- 快召唤伙伴们来围观吧
- 微博 QQ QQ空间 贴吧
- 文档嵌入链接
- 复制
- 微信扫一扫分享
- 已成功复制到剪贴板
MLflow with R
展开查看详情
1 . MLflow with R Javier Luraschi September 2018
2 .Overview What is MLflow? What is R? MLflow with R
3 .What is MLflow?
4 . Background Spark Summit from Andrej Karpathy at Tesla The toolchain for the (so ware) 2.0 tack does not exist.
5 . MLflow “Helps teams manage their machine learning lifecycle.” Tracking : Track experiments to record and compare params and results. Projects : Reuse and reproduce code to share or transfer to production. Models : Manage and deploy models from across libraries and platforms.
6 .What is R?
7 . R Language R is a programming language and free so ware environment for statistical computing and graphics. Interface language diagram by John Chambers - Rick Becker useR 2016.
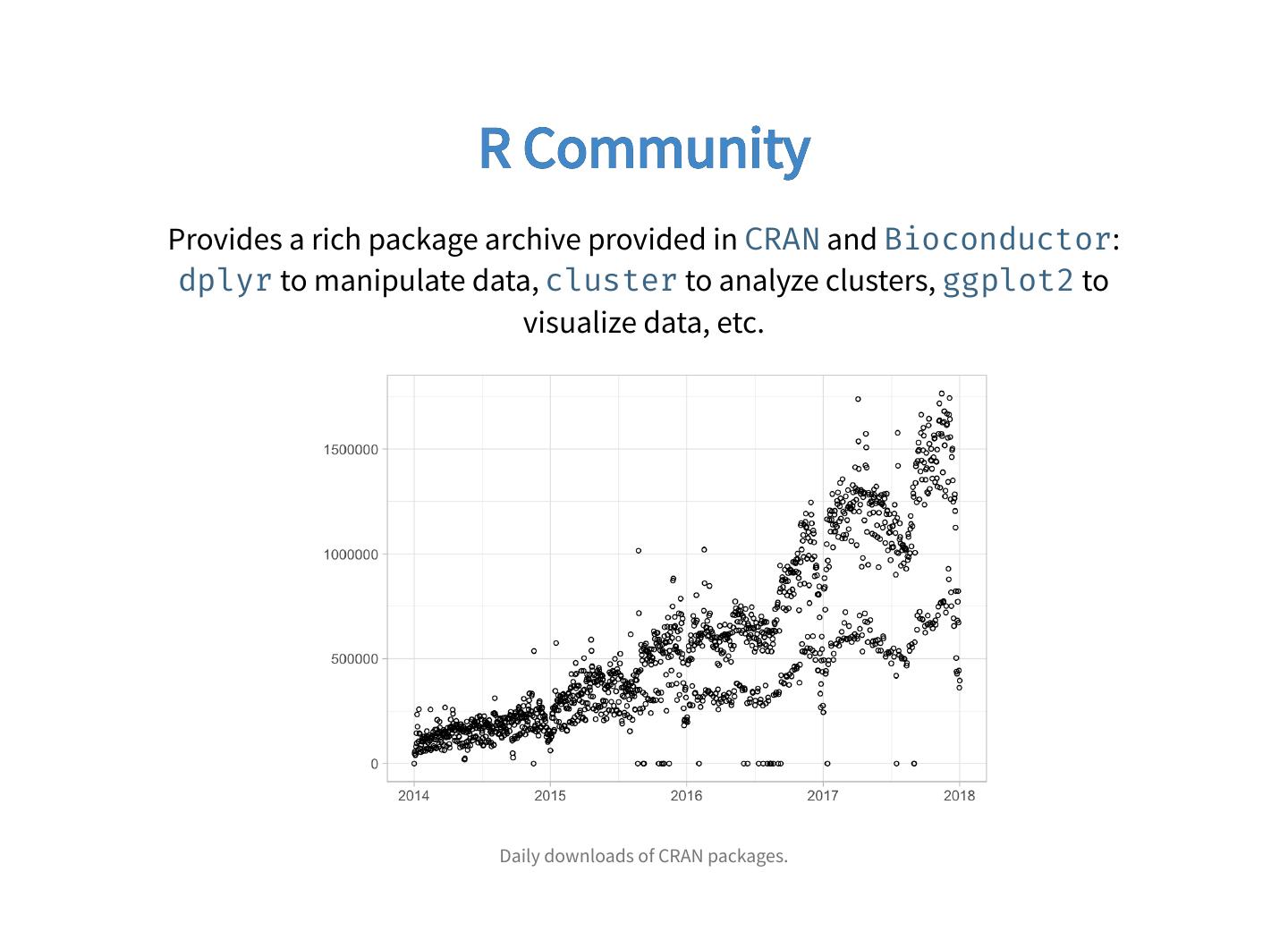
