- 快召唤伙伴们来围观吧
- 微博 QQ QQ空间 贴吧
- 文档嵌入链接
- 复制
- 微信扫一扫分享
- 已成功复制到剪贴板
14computer and network security--Network Security Protocols
展开查看详情
1 .Network Security Protocols and Defensive Mechanisms John Mitchell CS 155 Spring 2018
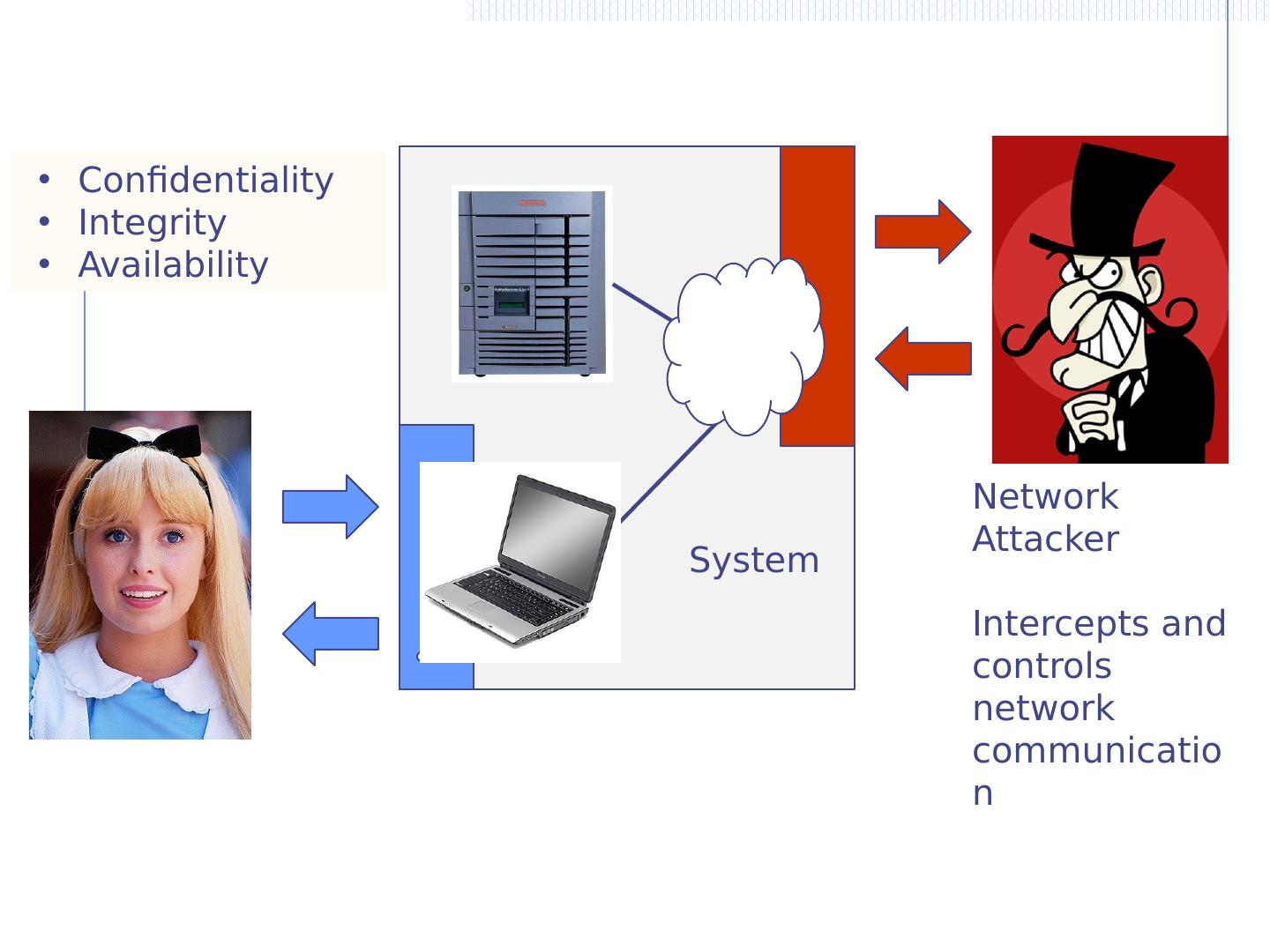
2 .Network security What is the network for? What properties might attackers destroy? Confidentiality : no information revealed to others Integrity : communication remains intact Availability : messages received in reasonable time
3 .Network Attacker Intercepts and controls network communication System Confidentiality Integrity Availability
4 .Plan for today Protecting network connections Wireless access– 802.11i/WPA2 IPSEC Perimeter network defenses Firewall Packet filter (stateless, stateful ), Application layer proxies Intrusion detection Anomaly and misuse detection Network infrastructure security BGP instability and S-BGP DNS rebinding and DNSSEC
