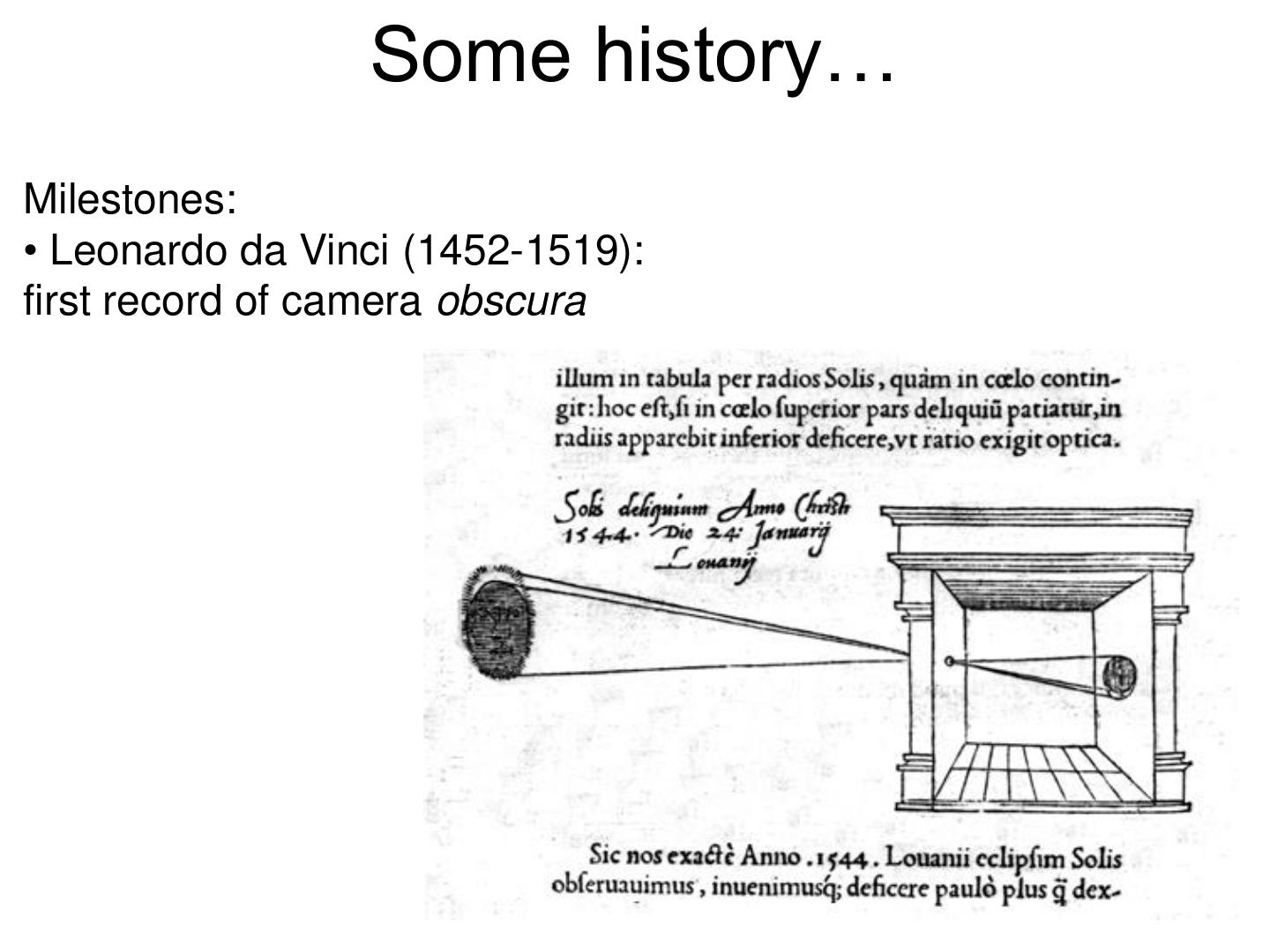
5 . Some history… Milestones: • Leonardo da Vinci (1452-1519): first record of camera obscura
6 . Some history… Milestones: • Leonardo da Vinci (1452-1519): first record of camera obscura • Johann Zahn (1685): first portable camera
7 . Some history… Milestones: • Leonardo da Vinci (1452-1519): first record of camera obscura • Johann Zahn (1685): first portable camera • Joseph Nicephore Niepce (1822): first photo - birth of photography Photography (Niepce, “La Table Servie,” 1822)