8 . R Community Provides a rich package archive provided in CRAN and Bioconductor: dplyr to manipulate data, cluster to analyze clusters, ggplot2 to visualize data, etc. Daily downloads of CRAN packages.
9 . R Language Language features I would highlighting: 2.1.1 Vectors 2.1.4 Expression objects 2.1.8 Promise objects 2.1.9 Dot-dot-dot 3.1.4 Operators cran.r project.org/doc/manuals/R-lang.html
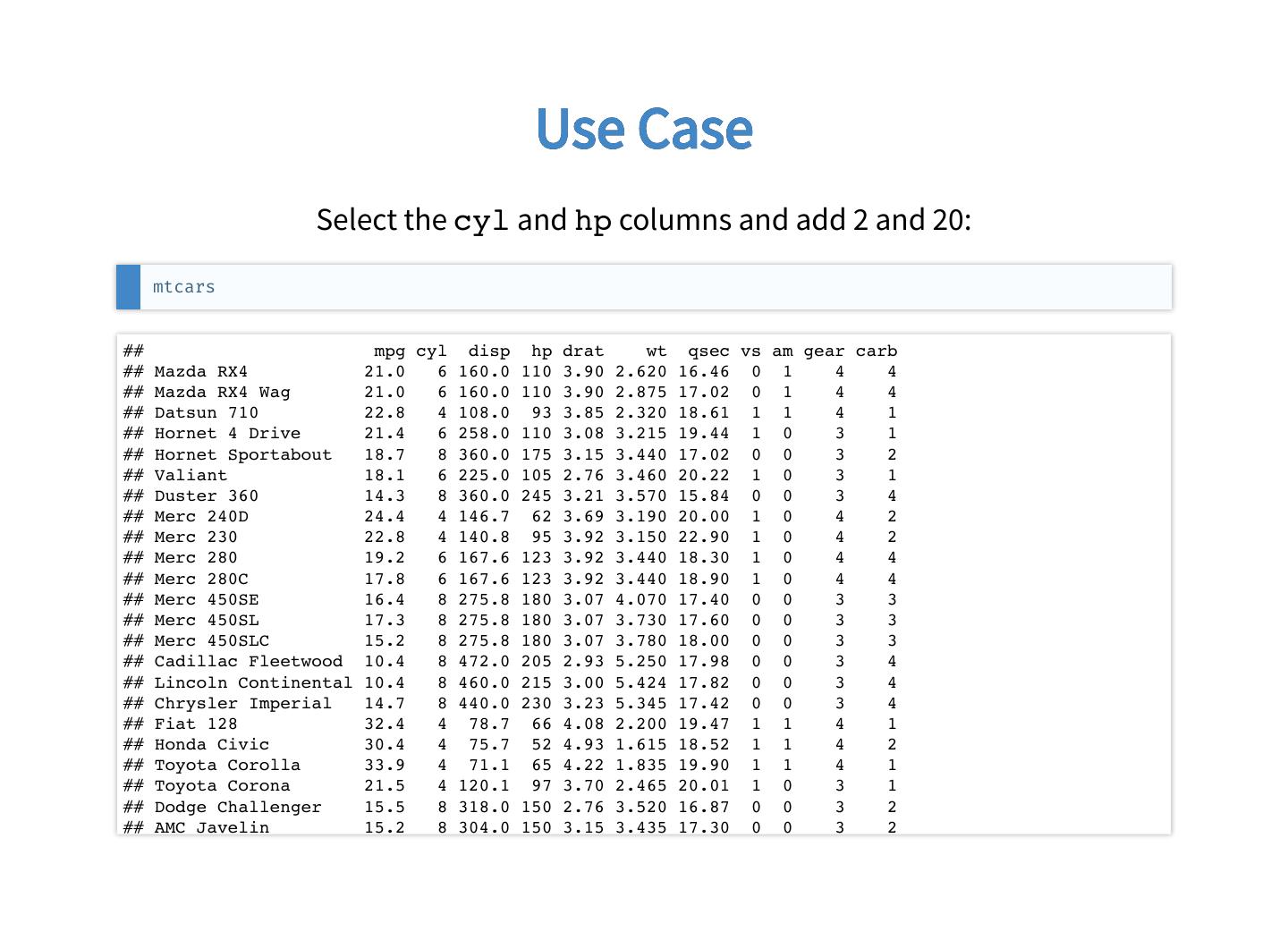
10 . Use Case Select the cyl and hp columns and add 2 and 20: mtcars ## mpg cyl disp hp drat wt qsec vs am gear carb ## Mazda RX4 21.0 6 160.0 110 3.90 2.620 16.46 0 1 4 4 ## Mazda RX4 Wag 21.0 6 160.0 110 3.90 2.875 17.02 0 1 4 4 ## Datsun 710 22.8 4 108.0 93 3.85 2.320 18.61 1 1 4 1 ## Hornet 4 Drive 21.4 6 258.0 110 3.08 3.215 19.44 1 0 3 1 ## Hornet Sportabout 18.7 8 360.0 175 3.15 3.440 17.02 0 0 3 2 ## Valiant 18.1 6 225.0 105 2.76 3.460 20.22 1 0 3 1 ## Duster 360 14.3 8 360.0 245 3.21 3.570 15.84 0 0 3 4 ## Merc 240D 24.4 4 146.7 62 3.69 3.190 20.00 1 0 4 2 ## Merc 230 22.8 4 140.8 95 3.92 3.150 22.90 1 0 4 2 ## Merc 280 19.2 6 167.6 123 3.92 3.440 18.30 1 0 4 4 ## Merc 280C 17.8 6 167.6 123 3.92 3.440 18.90 1 0 4 4 ## Merc 450SE 16.4 8 275.8 180 3.07 4.070 17.40 0 0 3 3 ## Merc 450SL 17.3 8 275.8 180 3.07 3.730 17.60 0 0 3 3 ## Merc 450SLC 15.2 8 275.8 180 3.07 3.780 18.00 0 0 3 3 ## Cadillac Fleetwood 10.4 8 472.0 205 2.93 5.250 17.98 0 0 3 4 ## Lincoln Continental 10.4 8 460.0 215 3.00 5.424 17.82 0 0 3 4 ## Chrysler Imperial 14.7 8 440.0 230 3.23 5.345 17.42 0 0 3 4 ## Fiat 128 32.4 4 78.7 66 4.08 2.200 19.47 1 1 4 1 ## Honda Civic 30.4 4 75.7 52 4.93 1.615 18.52 1 1 4 2 ## Toyota Corolla 33.9 4 71.1 65 4.22 1.835 19.90 1 1 