5 .Last lecture Basic network protocols IP, TCP, UDP, BGP, DNS Problems with them TCP/IP No SRC authentication: can’t tell where packet is from Packet sniffing Connection spoofing, sequence numbers BGP: advertise bad routes or close good ones DNS: cache poisoning, rebinding Web security mechanisms rely on DNS
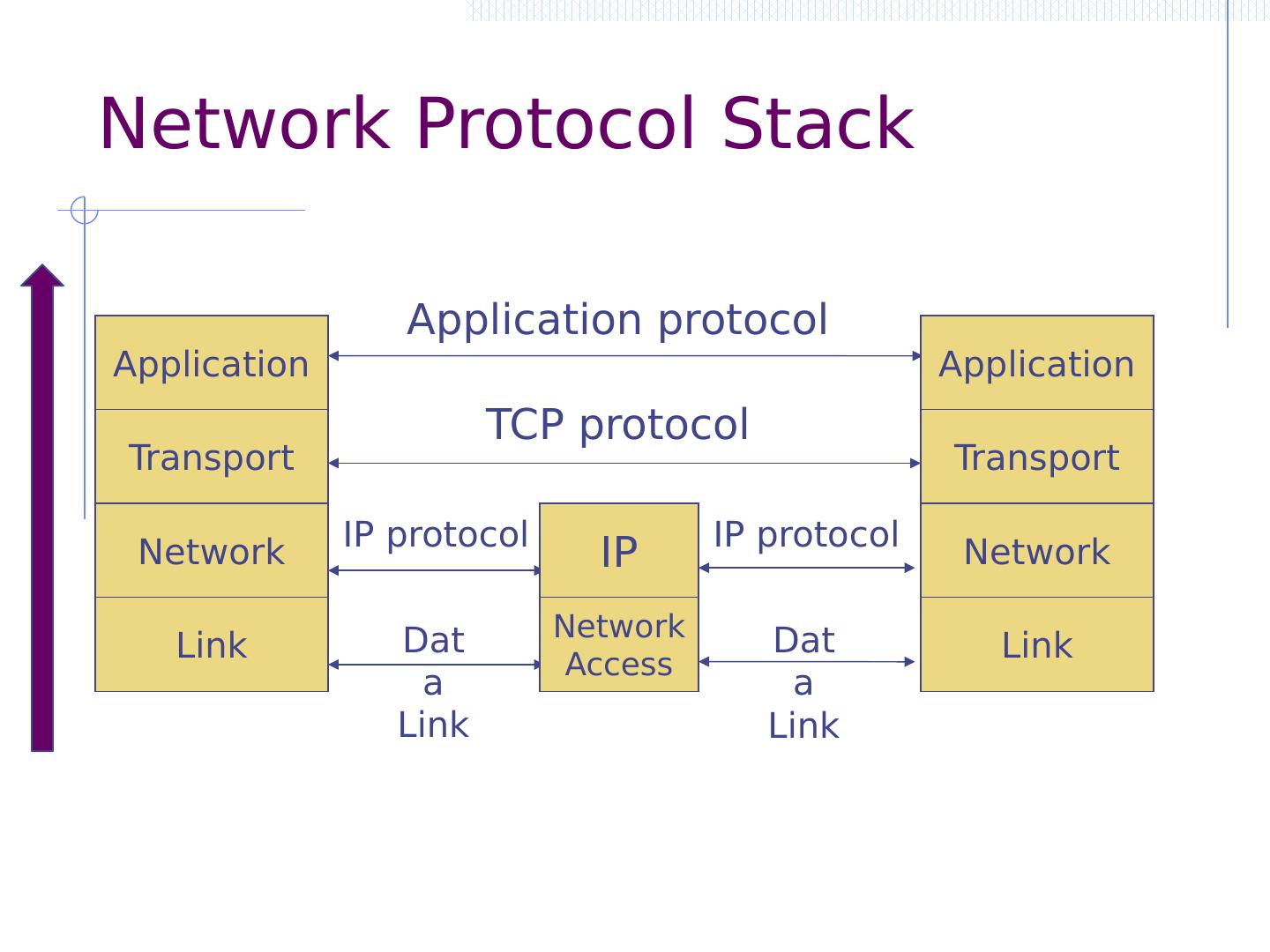
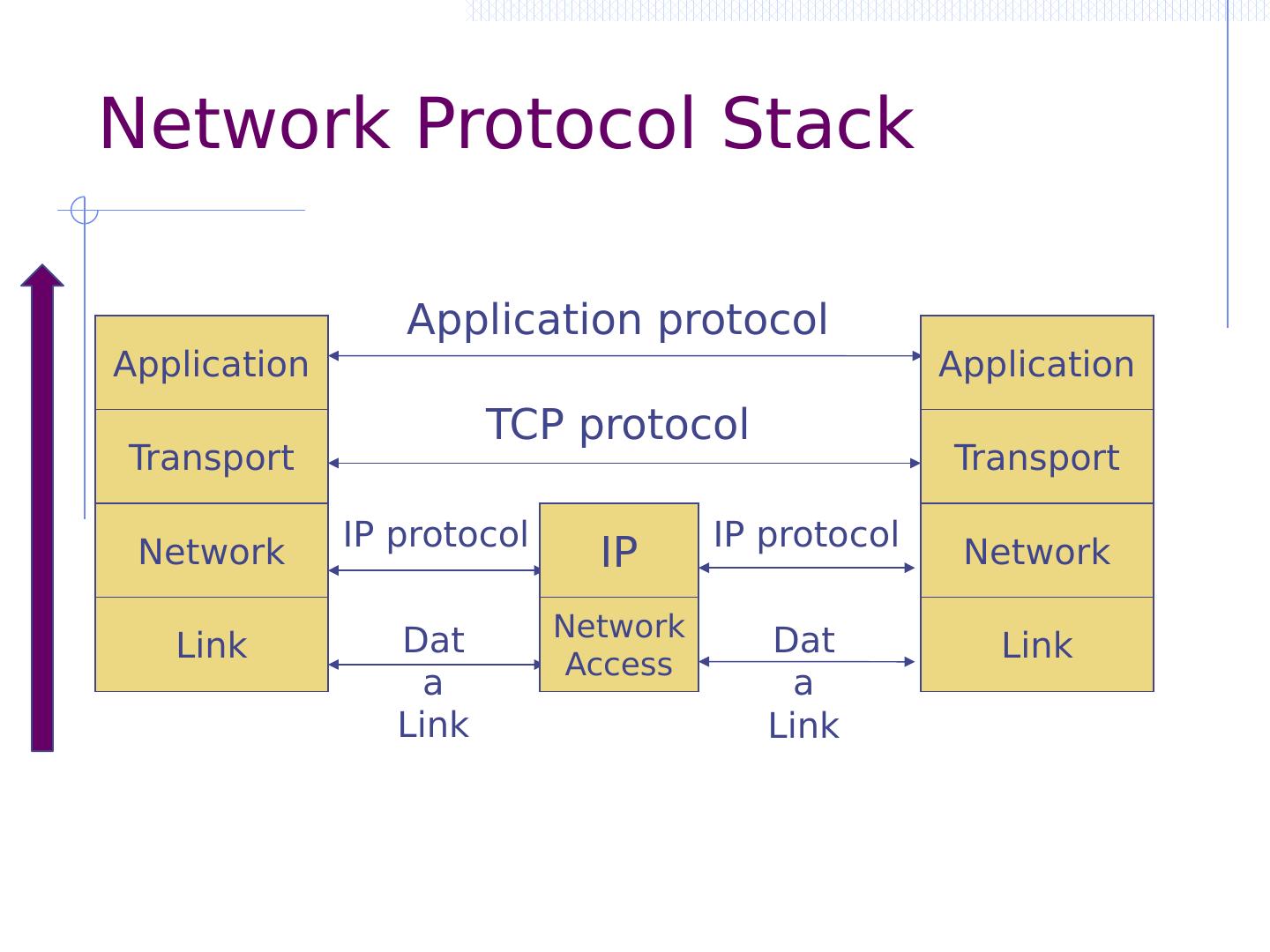
6 .Network Protocol Stack Application Transport Network Link Application protocol TCP protocol IP protocol Data Link IP Network Access IP protocol Data Link Application Transport Network Link
7 .Protocol and link-layer connectivity
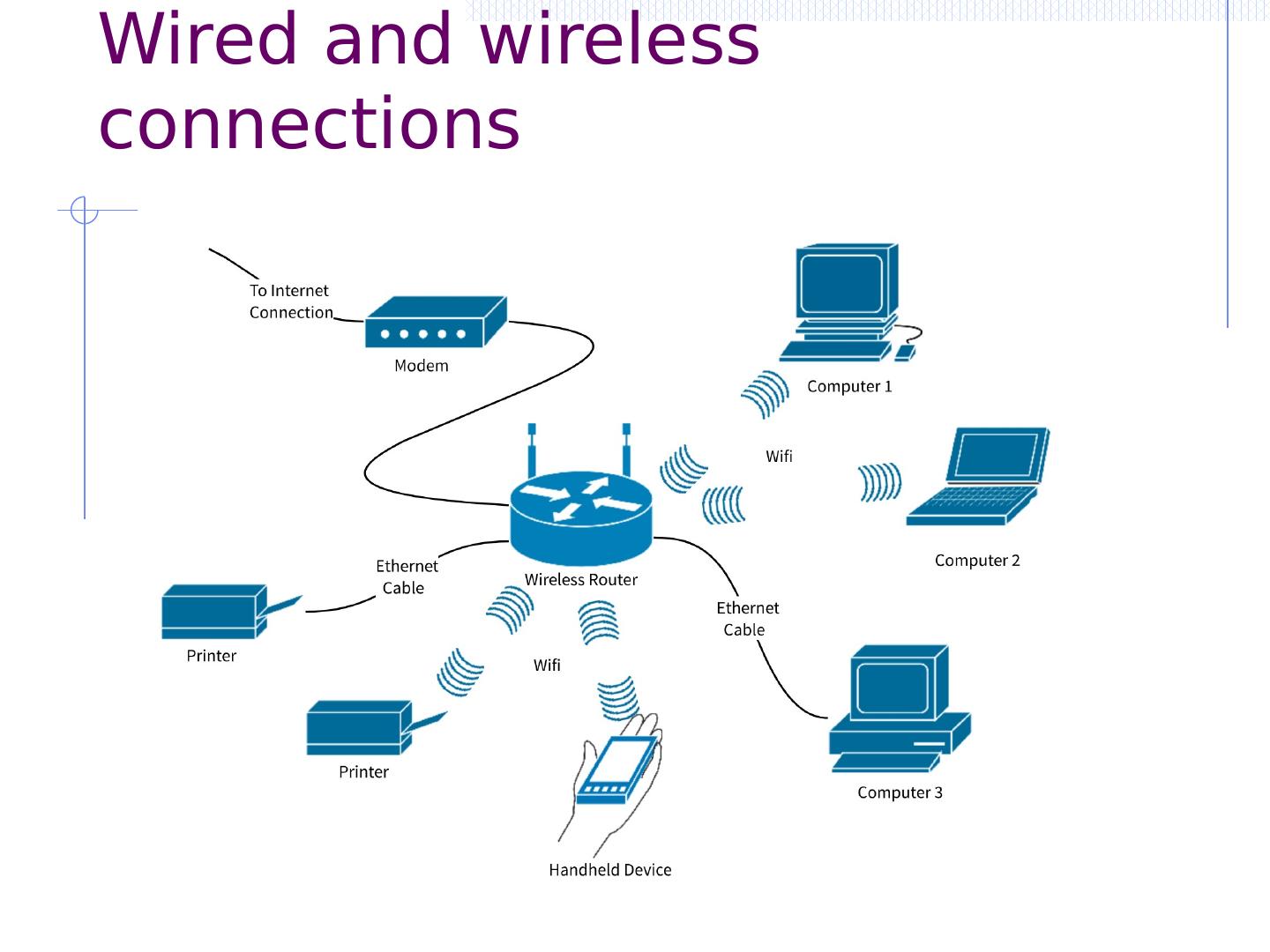
8 .Wired and wireless connections
9 .Wireless threats Passive eavesdropping / traffic analysys Message blocking and injection Masquerading as malicious access point Session hijacking Person-in-the-middle Denial of service
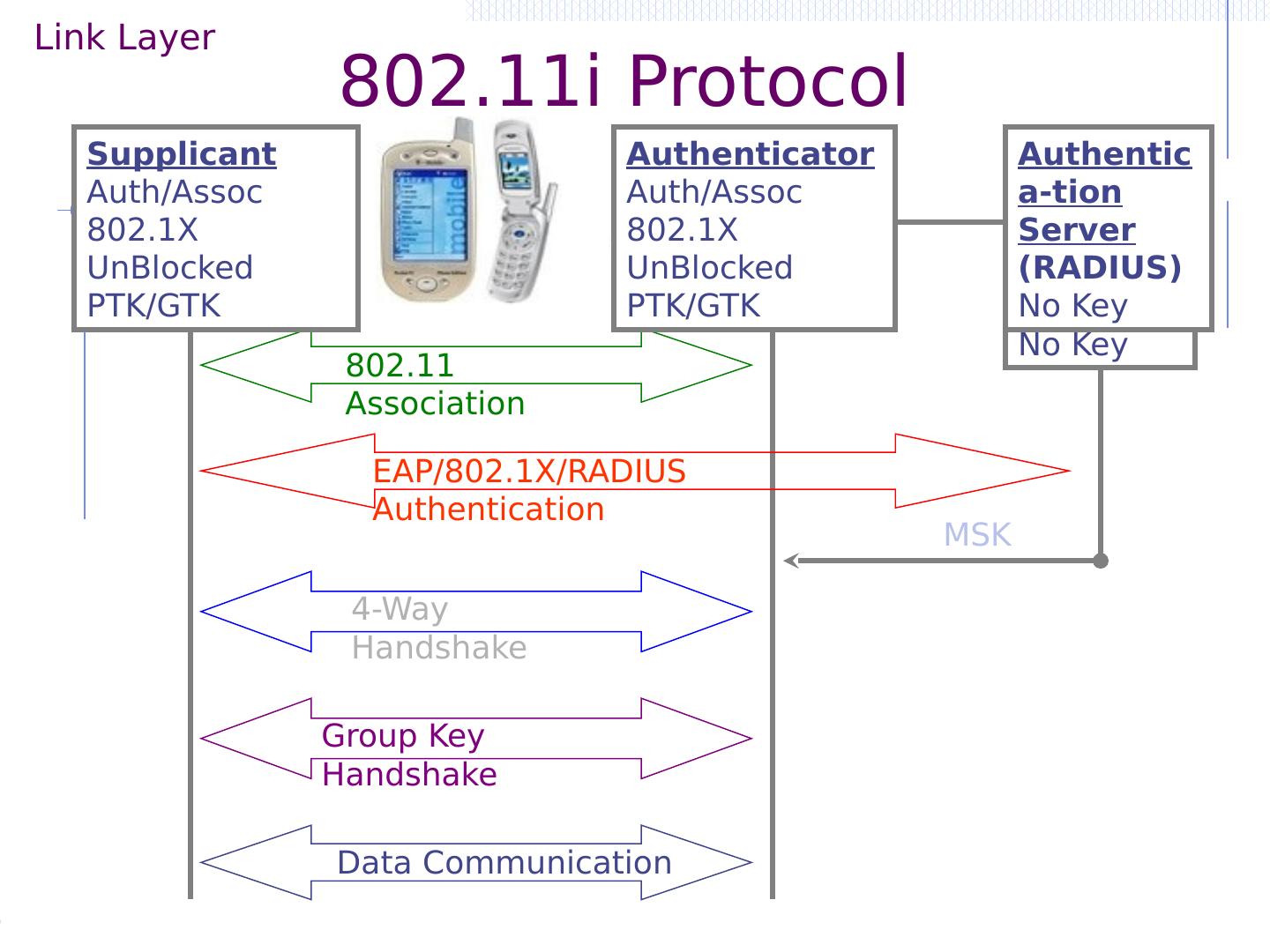