8 . Some history… Milestones: • Leonardo da Vinci (1452-1519): first record of camera obscura • Johann Zahn (1685): first portable camera • Joseph Nicephore Niepce (1822): first photo - birth of photography • Daguerréotypes (1839) • Photographic Film (Eastman, 1889) • Cinema (Lumière Brothers, 1895) • Color Photography (Lumière Brothers, 1908) Photography (Niepce, “La Table Servie,” 1822)
9 . Let’s also not forget… Motzu Aristotle Al-Kindi (c. 801–873) (468-376 BC) (384-322 BC) Ibn al-Haitham Oldest existent Also: Plato, Euclid (965-1040) book on geometry in China
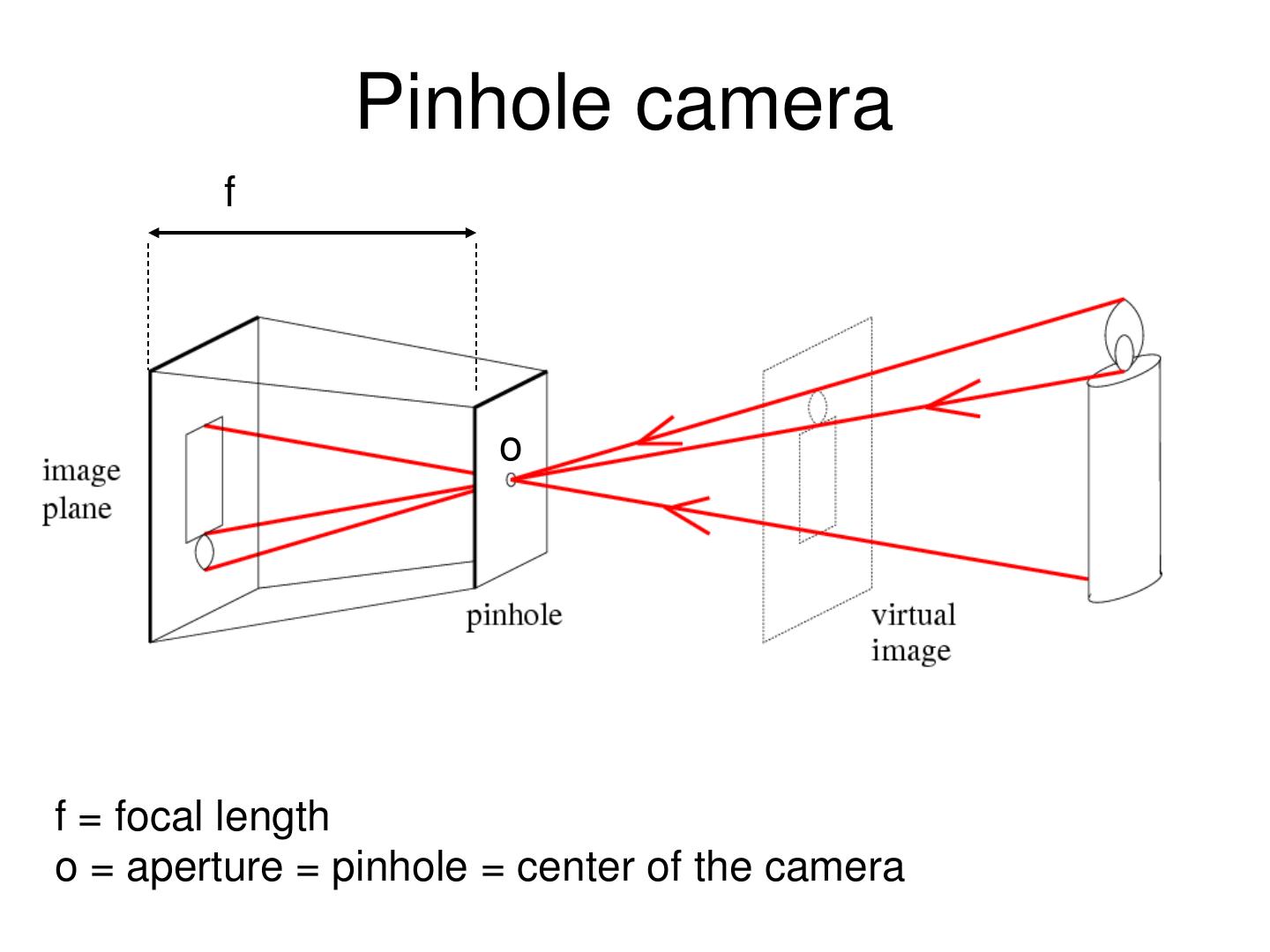
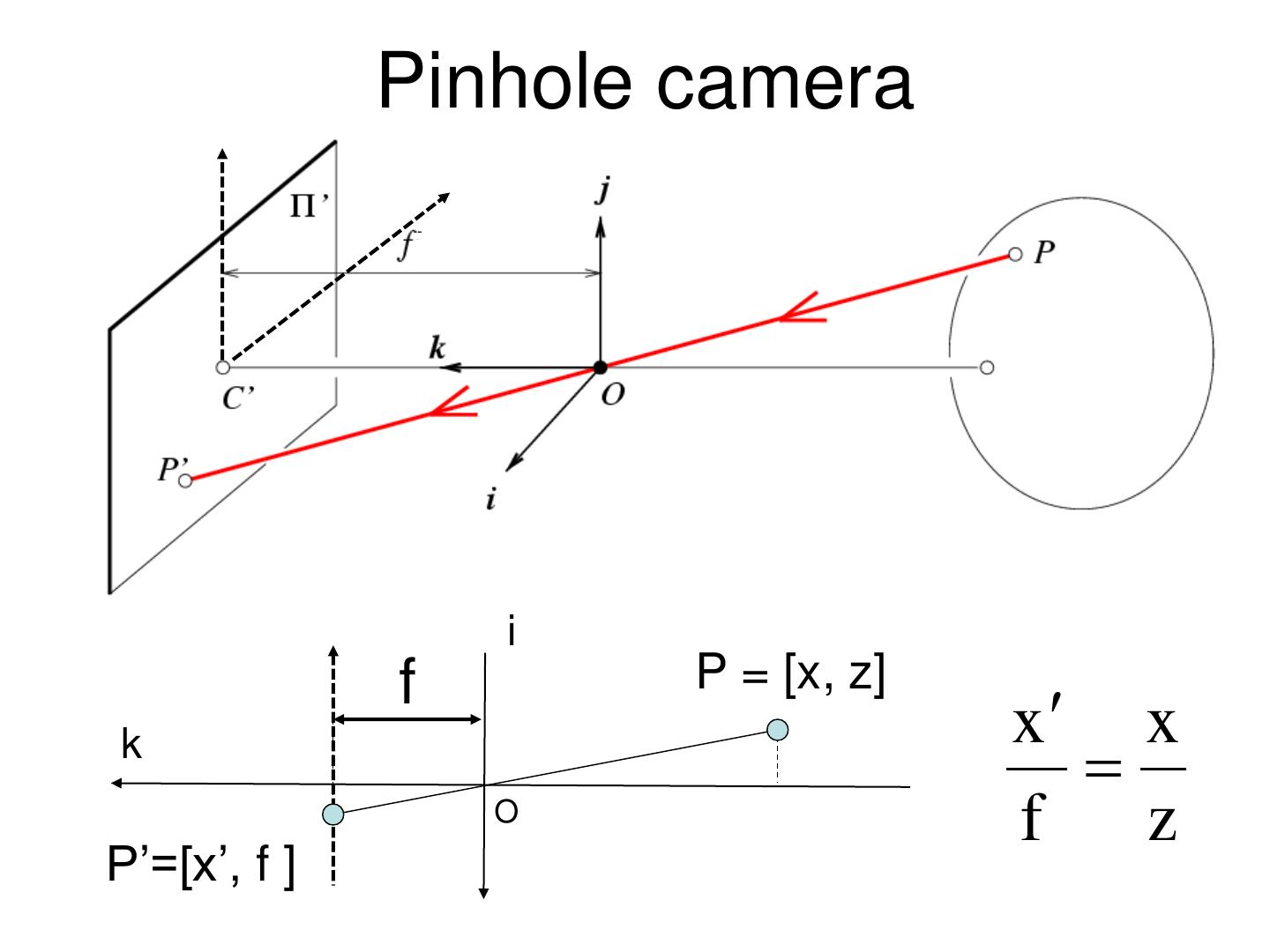
