- 快召唤伙伴们来围观吧
- 微博 QQ QQ空间 贴吧
- 文档嵌入链接
- 复制
- 微信扫一扫分享
- 已成功复制到剪贴板
图形-地面分割使用聚类算法
展开查看详情
1 . CS131 Foreground-‐Background Segmenta5on via Clustering Yuke Zhu November 7, 2014
2 . Overview • Use clustering algorithms to segment images • Evaluate by cats out of images • Not a lot of code! (< 100 lines) • Focus on experimenta5on
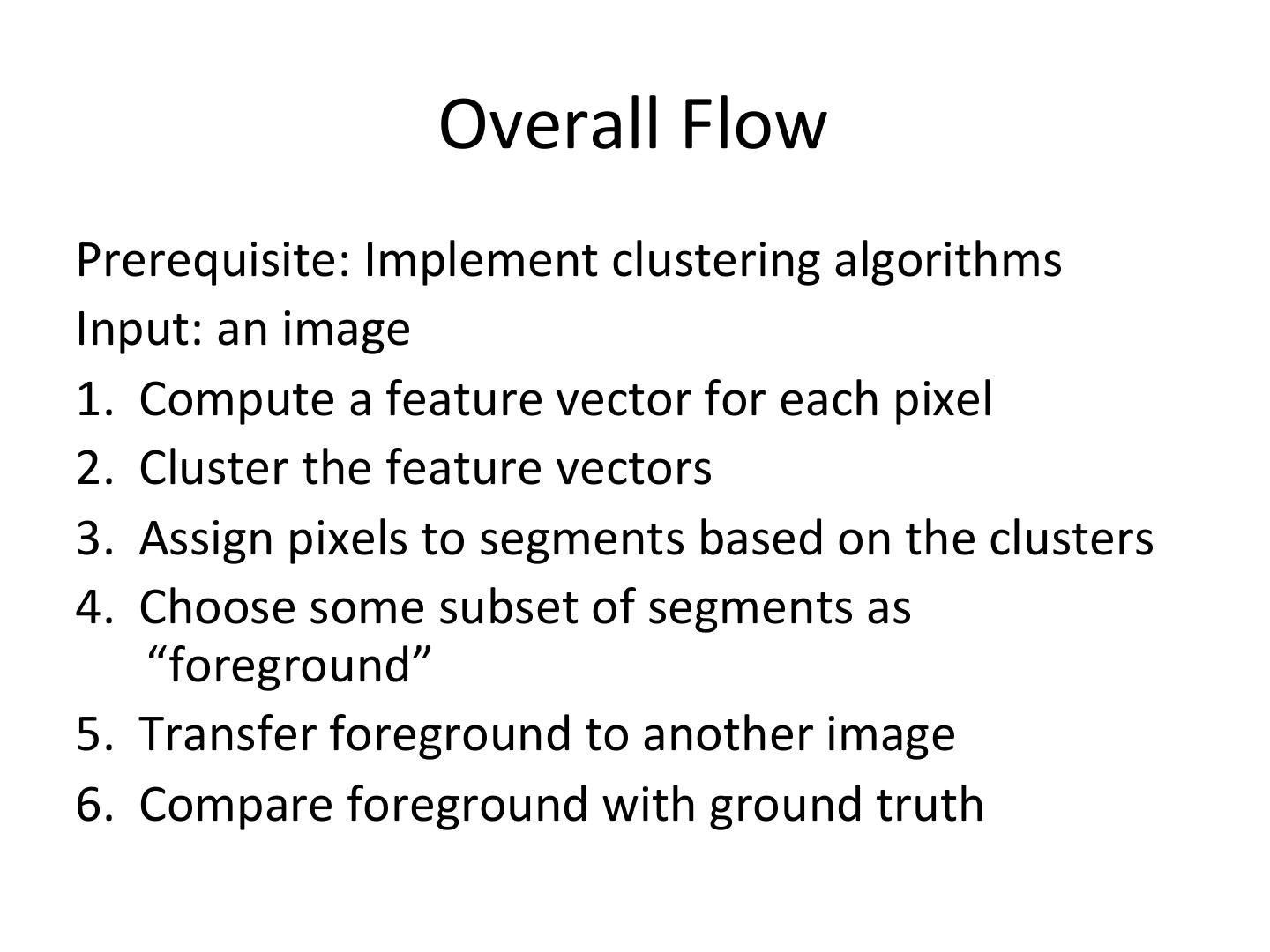
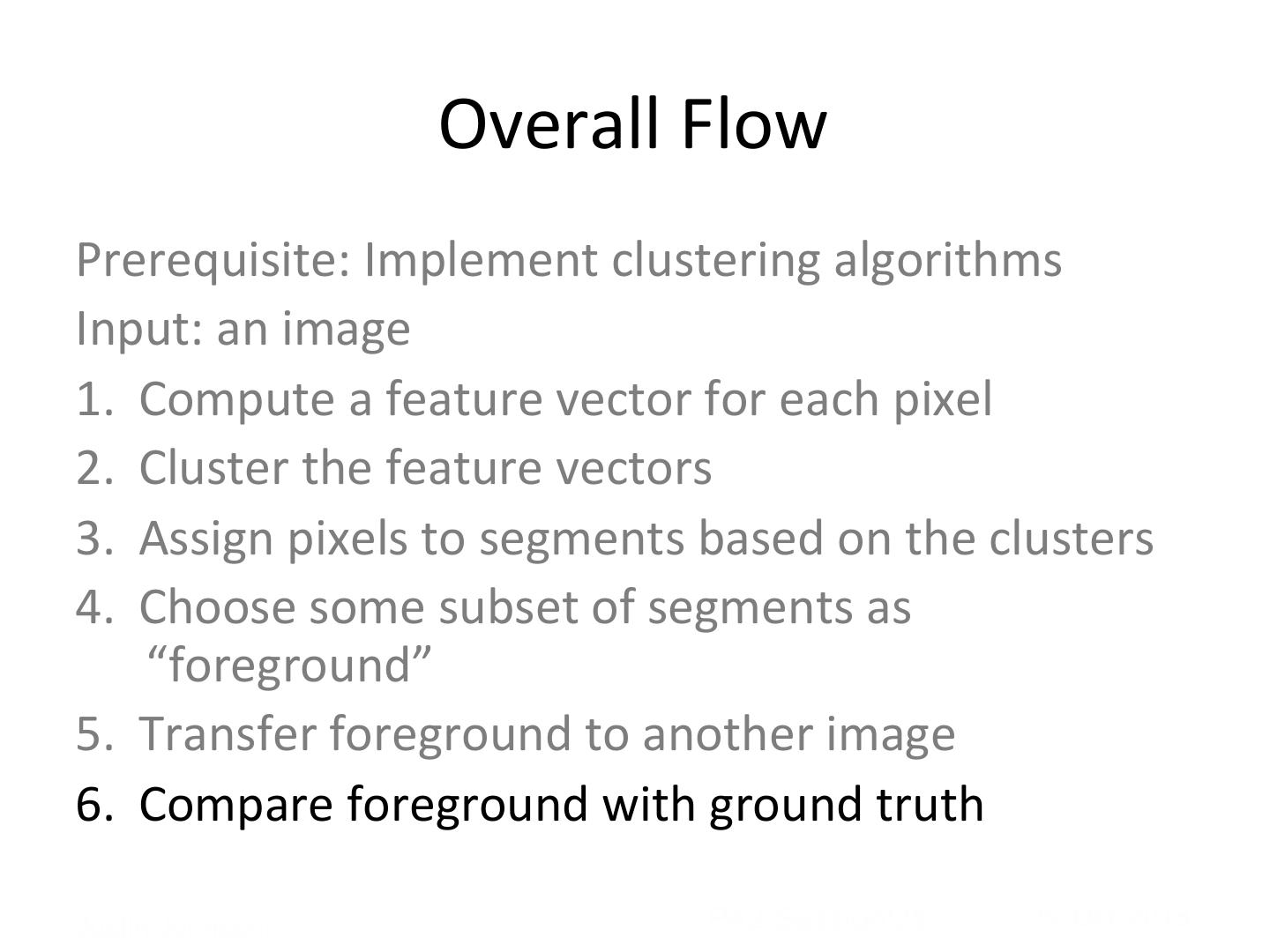
3 . Overall Flow Prerequisite: Implement clustering algorithms Input: an image 1. Compute a feature vector for each pixel 2. Cluster the feature vectors 3. Assign pixels to segments based on the clusters 4. Choose some subset of segments as “foreground” 5. Transfer foreground to another image 6. Compare foreground with ground truth
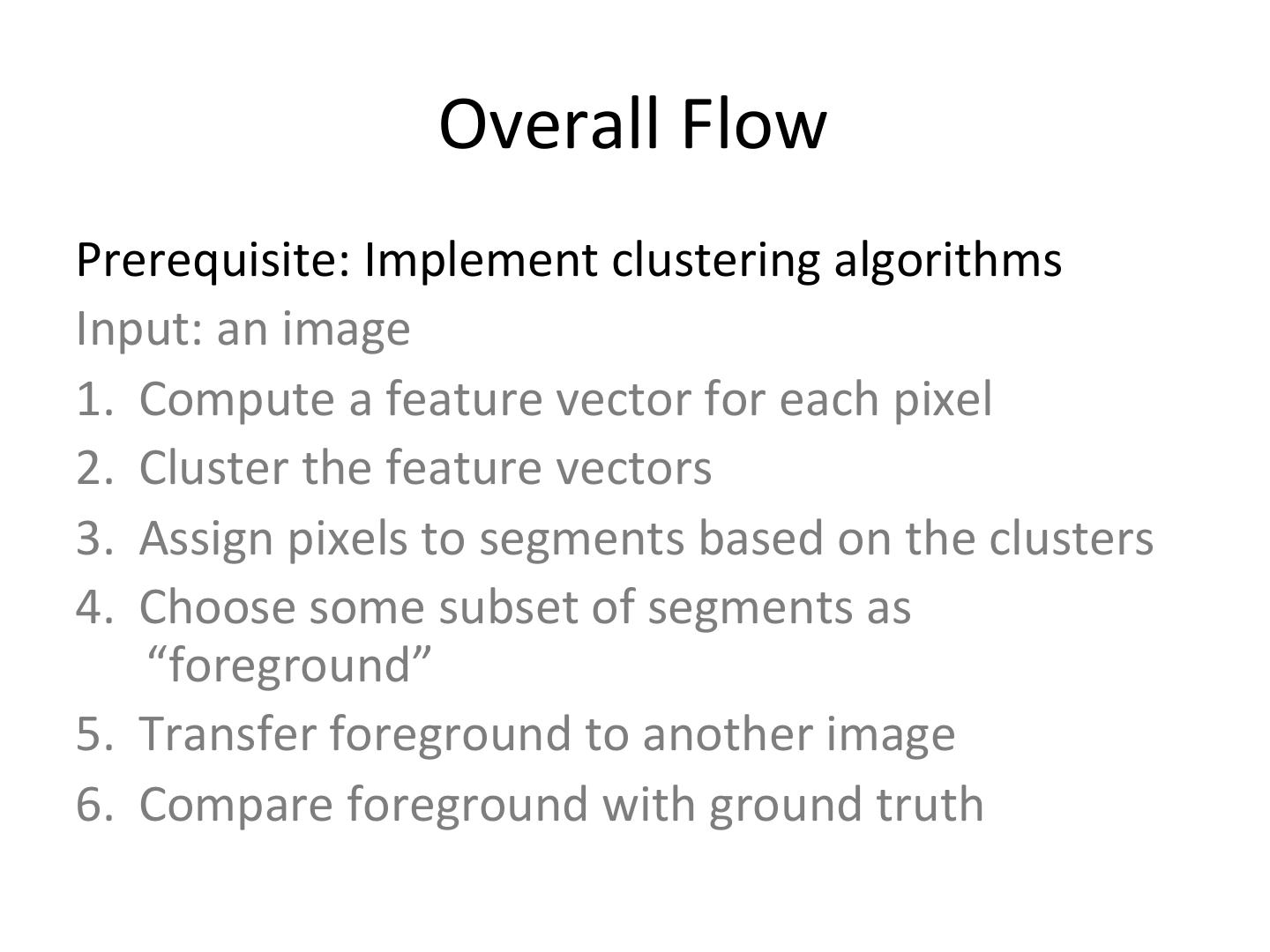
4 . Overall Flow Prerequisite: Implement clustering algorithms Input: an image 1. Compute a feature vector for each pixel 2. Cluster the feature vectors 3. Assign pixels to segments