10 .Authentica-tion Server (RADIUS) No Key Authenticator UnAuth/UnAssoc 802.1X Blocked No Key Supplicant UnAuth/UnAssoc 802.1X Blocked No Key Supplicant Auth/Assoc 802.1X Blocked No Key Authenticator Auth/Assoc 802.1X Blocked No Key Authentica-tion Server (RADIUS) No Key 802.11 Association EAP/802.1X/RADIUS Authentication Supplicant Auth/Assoc 802.1X Blocked MSK Authenticator Auth/Assoc 802.1X Blocked No Key Authentica-tion Server (RADIUS) MSK MSK Supplicant Auth/Assoc 802.1X Blocked PMK Authenticator Auth/Assoc 802.1X Blocked PMK Authentica-tion Server (RADIUS) No Key 4-Way Handshake Supplicant Auth/Assoc 802.1X UnBlocked PTK/GTK Authenticator Auth/Assoc 802.1X UnBlocked PTK/GTK Authentica-tion Server (RADIUS) No Key Group Key Handshake Supplicant Auth/Assoc 802.1X UnBlocked New GTK Authenticator Auth/Assoc 802.1X UnBlocked New GTK Authentica-tion Server (RADIUS) No Key 802.11i Protocol Data Communication Supplicant Auth/Assoc 802.1X UnBlocked PTK/GTK Authenticator Auth/Assoc 802.1X UnBlocked PTK/GTK Authentica-tion Server (RADIUS) No Key Link Layer