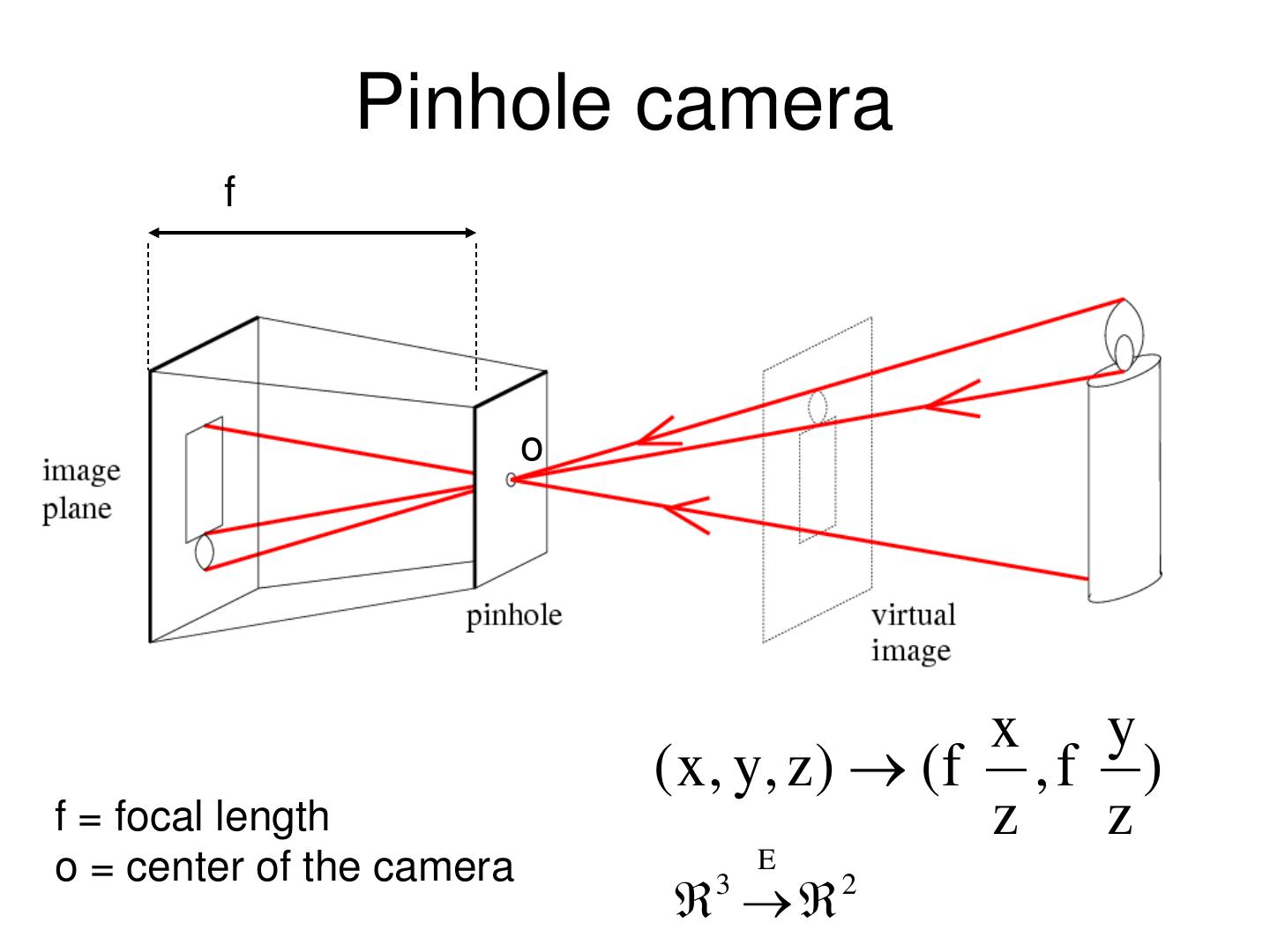
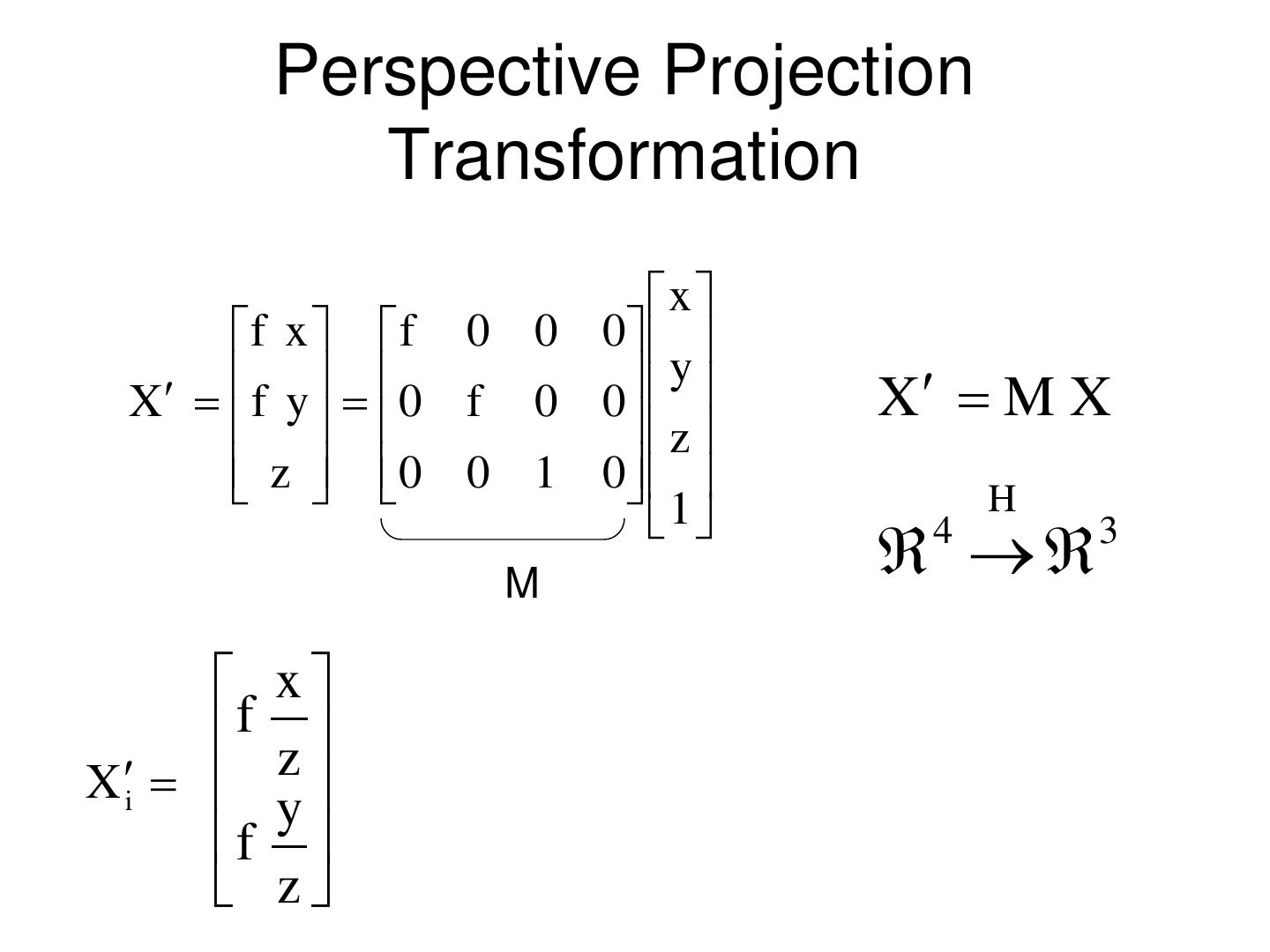
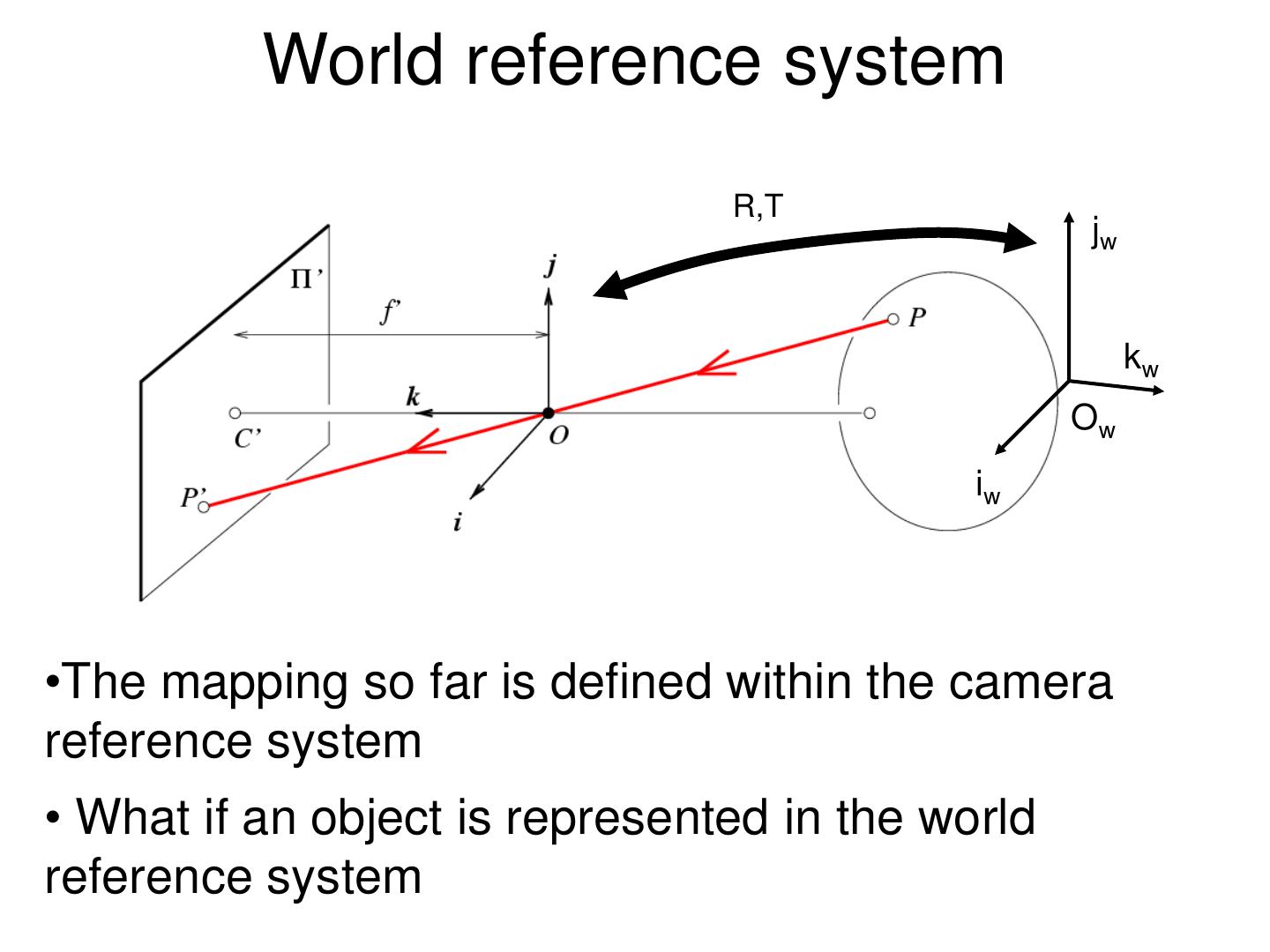
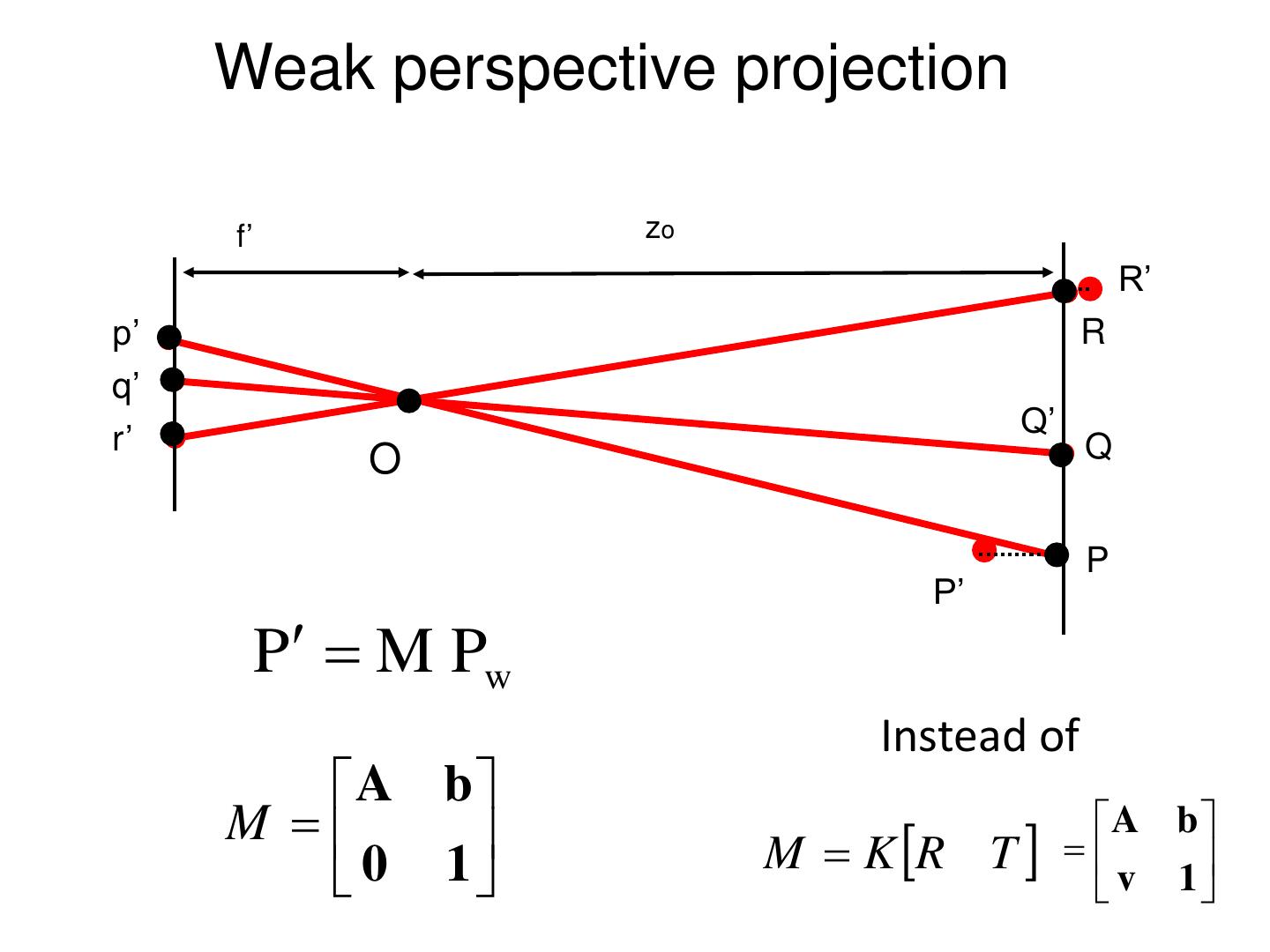
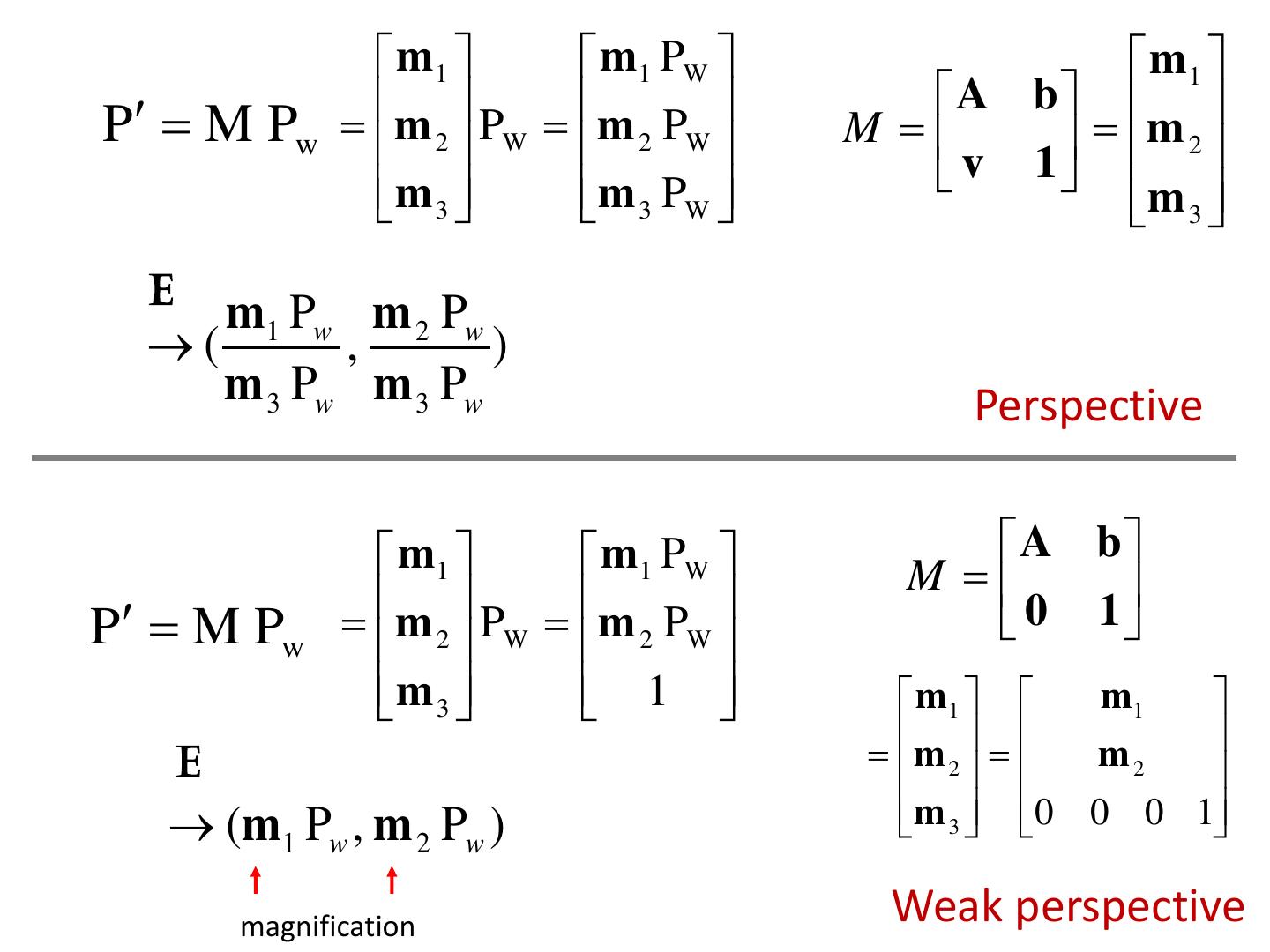
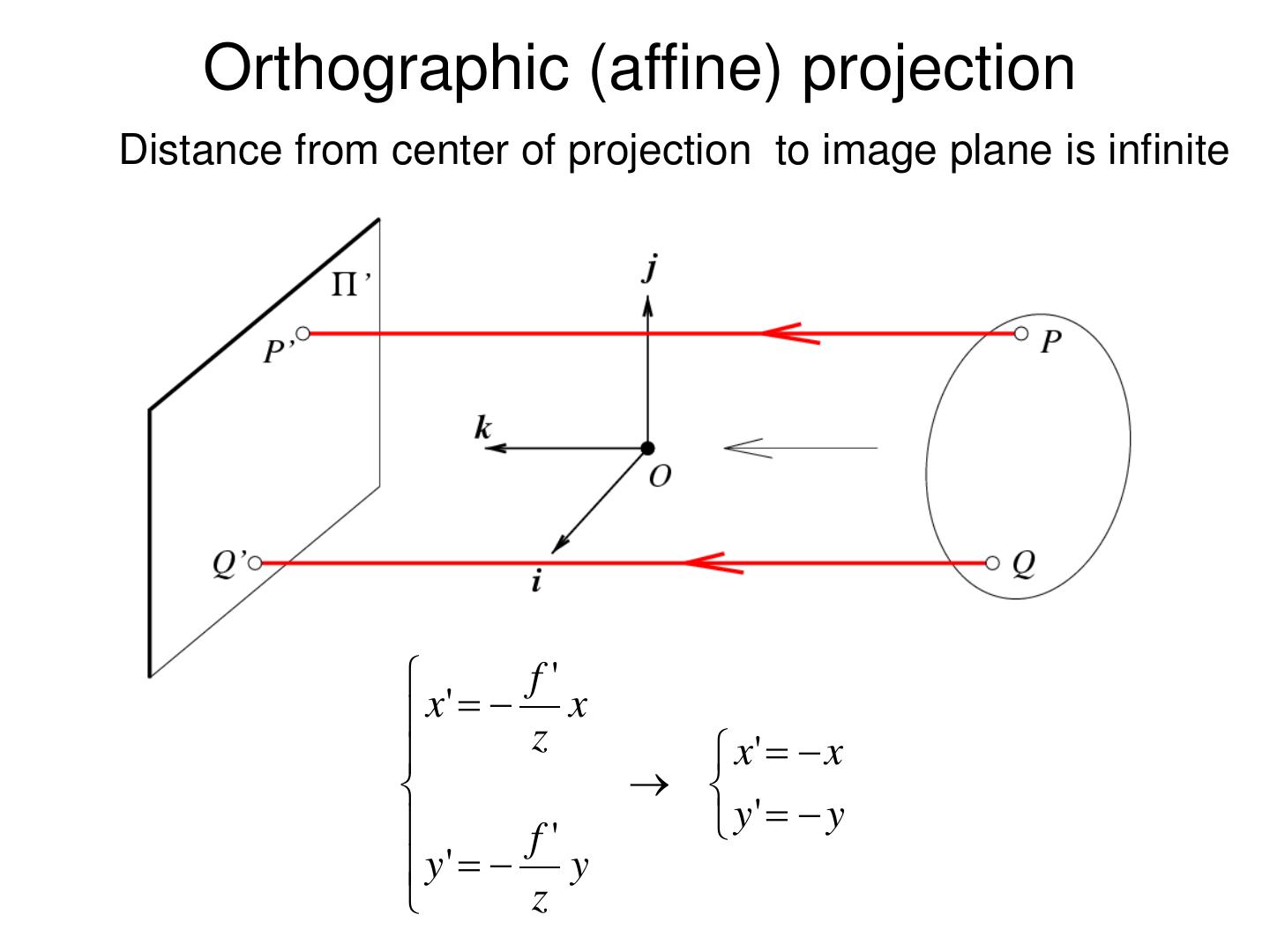
10 . Pinholeprojection Pinhole perspective camera f o f = focal length o = aperture = pinhole = center of the camera
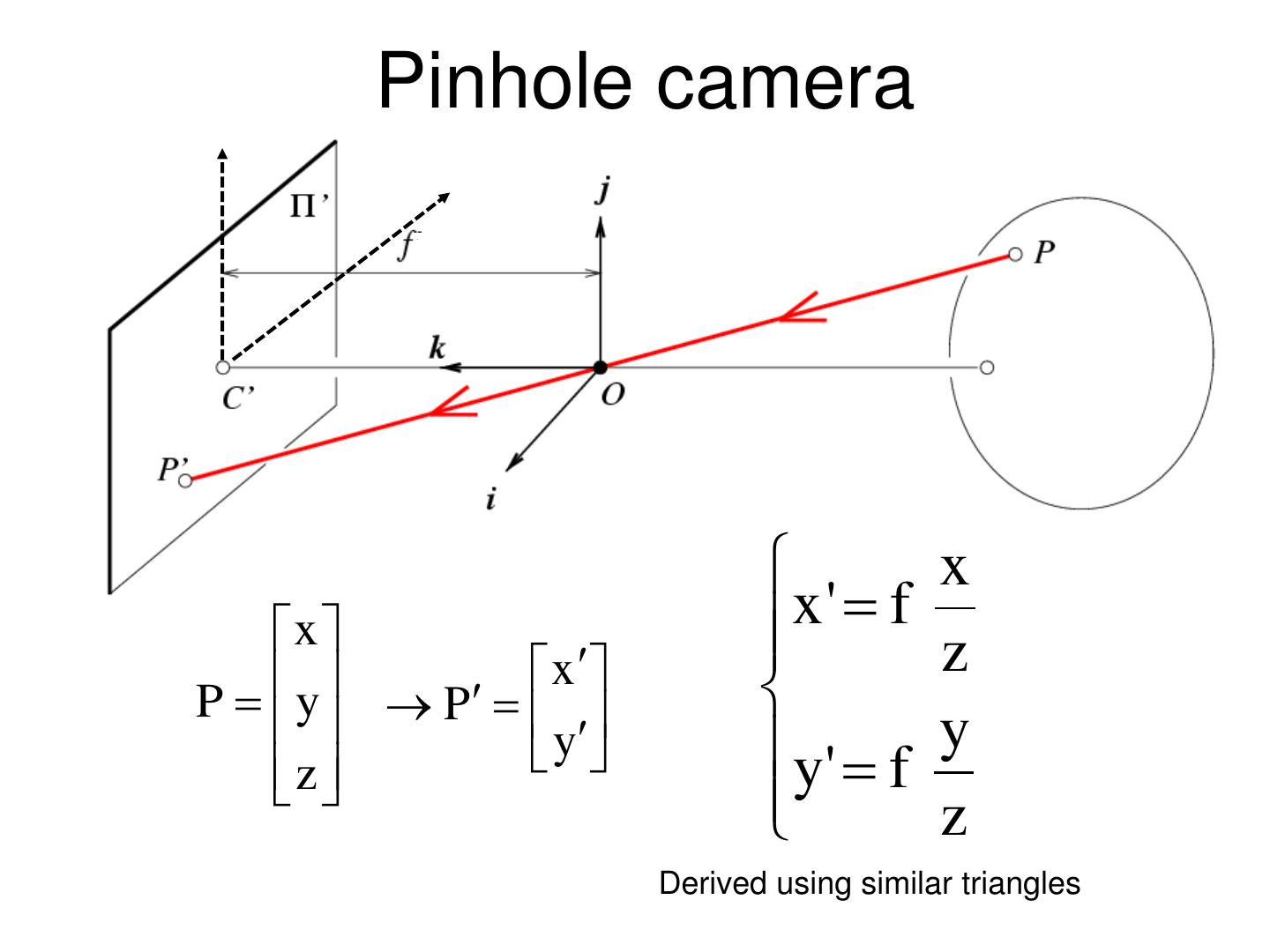
11 . Pinhole camera x x x' f x z P y P y y' f y z z Derived using similar triangles
12 . Pinhole camera i f P = [x, z] x x k O f z P’=[x’, f ]
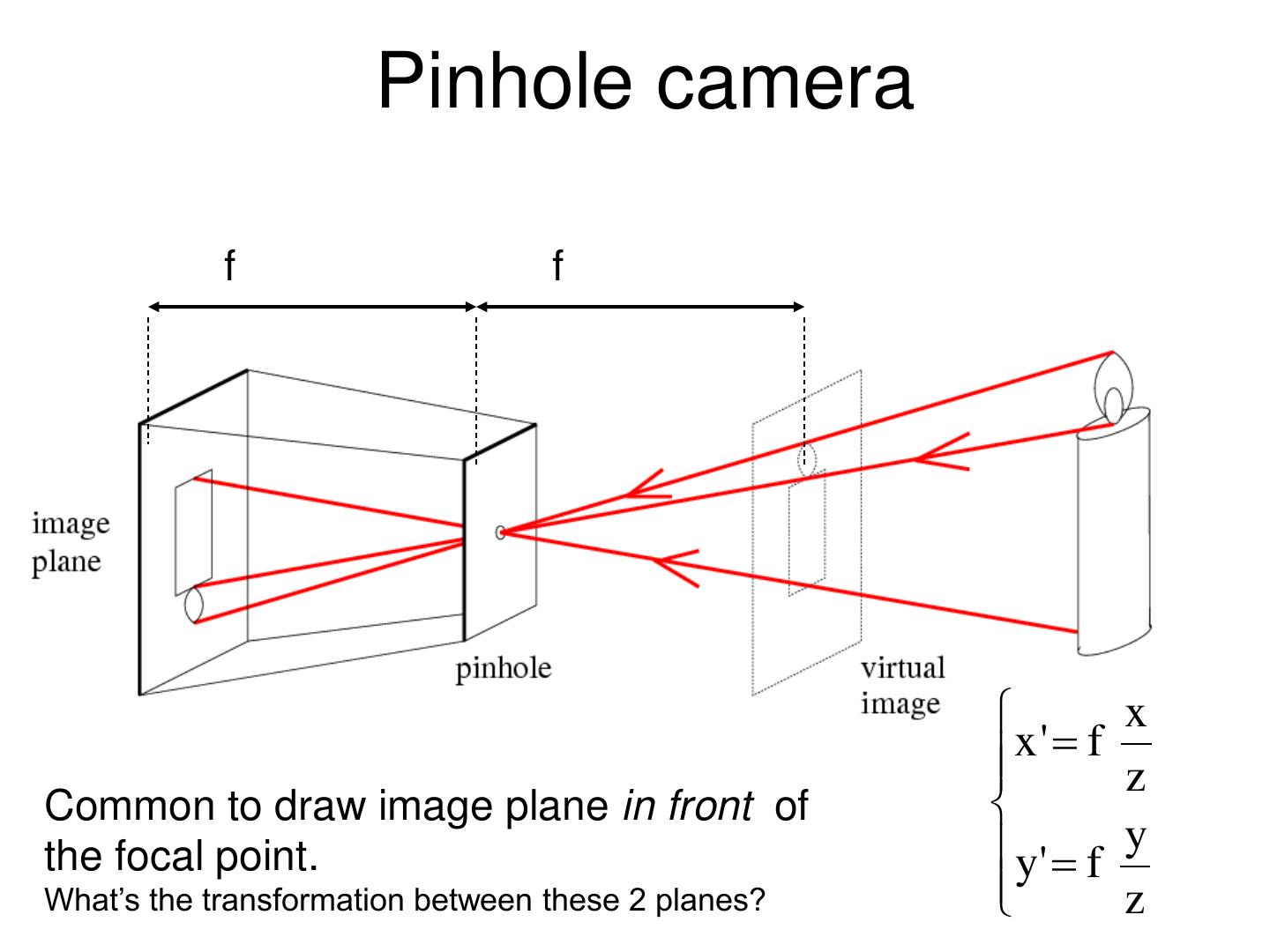