based on the clusters 4. Choose some subset of segments as “foreground” 5. Transfer foreground to another image 6. Compare foreground with ground truth
5 . Clustering Algorithms You need to implement 2 clustering methods: • K-‐Means Clustering - KMeansClustering.m - Covered in Lecture 13 • H ierarchical Agglomera5ve clustering - HAClustering.m - Covered in Lecture 12 Sec5on 2 of assignment Justin Johnson! PA2 Session!5 29-‐Oct-‐2013
6 . Clustering Algorithms: Interface function idx = KMeansClustering(X, k, visualize2D) function idx = HAClustering(X, k, visualize2D) X: Matrix where each row is a point k: Number of clusters visualize2D: If clustering 2D points, set this to true to see a visualiza5on idx: Vector giving computed assignments of points to clusters Use KMeansClusteringTest and HAClusteringTest to validate your implementa5on. Note: KMeansClustering has an addi5onal parameter centers that you don’t need to worry about
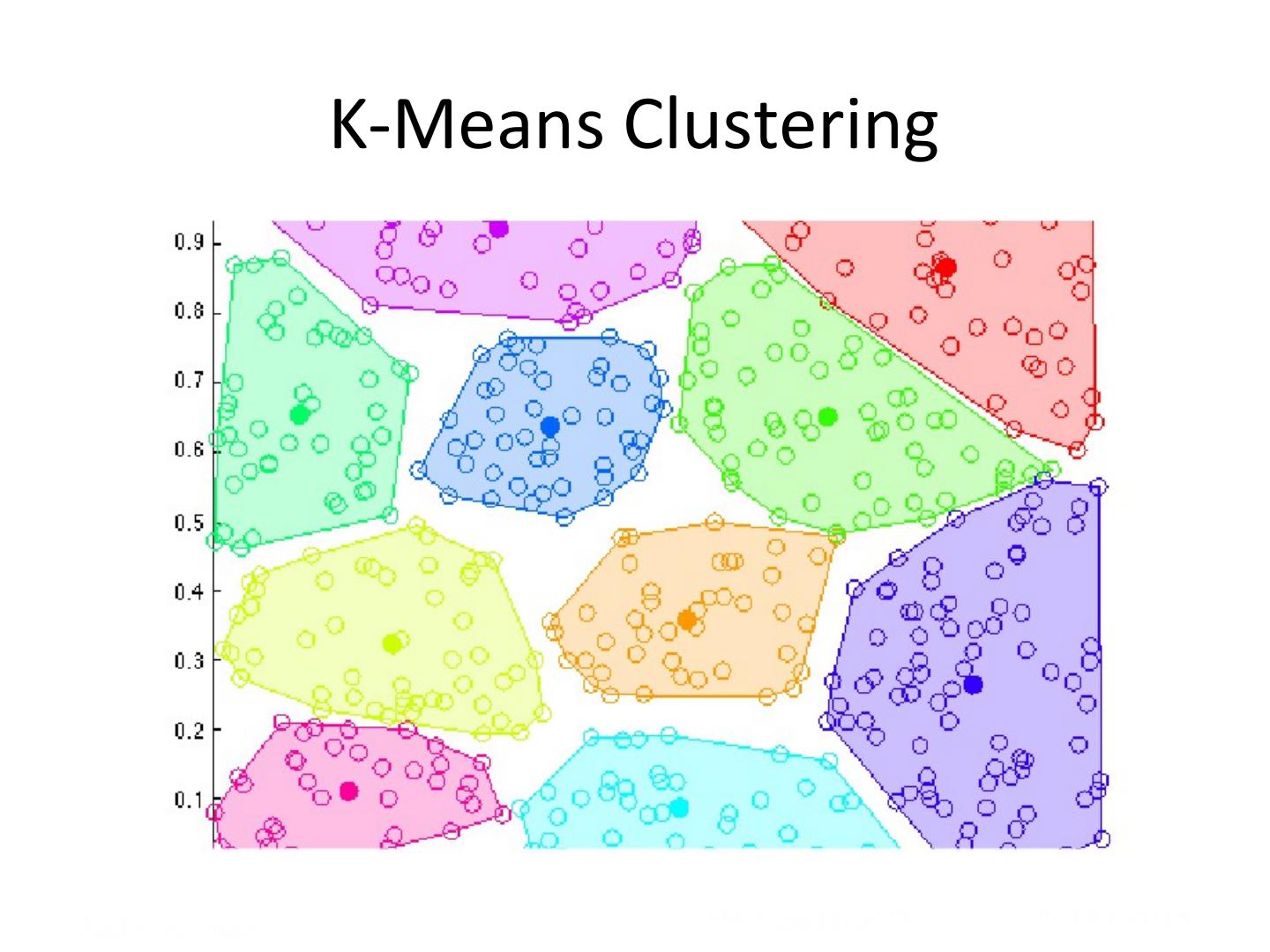