11 .Authentica-tion Server (RADIUS) No Key Authenticator UnAuth/UnAssoc 802.1X Blocked No Key Supplicant UnAuth/UnAssoc 802.1X Blocked No Key Supplicant Auth/Assoc 802.1X Blocked No Key Authenticator Auth/Assoc 802.1X Blocked No Key Authentica-tion Server (RADIUS) No Key 802.11 Association EAP/802.1X/RADIUS Authentication Supplicant Auth/Assoc 802.1X Blocked MSK Authenticator Auth/Assoc 802.1X Blocked No Key Authentica-tion Server (RADIUS) MSK MSK Supplicant Auth/Assoc 802.1X Blocked PMK Authenticator Auth/Assoc 802.1X Blocked PMK Authentica-tion Server (RADIUS) No Key 4-Way Handshake Supplicant Auth/Assoc 802.1X UnBlocked PTK/GTK Authenticator Auth/Assoc 802.1X UnBlocked PTK/GTK Authentica-tion Server (RADIUS) No Key Group Key Handshake Supplicant Auth/Assoc 802.1X UnBlocked New GTK Authenticator Auth/Assoc 802.1X UnBlocked New GTK Authentica-tion Server (RADIUS) No Key 802.11i Protocol Data Communication Supplicant Auth/Assoc 802.1X UnBlocked PTK/GTK Authenticator Auth/Assoc 802.1X UnBlocked PTK/GTK Authentica-tion Server (RADIUS) No Key Link Layer
12 .TCP/IP connectivity How can we isolate our conversation from attackers on the Internet?
13 .Basic Layer 2-3 Security Problems Network packets pass by untrusted hosts Eavesdropping, packet sniffing Especially easy when attacker controls a machine close to victim TCP state can be easy to guess Enables spoofing and session hijacking Transport layer security (from last lecture)
14 .Virtual Private Network (VPN) Three different modes of use: Remote access client connections LAN-to-LAN internetworking Controlled access within an intranet Several different protocols PPTP – Point-to-point tunneling protocol L2TP – Layer-2 tunneling protocol IPsec (Layer-3: network layer) Data layer