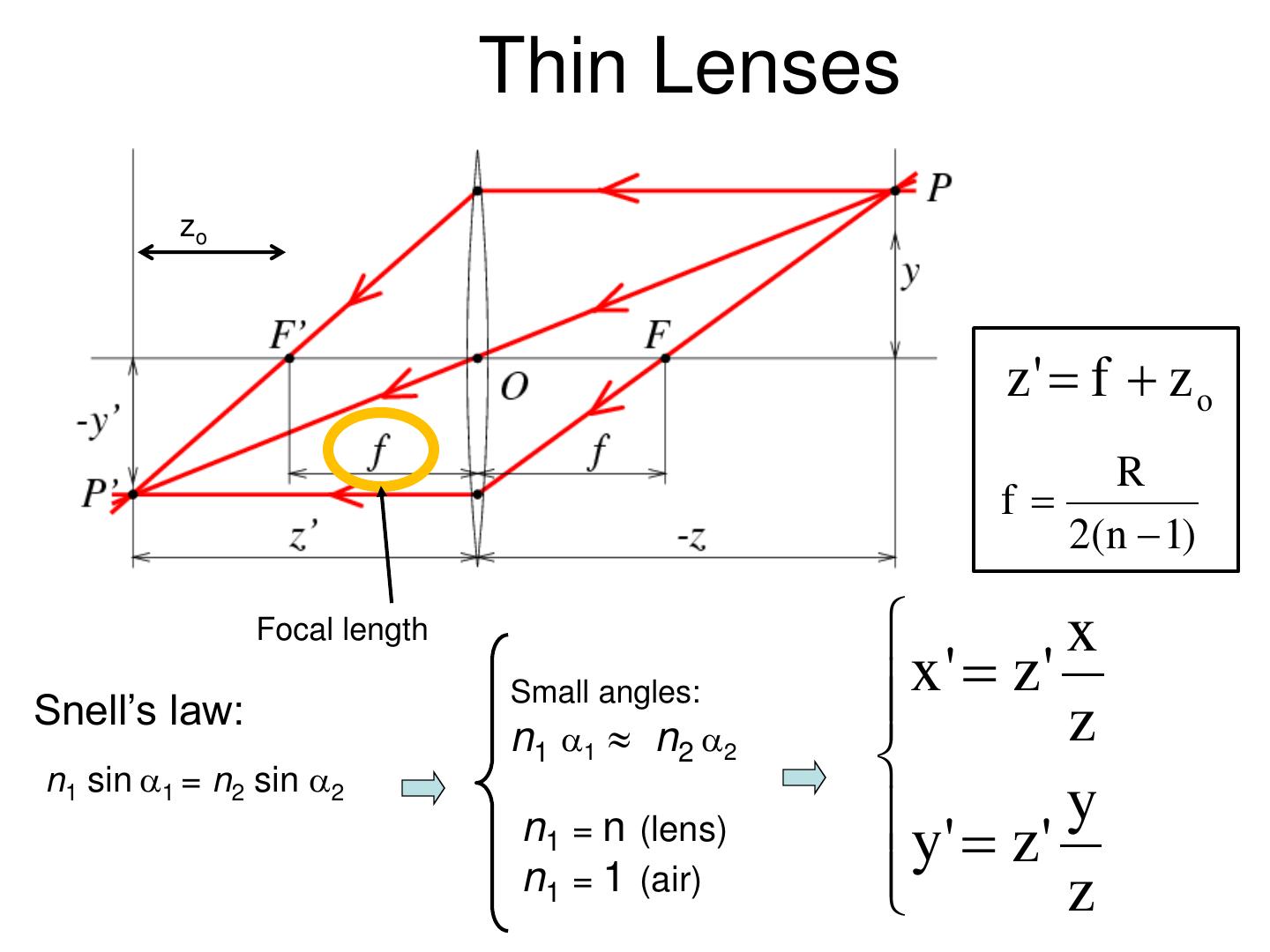
13 . Pinhole camera f f x x' f z Common to draw image plane in front of the focal point. y' f y What’s the transformation between these 2 planes? z
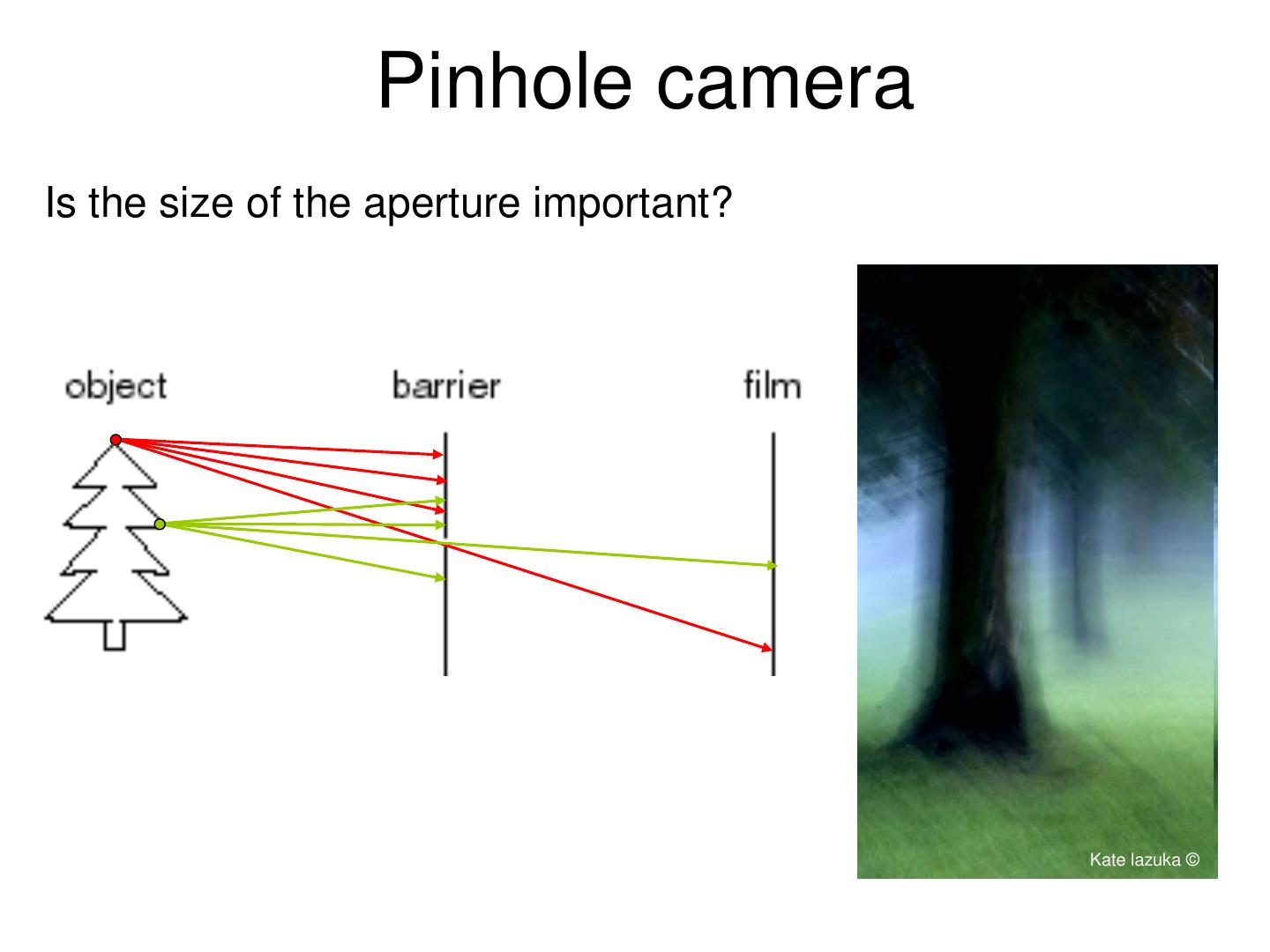
14 . Pinhole camera Is the size of the aperture important? Kate lazuka ©
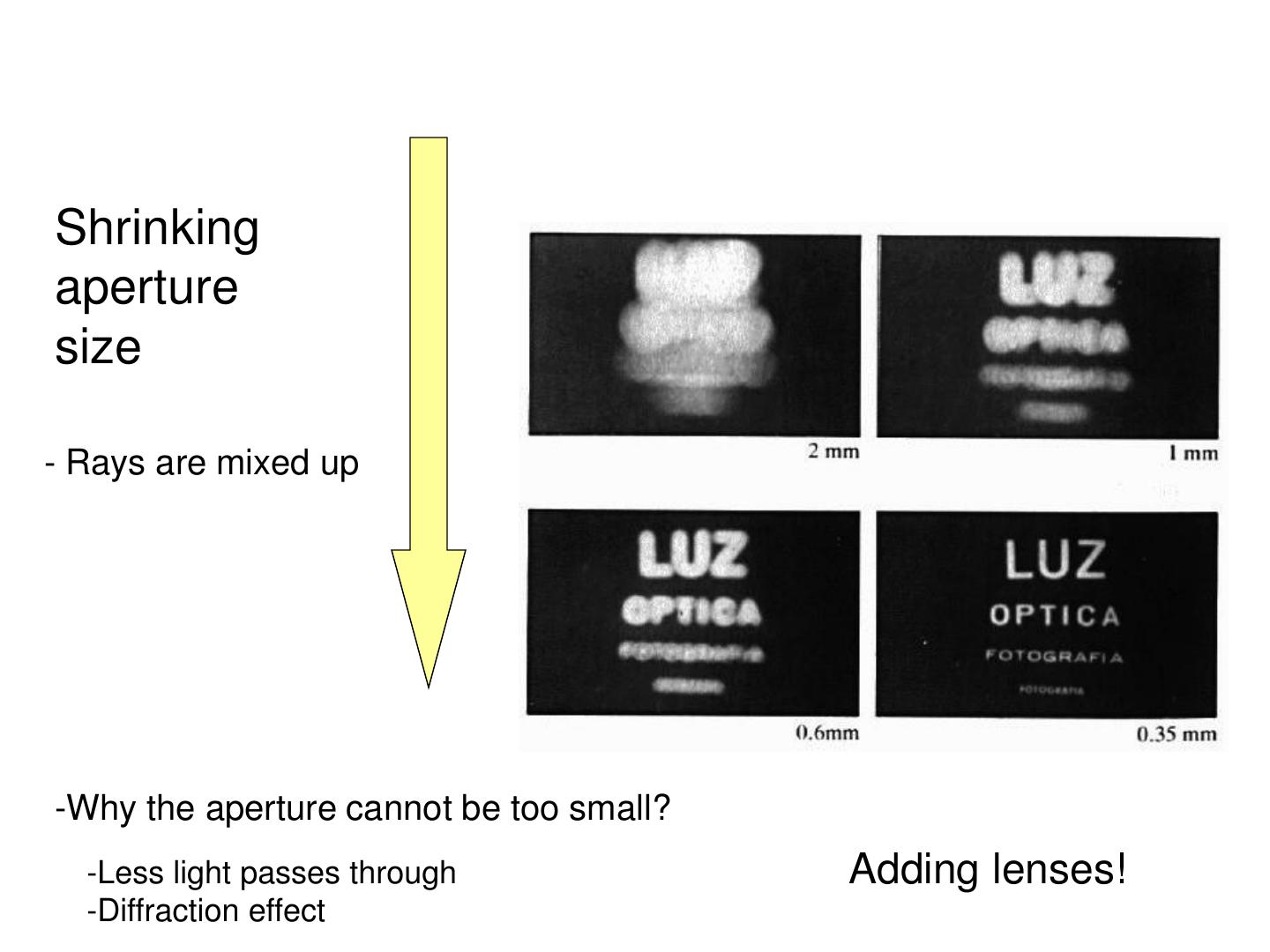
15 .Shrinking aperture size - Rays are mixed up -Why the aperture cannot be too small? -Less light passes through Adding lenses! -Diffraction effect
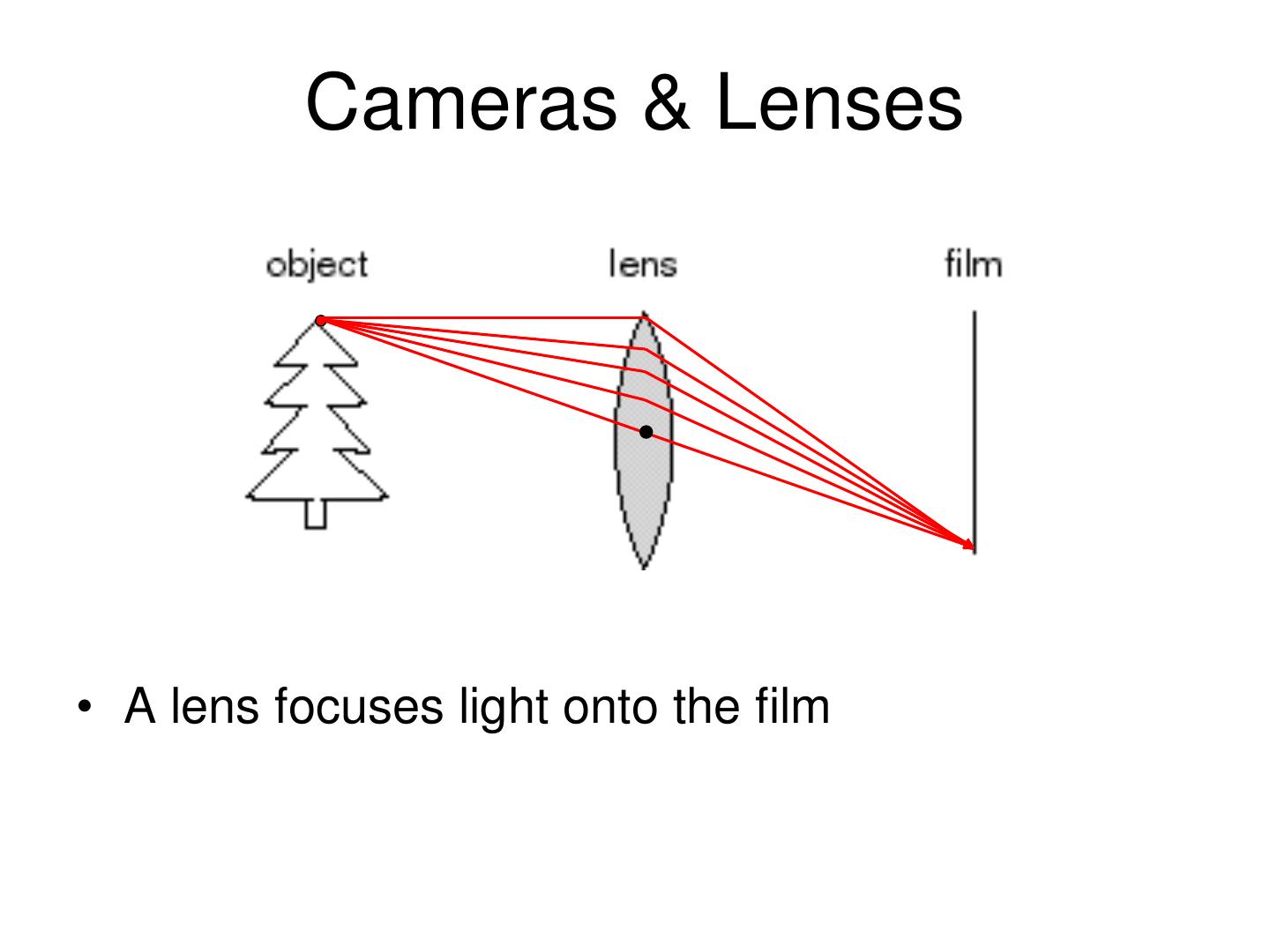
16 . Cameras & Lenses • A lens focuses light onto the film