7 .K-‐Means Clustering
8 .K-‐Means Clustering
9 . K-‐Means Clustering Justin Johnson! PA2 Session!9 29-‐Oct-‐2013
10 . K-‐Means Clustering Justin Johnson! PA2 Session!10 29-‐Oct-‐2013
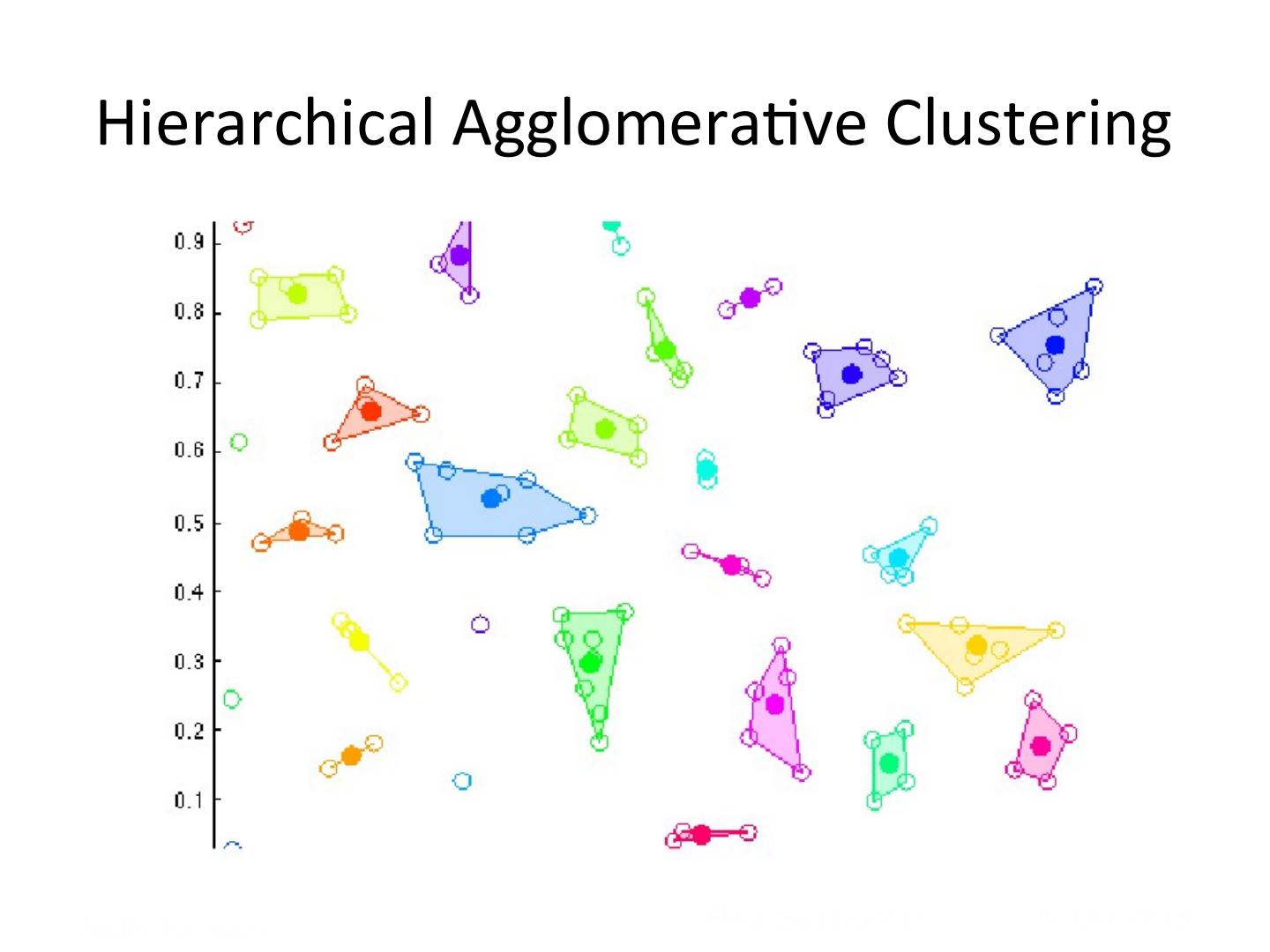
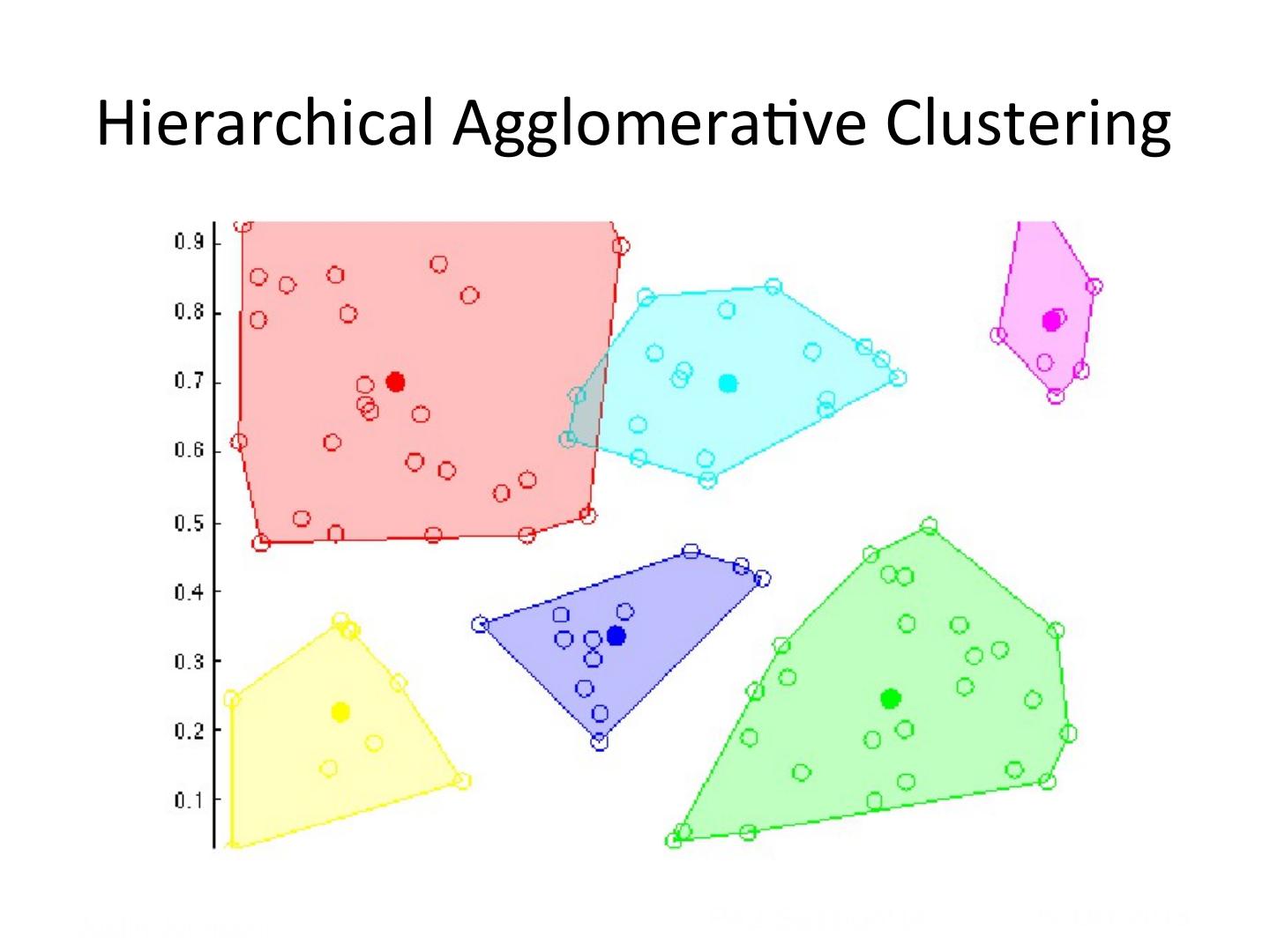
11 . Hierarchical Agglomera5ve Clustering Justin Johnson! PA2 Session!11 29-‐Oct-‐2013
12 . Hierarchical Agglomera5ve Clustering Justin Johnson! PA2 Session!12 29-‐Oct-‐2013
13 . Hierarchical Agglomera5ve Clustering Justin Johnson! PA2 Session!13 29-‐Oct-‐2013
14 . Hierarchical Agglomera5ve Clustering Justin Johnson! PA2 Session!14 29-‐Oct-‐2013
15 . Clustering: Efficiency Maeers! • For loops are SLOW in MATLAB; avoid them wherever possible! • Useful MATLAB func5ons: min, mean, pdist2, ind2sub, randperm • HAClustering.m: - Your code can be wrieen with no for loops - For reference: clustering 5000 5D points on my laptop takes about 90 seconds • KMeansClustering.m - For reference: clustering 5000 5D points on my laptop takes < 1 second Justin Johnson! PA2 Session!15 29-‐Oct-‐2013