4 1 ## Toyota Corona 21.5 4 120.1 97 3.70 2.465 20.01 1 0 3 1 ## Dodge Challenger 15.5 8 318.0 150 2.76 3.520 16.87 0 0 3 2 ## AMC Javelin 15.2 8 304.0 150 3.15 3.435 17.30 0 0 3 2
11 . How to NOT write R code This is how I would have written R code as a so ware engineer before knowing R: # Select columns subset data = data.frame(mtcars$cyl, mtcars$hp) colnames(data) = c("cyl", "hp") # Transform each row for (idx in 1:nrow(data)) { data$cyl[idx] = data$cyl[idx] + 2 } # One column at a time to use the CPU cache efficiently for (idx in 1:nrow(data)) { data$hp[idx] = data$hp[idx] + 20 }
12 . 2.1.1 Vectors Everything is a vector in R: # Select columns subset data = data.frame(mtcars$cyl, mtcars$hp) colnames(data) = c("cyl", "hp") # Transform each row data$cyl = data$cyl + 2 # One column at a time to use the CPU cache efficiently data$hp = data$hp + 20
13 . 2.1.9 Dot-dot-dot Dynamic parameters using the ... parameter: # Select columns subset data = data.frame(cyl = mtcars$cyl, hp = mtcars$hp) # Transform each row data$cyl = data$cyl + 2 # One column at a time to use the CPU cache efficiently data$hp = data$hp + 20
14 .2.1.4/2.1.8 Expression and Promise objects One can lazily evaluate operations and operate over expressions: # Select columns subset data = select(mtcars, cyl, hp) # Transform each row data = mutate(data, cyl = cyl + 2) # One column at a time to use the CPU cache efficiently data = mutate(data, hp = hp + 20)
15 . 3.1.4 Operators Use <- for assignment, or the newer %>% pipe: data mtcars %>% select(mtcars, cyl, hp) %>% mutate(data, cyl = cyl + 2) %>% mutate(data, hp = hp + 20)
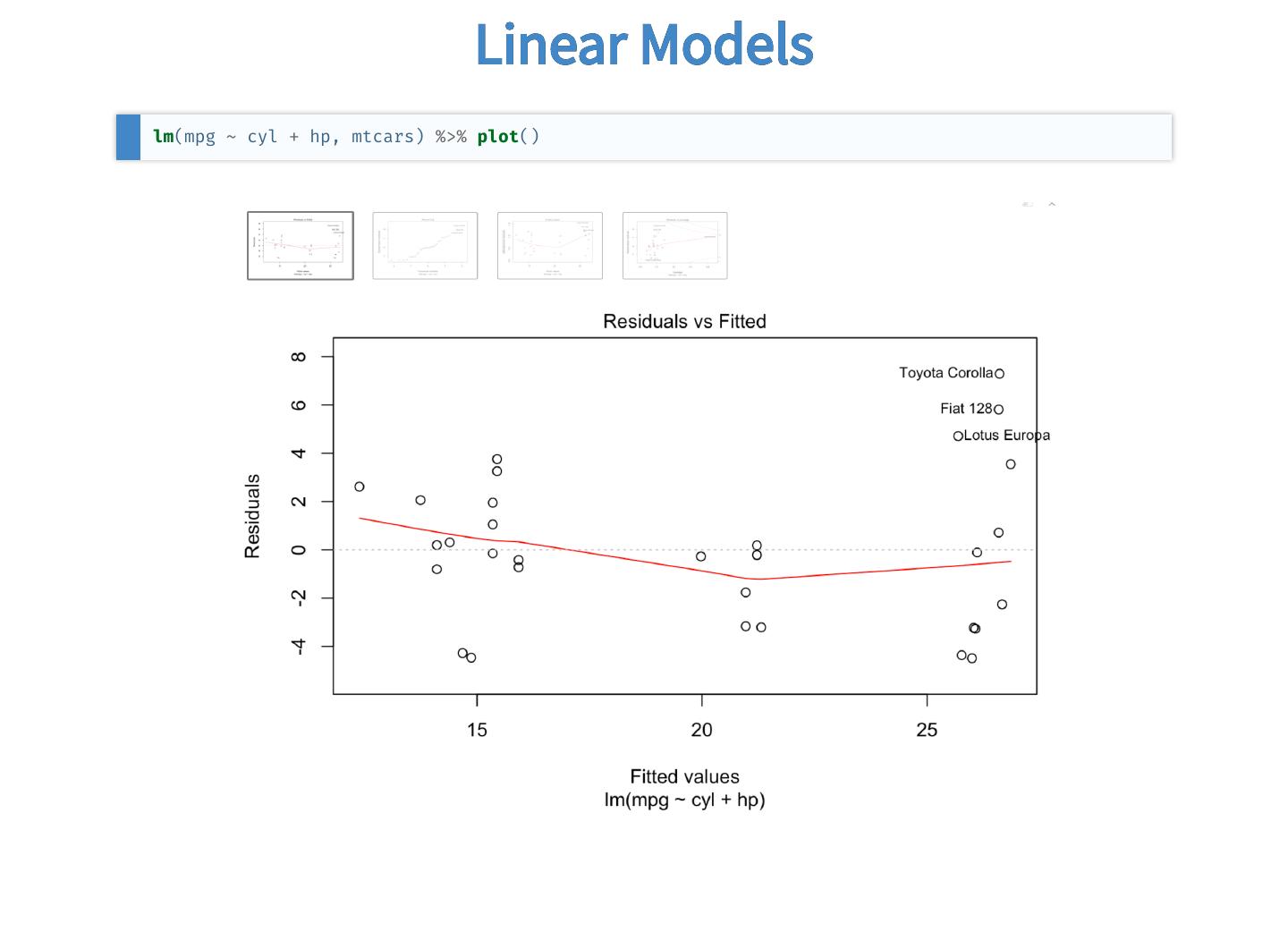
16 . Linear Models lm(mpg ~ cyl + hp, mtcars) %>% plot()