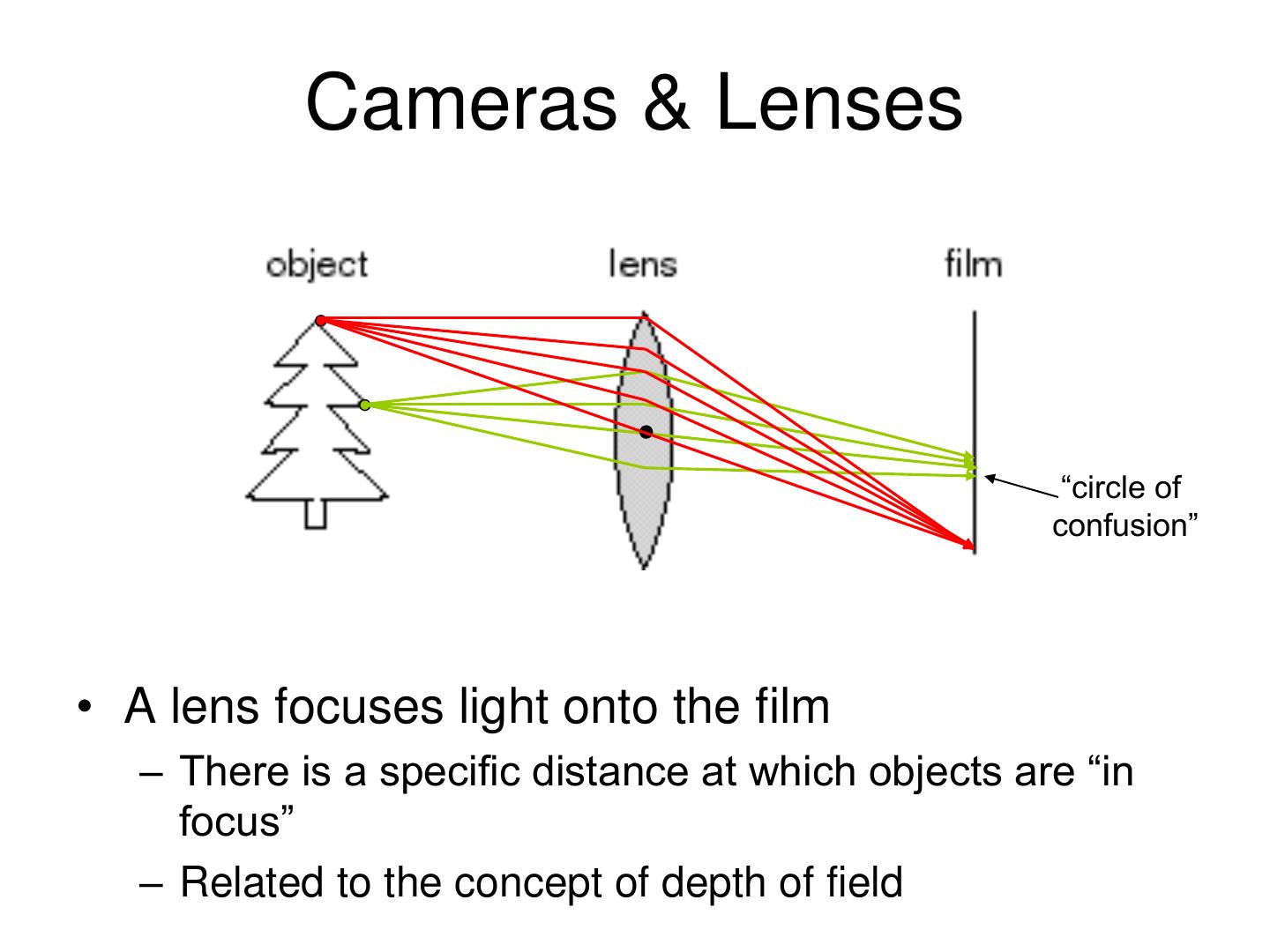
17 . Cameras & Lenses “circle of confusion” • A lens focuses light onto the film – There is a specific distance at which objects are “in focus” – Related to the concept of depth of field
18 . Cameras & Lenses • A lens focuses light onto the film – There is a specific distance at which objects are “in focus” – Related to the concept of depth of field
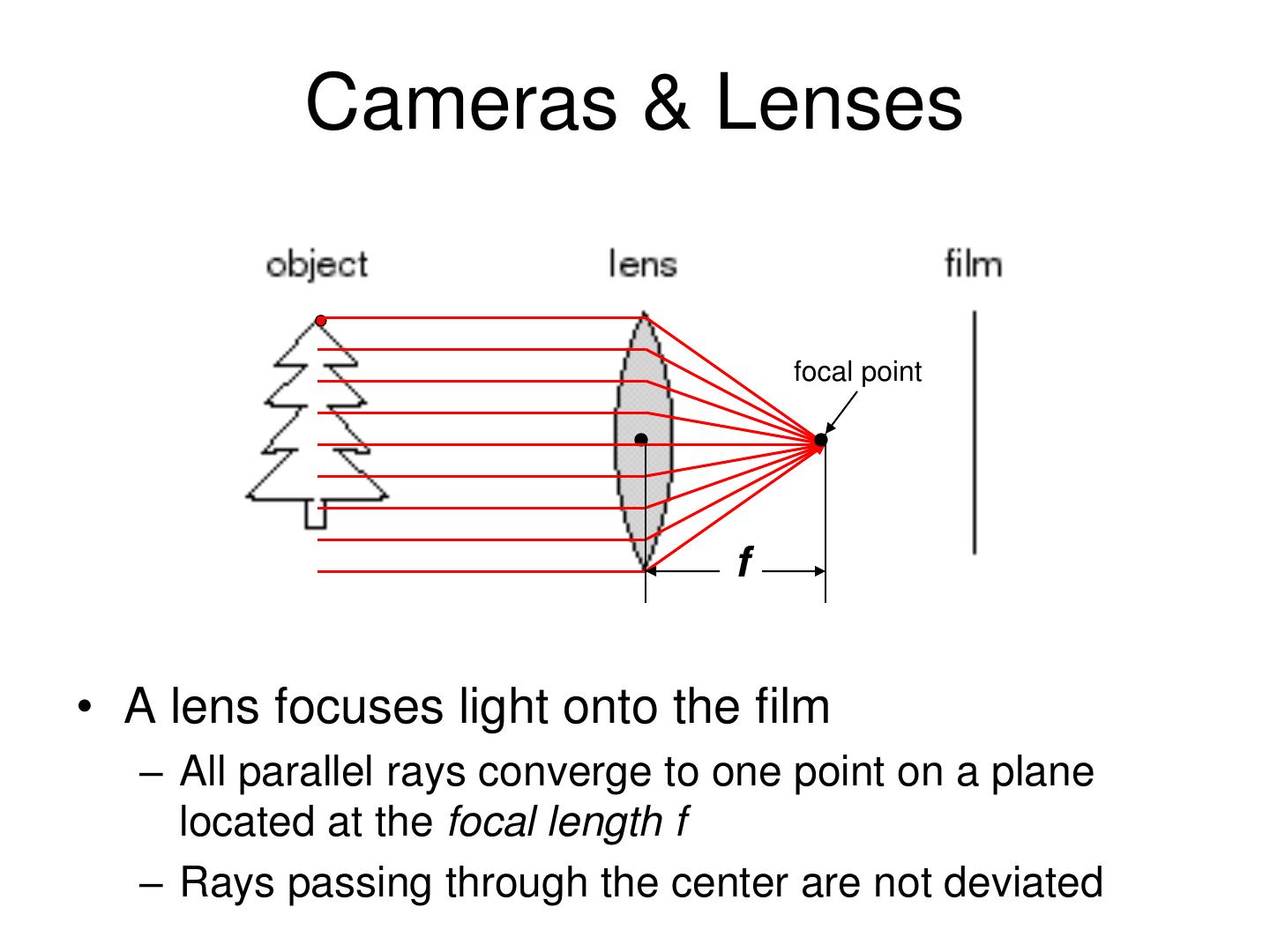
19 . Cameras & Lenses focal point f • A lens focuses light onto the film – All parallel rays converge to one point on a plane located at the focal length f – Rays passing through the center are not deviated