16 . Overall Flow Prerequisite: Implement clustering algorithms Input: an image 1. Compute a feature vector for each pixel 2. Cluster the feature vectors 3. Assign pixels to segments based on the clusters 4. Choose some subset of segments as “foreground” 5. Transfer foreground to another image 6. Compare foreground with ground truth Justin Johnson! PA2 Session!16 29-‐Oct-‐2013
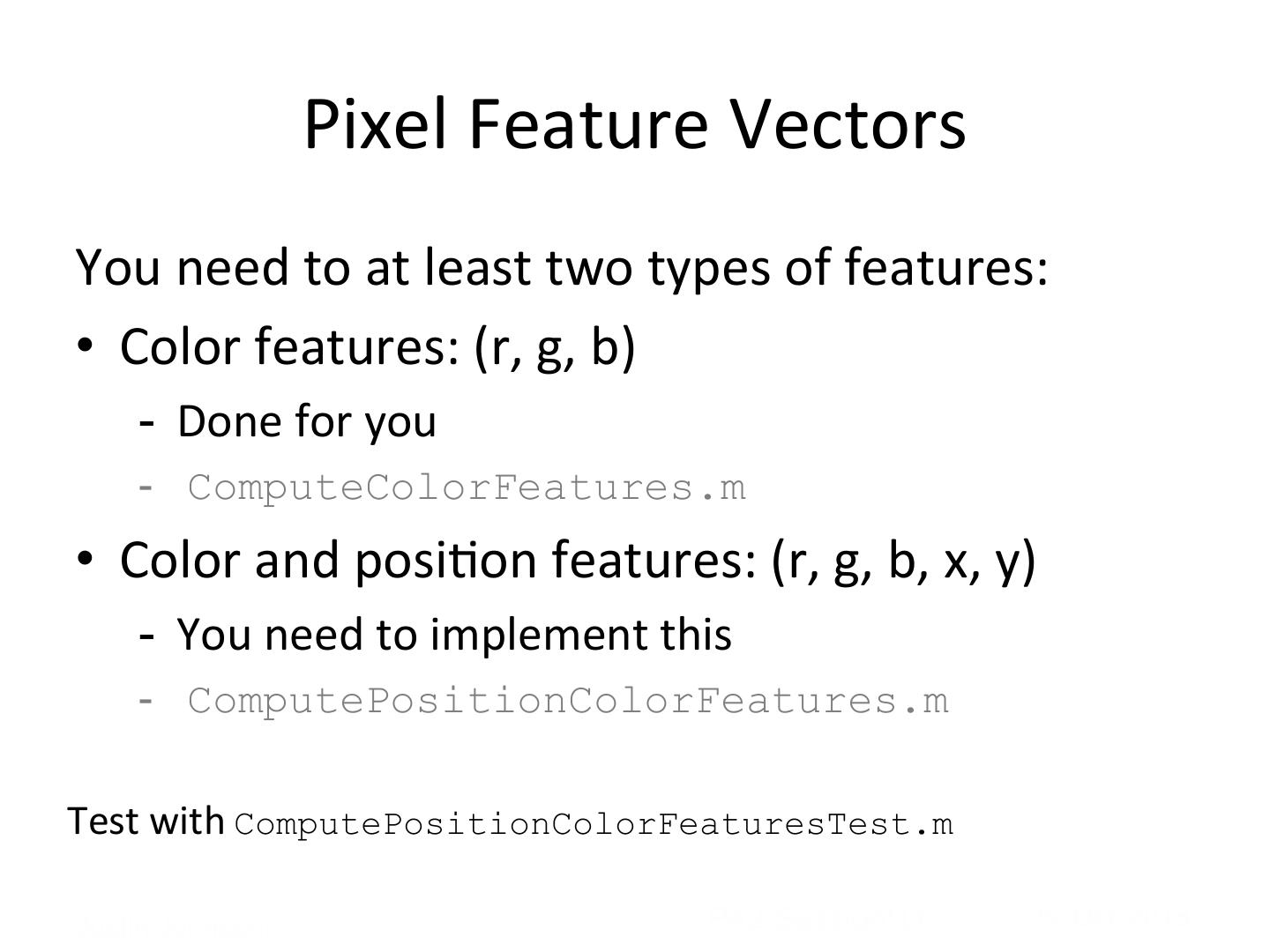
17 . Pixel Feature Vectors You need to at least two types of features: • Color features: (r, g, b) - Done for you - ComputeColorFeatures.m • Color and posi5on features: (r, g, b, x, y) - You need to implement this - ComputePositionColorFeatures.m Test with ComputePositionColorFeaturesTest.m Justin Johnson! PA2 Session!17 29-‐Oct-‐2013
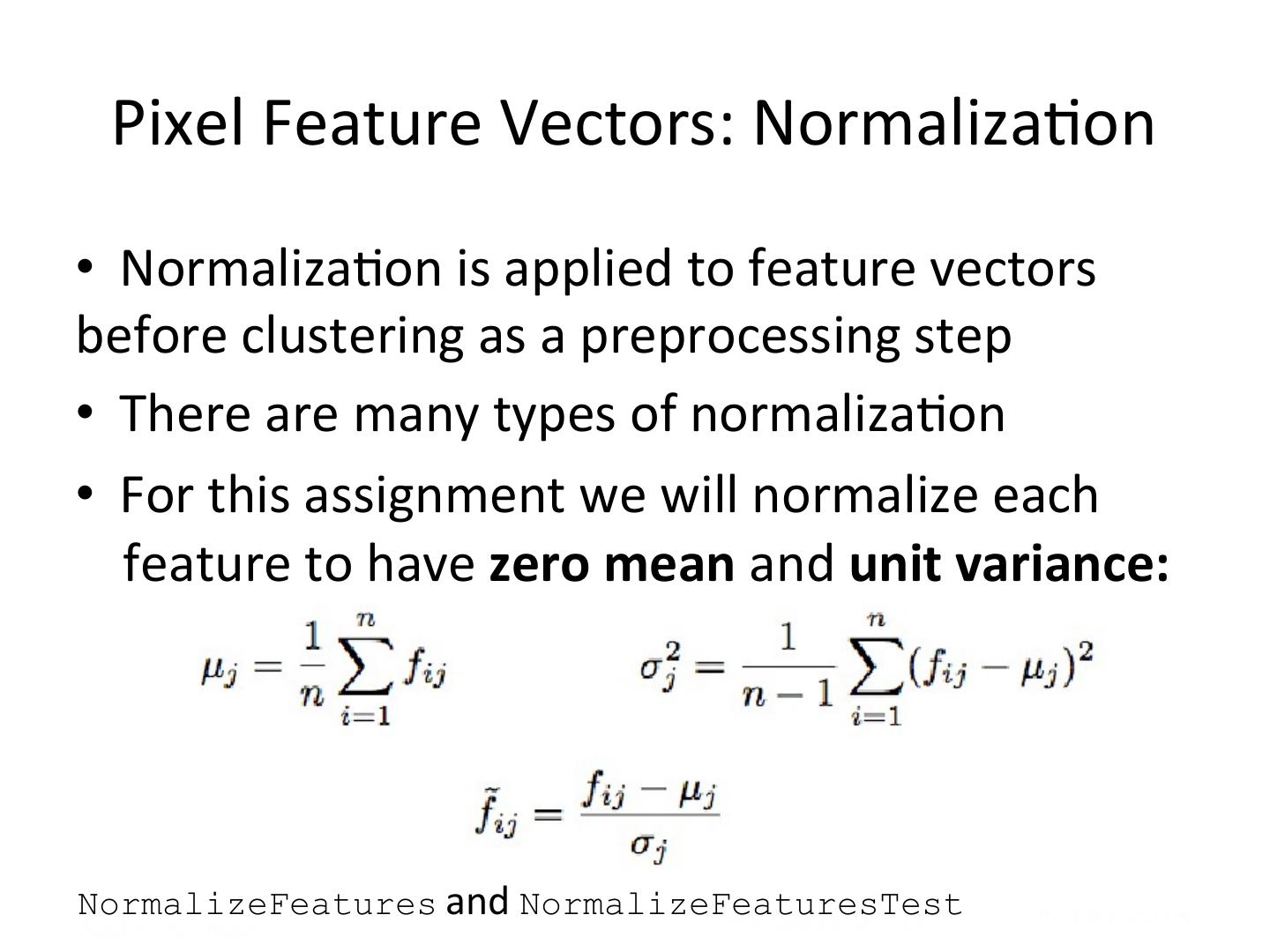