15 .Credit: Checkpoint
16 .IPSEC Security extensions for IPv4 and IPv6 IP Authentication Header (AH) Authentication and integrity of payload and header IP Encapsulating Security Protocol (ESP) Confidentiality of payload ESP with optional ICV (integrity check value) Confidentiality, authentication and integrity of payload
17 .Recall packet formats and layers Application Transport (TCP, UDP) Network (IP) Link Layer Application message - data TCP data TCP data TCP data TCP Header data TCP IP IP Header data TCP IP ETH ETF Link (Ethernet) Header Link (Ethernet) Trailer segment packet frame message
18 .IPSec Transport Mode: IPSEC instead of IP header http://www.tcpipguide.com/free/t_IPSecModesTransportandTunnel.htm
19 .IPSEC Tunnel Mode
20 .IPSec Tunnel Mode: IPSEC header + IP header
21 .Mobile IPv6 Architecture IPv6 Mobile Node (MN) Corresponding Node (CN) Home Agent (HA) Direct connection via binding update Authentication is a requirement Early proposals weak RFC 6618 – use IPSec Mobility
22 .Summary Protecting network connections Wireless access– 802.11i/WPA2 Several subprotocols provide encrypted link between user device and wireless access point Ideally – wireless attacker in range of access point has no better chance for attack than a remote attacker IPSEC Give external Internet connections equivalent security to local area network connections Mobility Preserve network connections when a device moves to different physical portions of the network Ideally – no attacks other than against non-mobile user
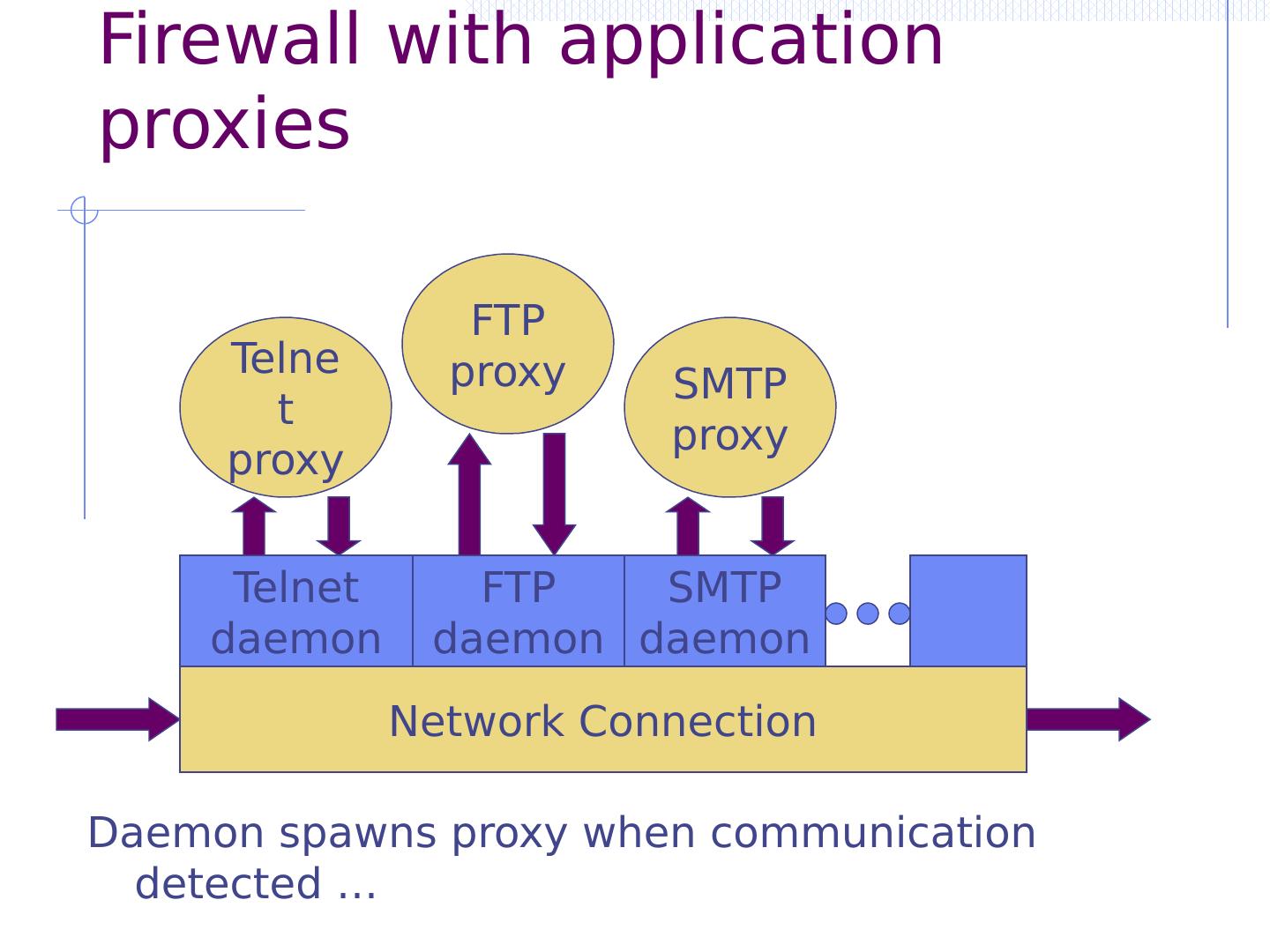
23 .Second topic of today’s lecture Perimeter defenses for local networks Firewall Packet filter (stateless, stateful ) Application layer proxies Intrusion detection Anomaly and misuse detection
24 .Local area Network How can we protect our local area network from attackers on the external Internet?