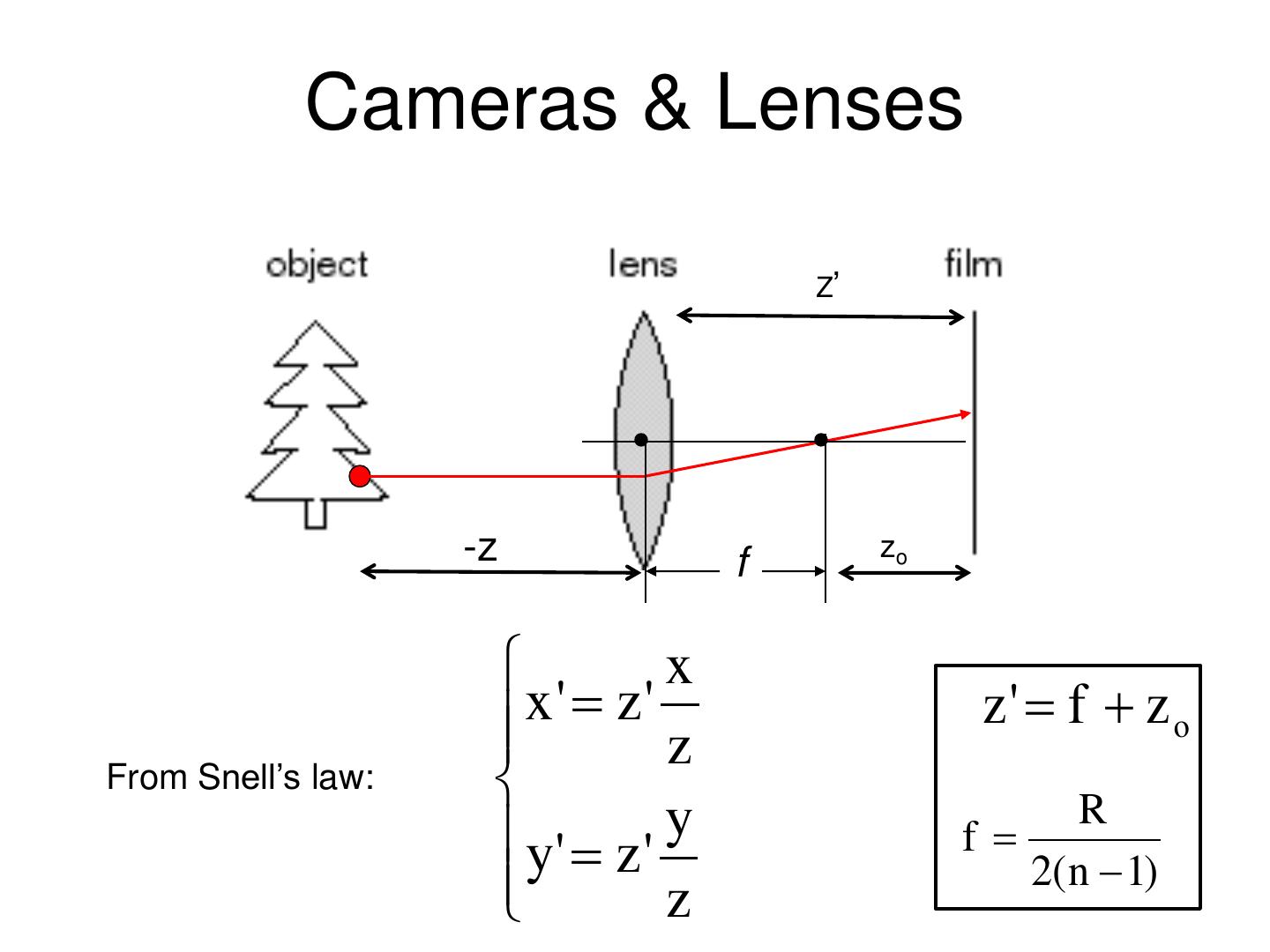
20 . Cameras & Lenses Z’ -z f zo x x ' z' z z' f z o From Snell’s law: R y' z ' y f 2( n 1) z
21 . Thin Lenses zo z' f z o R f 2( n 1) Focal length x Small angles: x ' z ' Snell’s law: z n1 1 n2 2 n1 sin 1 = n2 sin 2 n1 = n (lens) y' z ' y n1 = 1 (air) z
22 .Issues with lenses: Radial Distortion – Deviations are most noticeable for rays that pass through the edge of the lens No distortion Pin cushion Barrel (fisheye lens) Image magnification decreases with distance from the optical axis