18 . Pixel Feature Vectors: Normaliza5on • Normaliza5on is applied to feature vectors before clustering as a preprocessing step • There are many types of normaliza5on • For this assignment we will normalize each feature to have zero mean and unit variance: NormalizeFeatures and NormalizeFeaturesTest PA2 Session!18 29-‐Oct-‐2013 Justin Johnson!
19 . Pixel Feature Vectors: Extra Credit Implement your own feature vectors and see how they perform Some ideas: • Gradients • Edges • SIFT descriptors Use ComputeFeatures.m as a star5ng point Justin Johnson! PA2 Session!19 29-‐Oct-‐2013
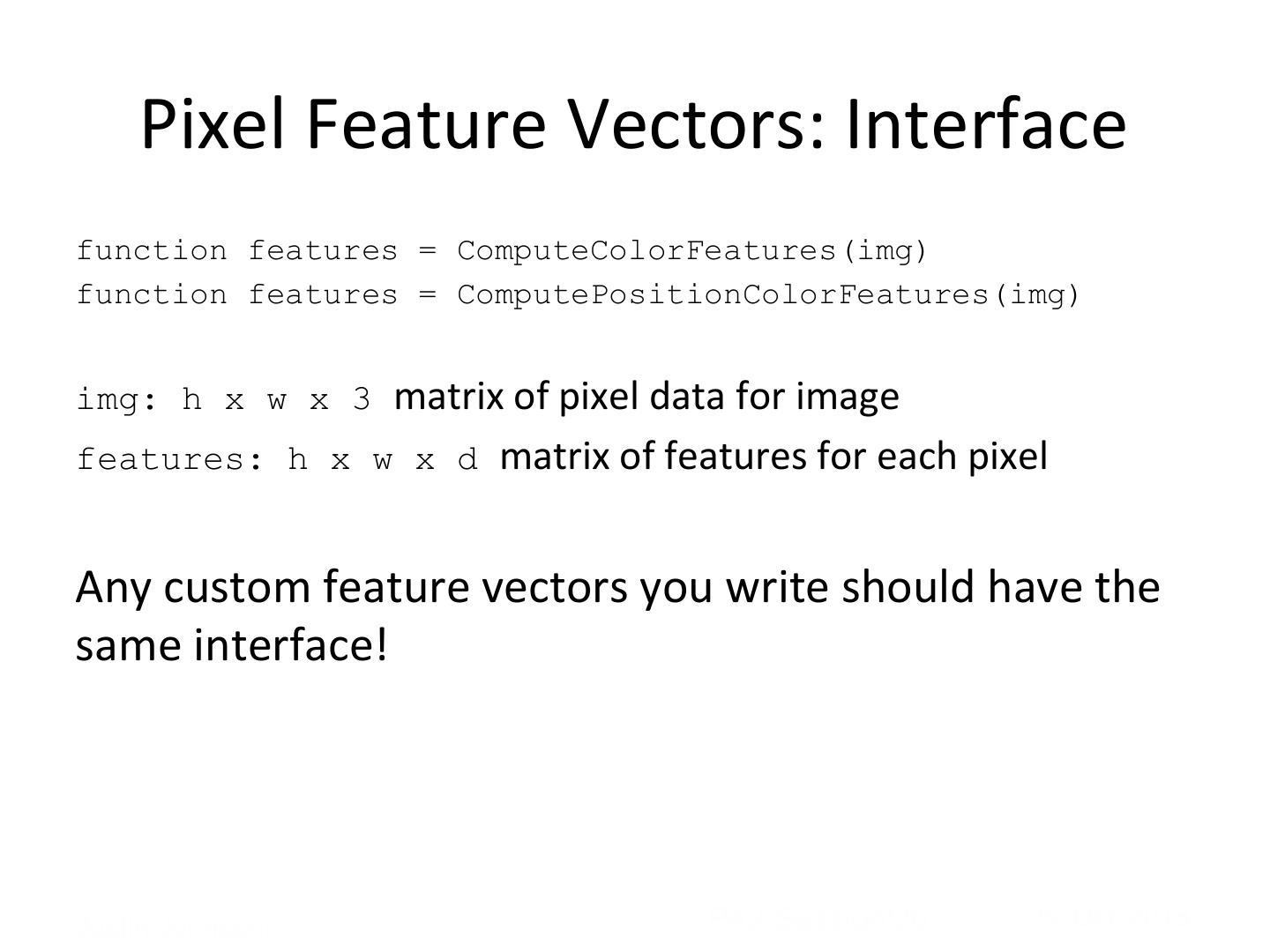
20 . Pixel Feature Vectors: Interface function features = ComputeColorFeatures(img) function features = ComputePositionColorFeatures(img) img: h x w x 3 matrix of pixel data for image features: h x w x d matrix of features for each pixel Any custom feature vectors you write should have the same interface! Justin Johnson! PA2 Session!20 29-‐Oct-‐2013