25 .Basic Firewall Concept Separate local area net from internet Router Firewall All packets between LAN and internet routed through firewall Local network Internet Perimeter security
26 .Screened Subnet Using Two Routers
27 .Alternate 1: Dual-Homed Host
28 .Alternate 2: Screened Host
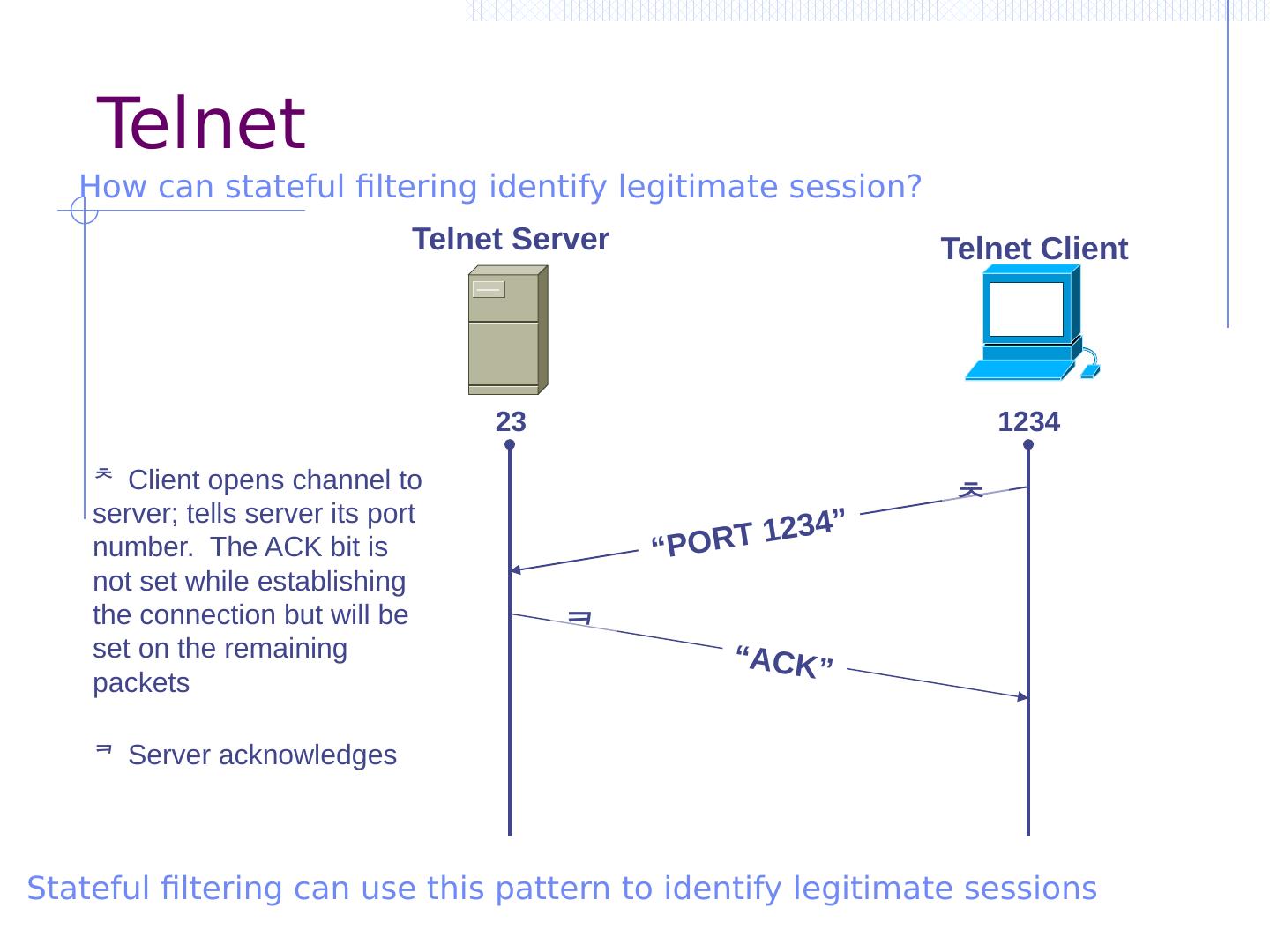
29 .Basic Packet Filtering Uses transport-layer information only IP Source Address, Destination Address Protocol (TCP, UDP, ICMP, etc) TCP or UDP source & destination ports TCP Flags (SYN, ACK, FIN, RST, PSH, etc) ICMP message type Examples DNS uses port 53 Block incoming port 53 packets except known trusted servers Issues Stateful filtering Encapsulation: address translation, other complications Fragmentation