23 .Lecture 2 Camera Models • Pinhole cameras • Cameras & lenses • The geometry of pinhole cameras • Intrinsic • Extrinsic • Other camera models Silvio Savarese Lecture 8 - 15-Oct-14
24 . Pinholeprojection Pinhole perspective camera f o x y ( x , y, z ) ( f , f ) f = focal length z z o = center of the camera E 3 2
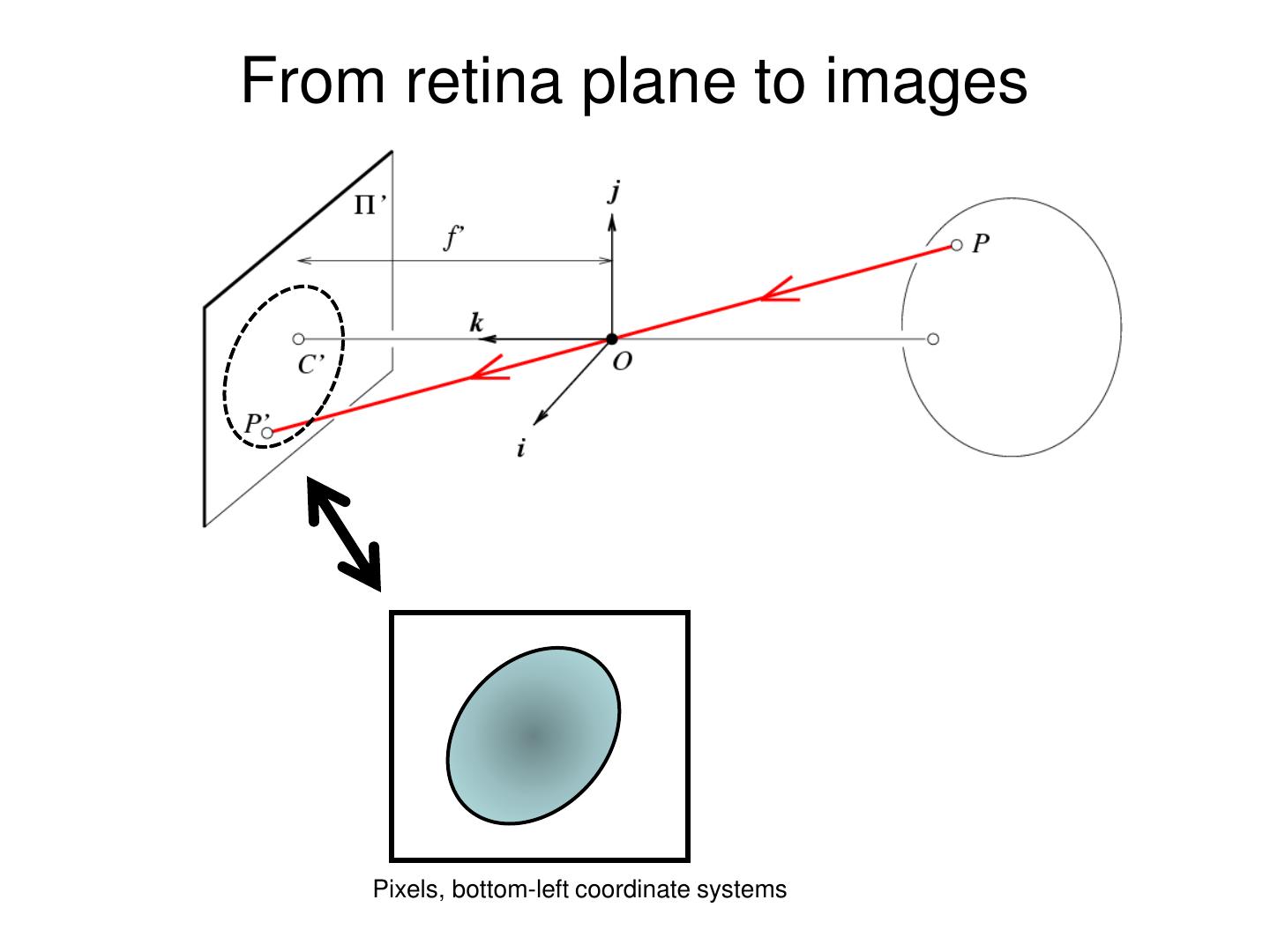
25 .From retina plane to images Pixels, bottom-left coordinate systems
26 . Coordinate systems yc xc
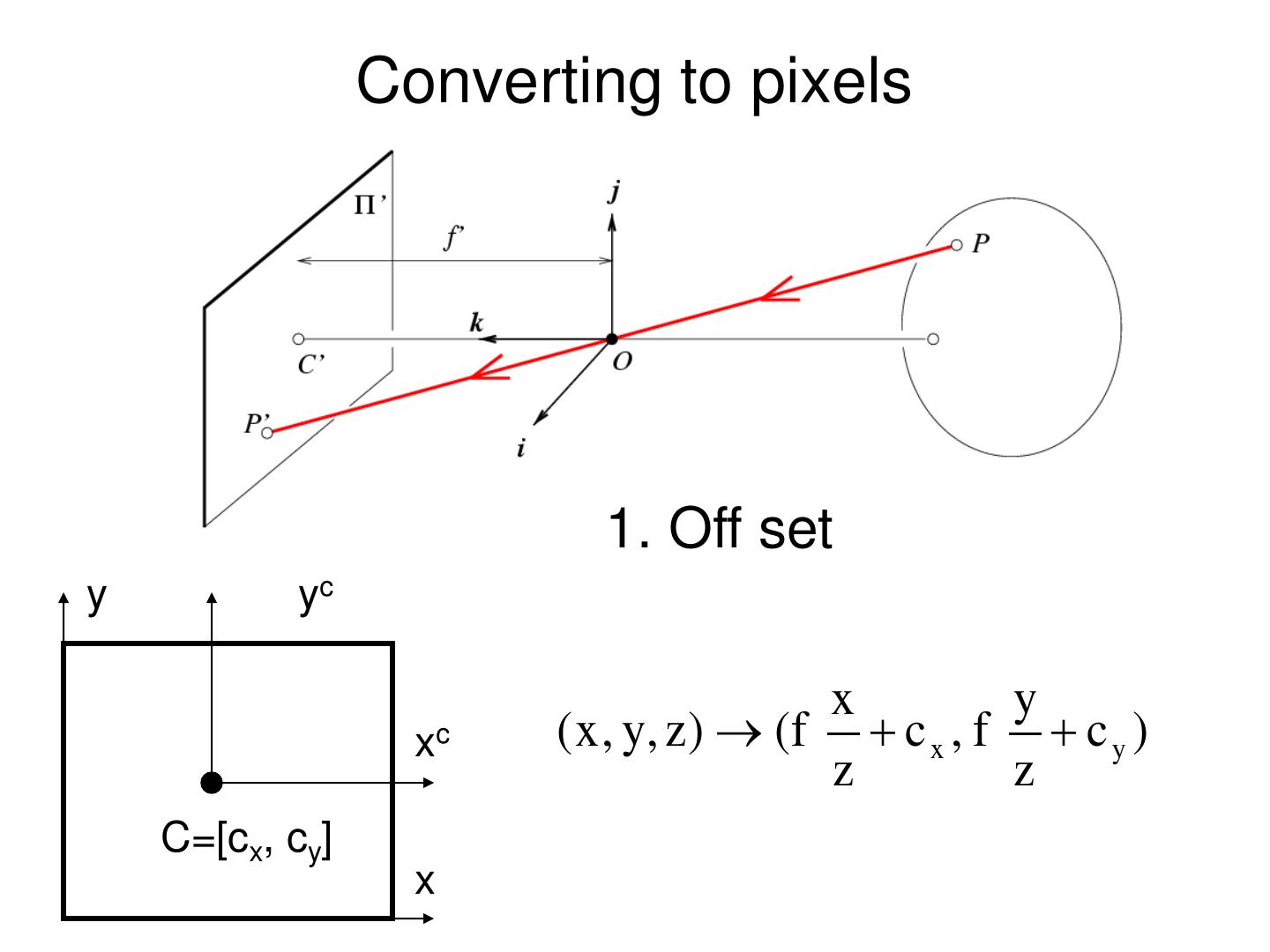
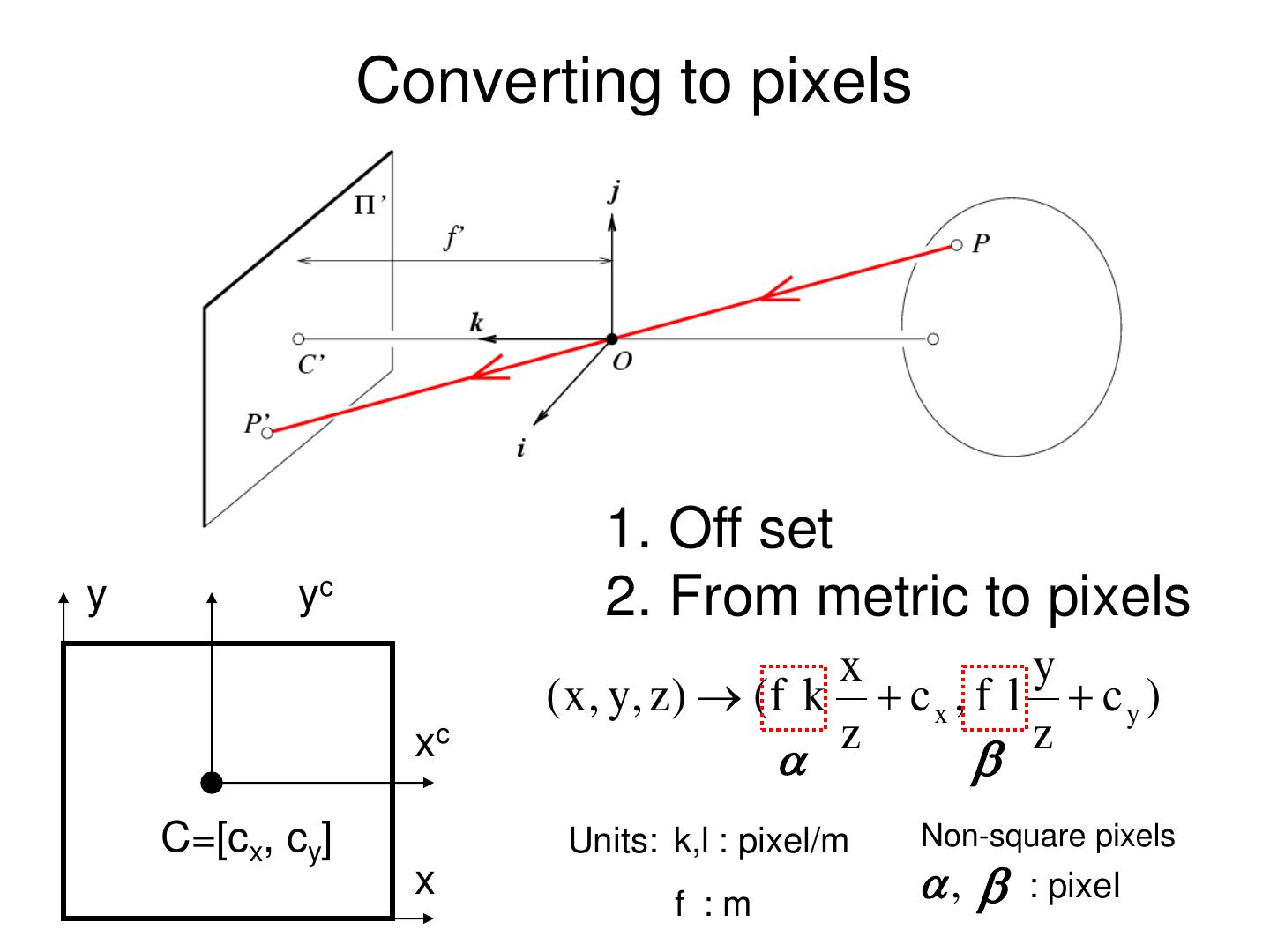
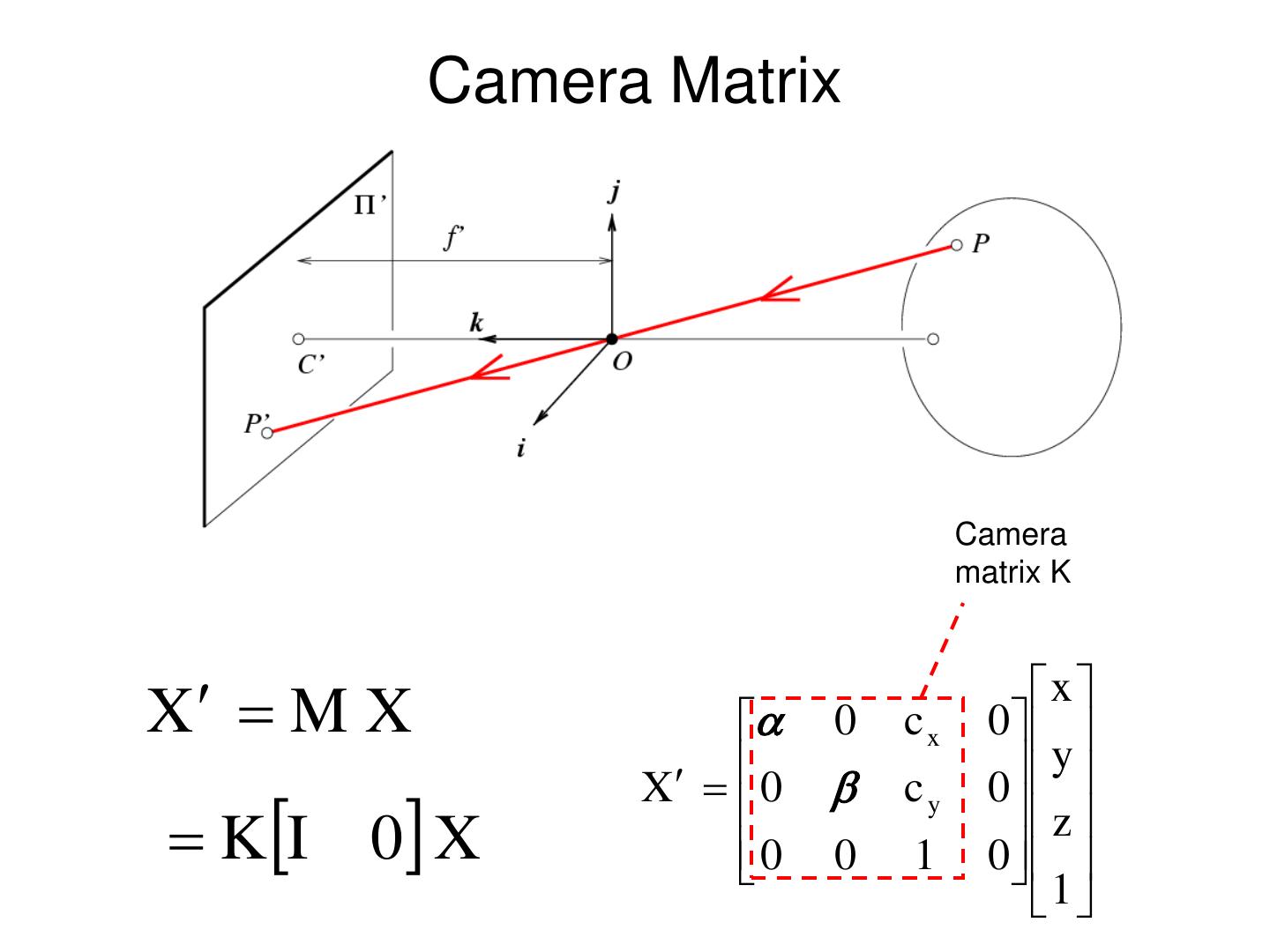