21 . Overall Flow Prerequisite: Implement clustering algorithms Input: an image 1. Compute a feature vector for each pixel 2. Cluster the feature vectors 3. Assign pixels to segments based on the clusters 4. Choose some subset of segments as “foreground” 5. Transfer foreground to another image 6. Compare foreground with ground truth Justin Johnson! PA2 Session!21 29-‐Oct-‐2013
22 .Cluster Feature Vectors + Assign Pixels • This is done for you in ComputeSegmentation.m and MakeSegments.m • ComputeSegmentation.m has many tunable parameters -‐ read the documenta5on in the file! • T he data structure used to store a segmenta5on is described in MakeSegments.m • U se RunComputeSegmentation.m as a star5ng point for your custom feature vectors Justin Johnson! PA2 Session!22 29-‐Oct-‐2013
23 . Resizing to Speed up Segmenta5on Downsample Segment Upsample Segm en result t – beeer s, but slowe r Implemented for you in ComputeSegmentation.m -‐ just set the resize parameter! Justin Johnson! PA2 Session!23 29-‐Oct-‐2013
24 . Overall Flow Prerequisite: Implement clustering algorithms Input: an image 1. Compute a feature vector for each pixel 2. Cluster the feature vectors 3. Assign pixels to segments based on the clusters 4. Choose some subset of segments as “foreground” 5. Transfer foreground to another image 6. Compare foreground with ground truth Justin Johnson! PA2 Session!24 29-‐Oct-‐2013
25 . Choose Foreground Segments • Aoer segmen5ng an image, foreground object may be split across several segments • Use ChooseSegments.m to pick a subset of segments as foreground Justin Johnson! PA2 Session!25 29-‐Oct-‐2013
26 . Overall Flow Prerequisite: Implement clustering algorithms Input: an image 1. Compute a feature vector for each pixel 2. Cluster the feature vectors 3. Assign pixels to segments based on the clusters 4. Choose some subset of segments as “foreground” 5. Transfer foreground to another image 6. Compare foreground with ground truth Justin Johnson! PA2 Session!26 29-‐Oct-‐2013
27 . Transfer Foreground • Just use ChooseSegments.m but pass in a background image Justin Johnson! PA2 Session!27 29-‐Oct-‐2013
28 . Overall Flow Prerequisite: Implement clustering algorithms Input: an image 1. Compute a feature vector for each pixel 2. Cluster the feature vectors 3. Assign pixels to segments based on the clusters 4. Choose some subset of segments as “foreground” 5. Transfer foreground to another image 6. Compare foreground with ground truth Justin Johnson! PA2 Session!28 29-‐Oct-‐2013
29 . Compare with Ground Truth • We provide a small dataset of 17 pictures of cats with correct segmenta5ons • The accuracy of a segmenta5on is the frac5on of pixels that are correctly labeled as foreground / background • EvaluateSegmentation.m computes the accuracy of a segmenta5on • Use EvaluateAllSegmentations.m as a star5ng point to evaluate your method on all images in the dataset (> 0.8) Justin Johnson! PA2 Session!29 29-‐Oct-‐2013