27 . Converting to pixels 1. Off set y yc x y xc ( x , y, z ) ( f c x , f c y ) z z C=[cx, cy] x
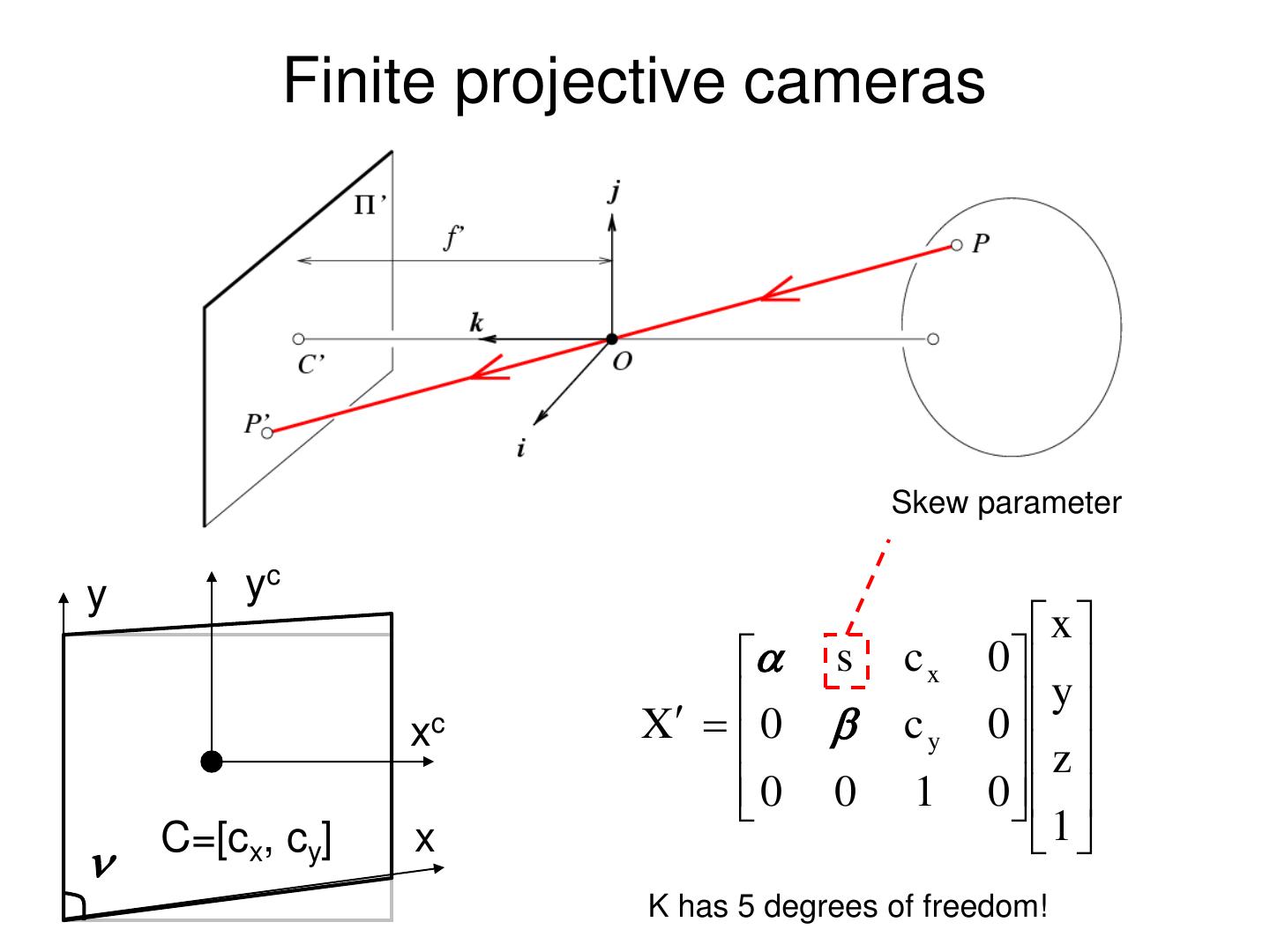
28 . Converting to pixels 1. Off set y yc 2. From metric to pixels x y ( x , y, z ) ( f k c x , f l c y ) z z xc C=[cx, cy] Units: k,l : pixel/m Non-square pixels x f :m , : pixel
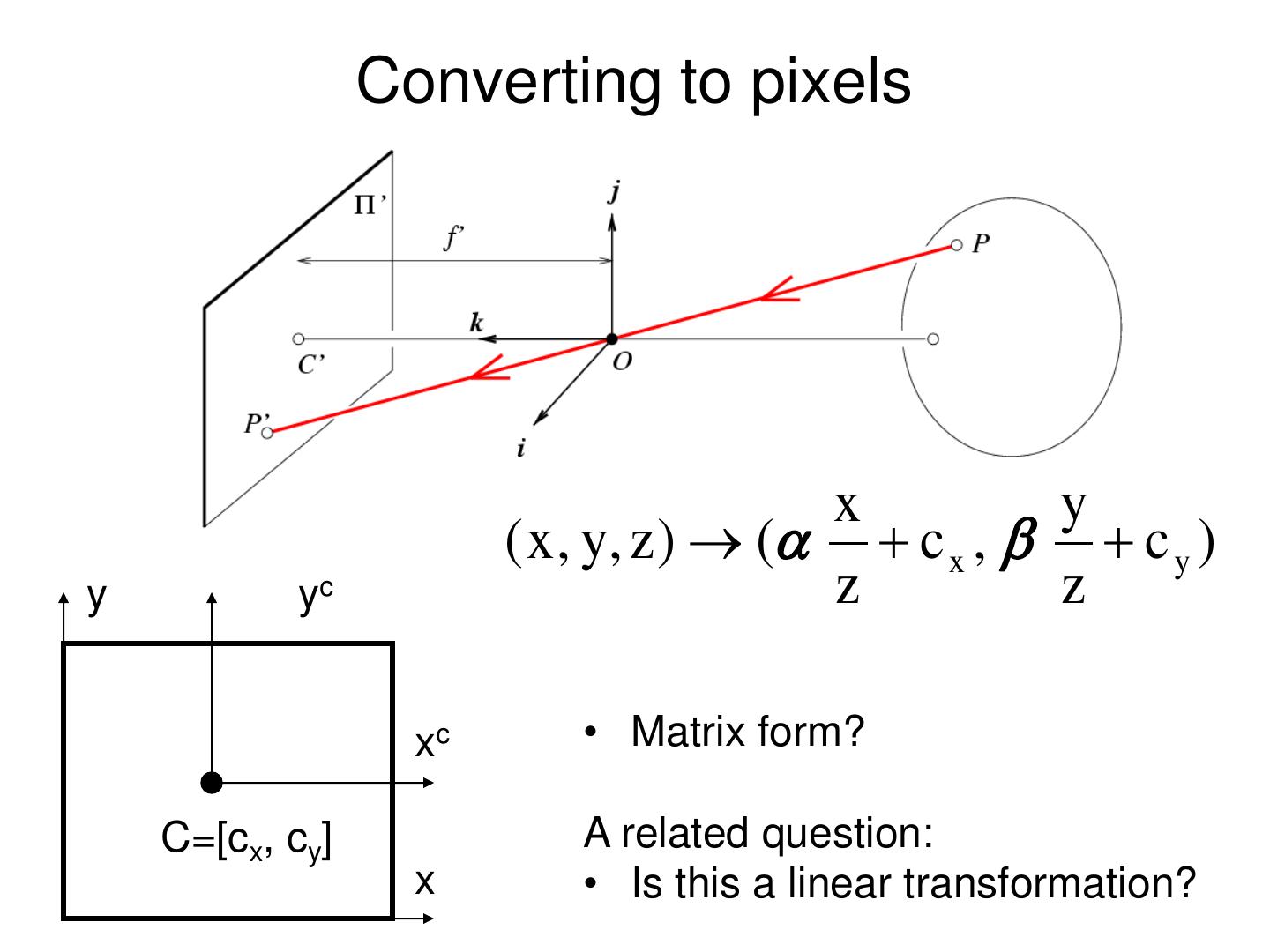
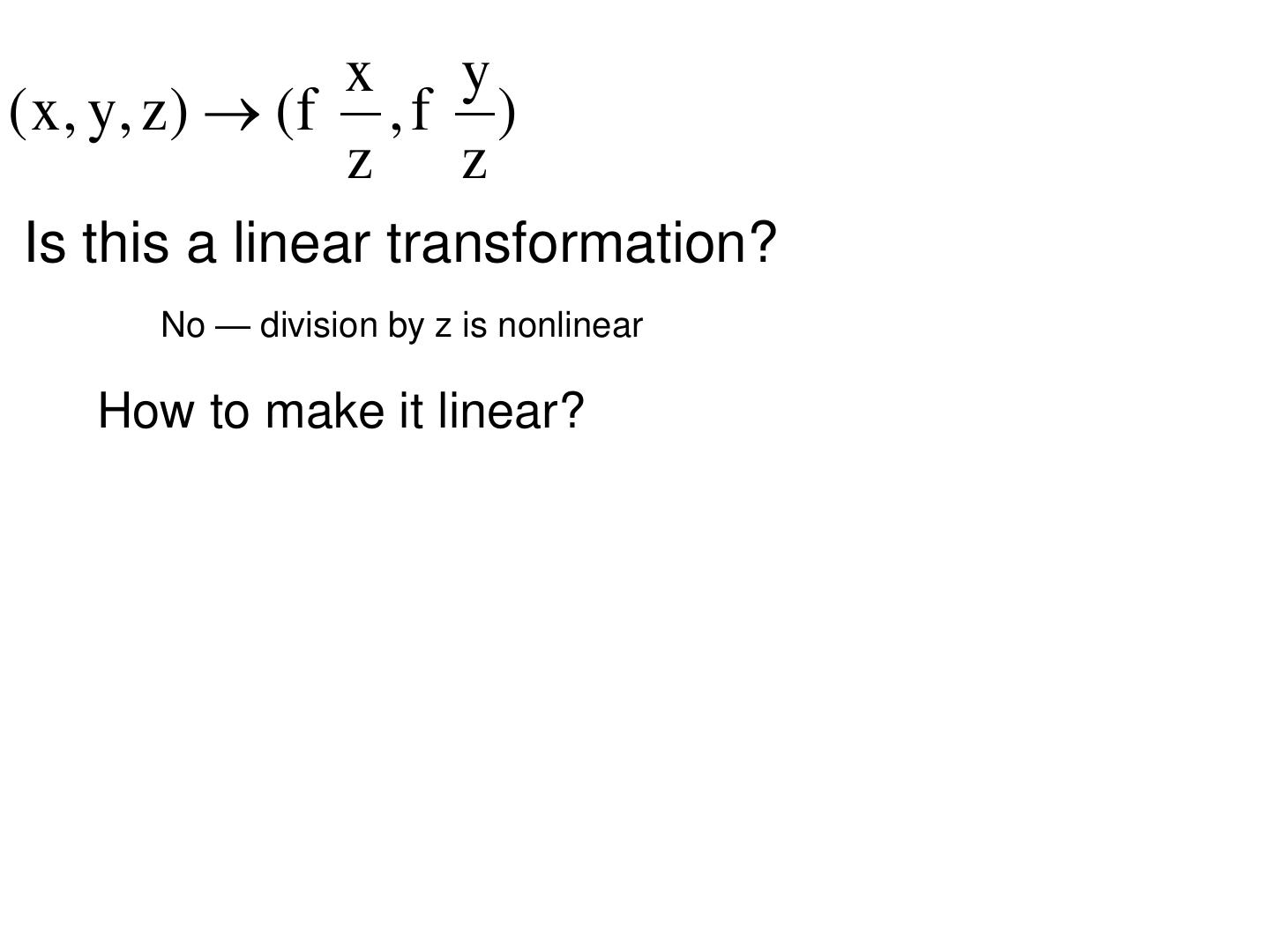
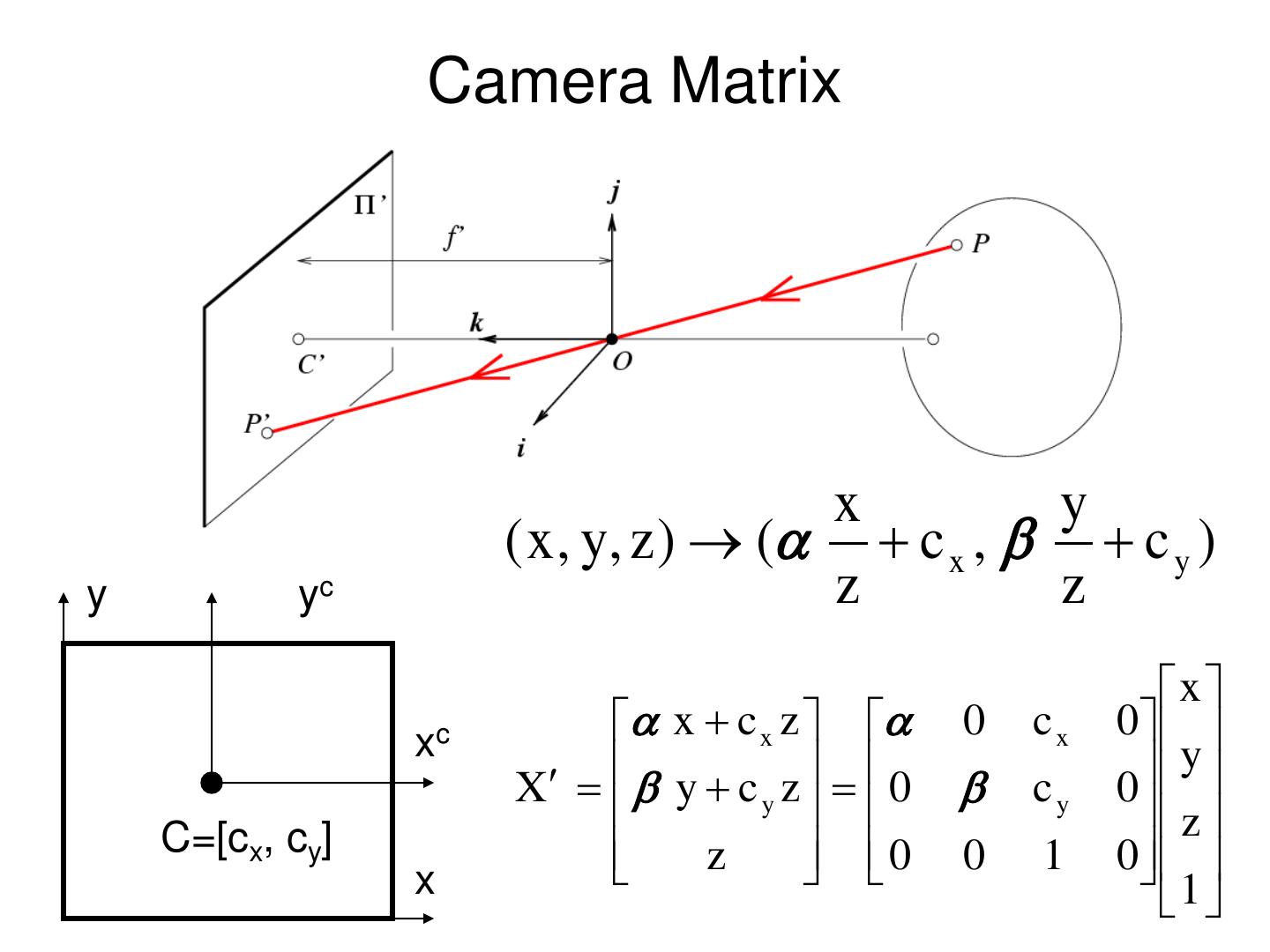
29 . Converting to pixels x y ( x , y, z ) ( c x , c y ) y yc z z xc • Matrix form? C=[cx, cy] A related question: x • Is this a linear transformation?