17 .MLflow with R
18 . Principles Parity with Python API. Designed for the R user.
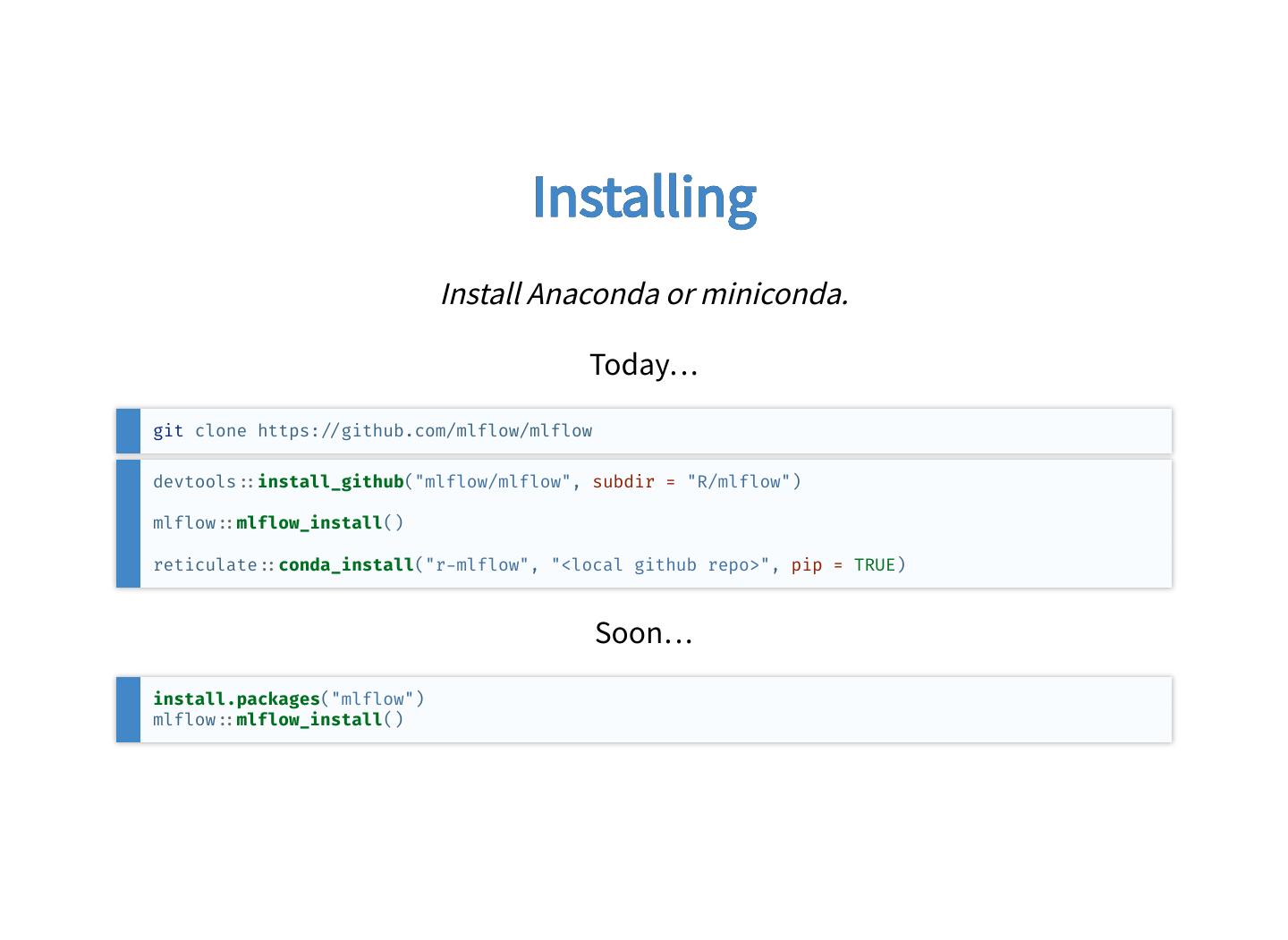
19 . Installing Install Anaconda or miniconda. Today… git clone https: github.com/mlflow/mlflow devtools install_github("mlflow/mlflow", subdir = "R/mlflow") mlflow mlflow_install() reticulate conda_install("r mlflow", "<local github repo>", pip = TRUE) Soon… install.packages("mlflow") mlflow mlflow_install()
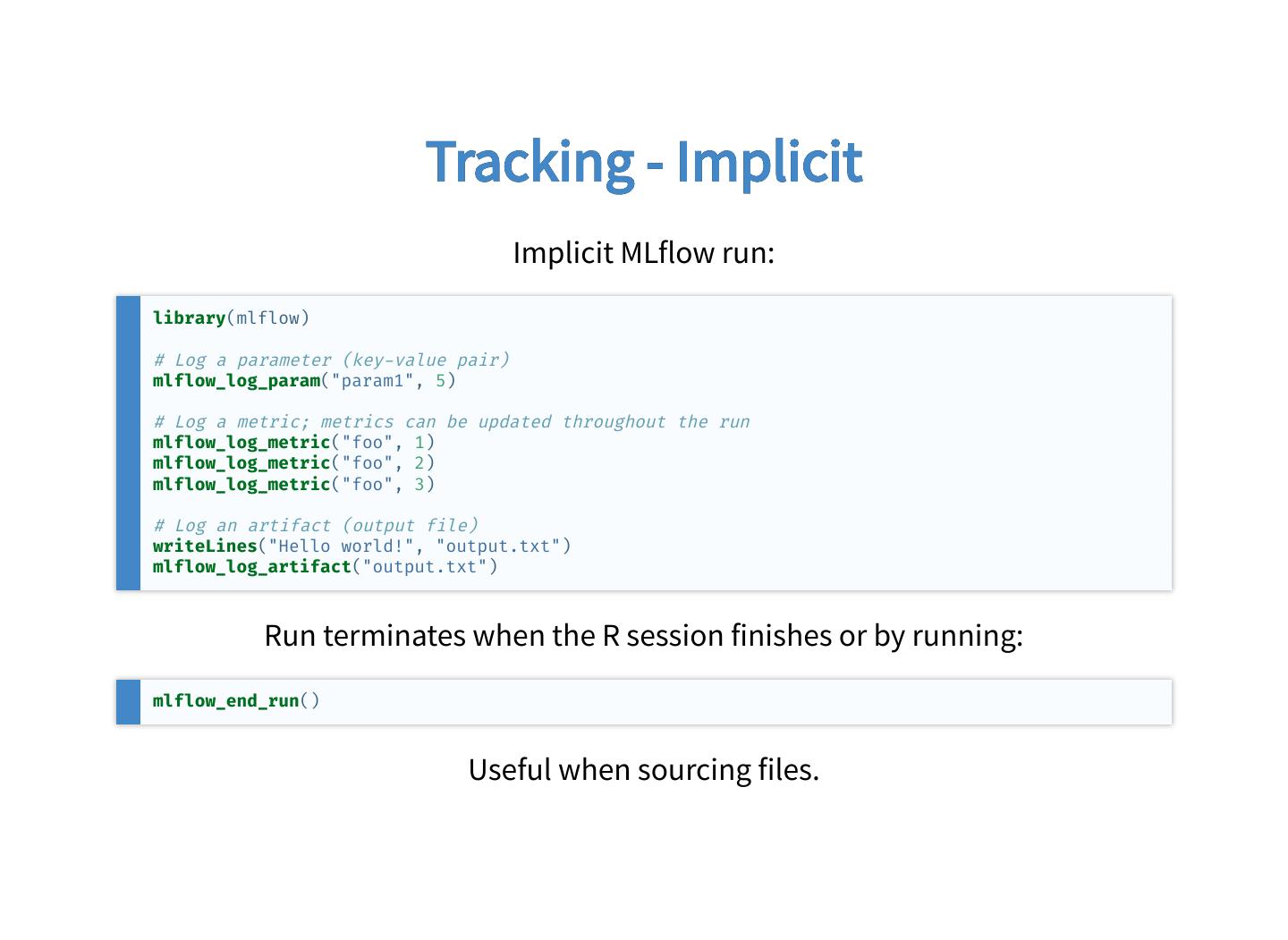
20 . Tracking - Implicit Implicit MLflow run: library(mlflow) # Log a parameter (key value pair) mlflow_log_param("param1", 5) # Log a metric; metrics can be updated throughout the run mlflow_log_metric("foo", 1) mlflow_log_metric("foo", 2) mlflow_log_metric("foo", 3) # Log an artifact (output file) writeLines("Hello world!", "output.txt") mlflow_log_artifact("output.txt") Run terminates when the R session finishes or by running: mlflow_end_run() Useful when sourcing files.
21 . Tracking - Explicit Explicit MLflow run: library(mlflow) with(mlflow_start_run(), { # Log a parameter (key value pair) mlflow_log_param("param1", 5) # Log a metric; metrics can be updated throughout the run mlflow_log_metric("foo", 1) mlflow_log_metric("foo", 2) mlflow_log_metric("foo", 3) # Log an artifact (output file) writeLines("Hello world!", "output.txt") mlflow_log_artifact("output.txt") })
22 . Tracking - Sources mlflow_run("R/tracking.R") Or adding the following to tracking.R in RStudio 1.2: # !source mlflow mlflow_run(entry_point = .file)
23 . Tracking - UI mlflow_ui()
24 . Projects - Snapshots Create dependencies snapshot: mlflow_snapshot() Then restore snapshot: mlflow_restore_snapshot()
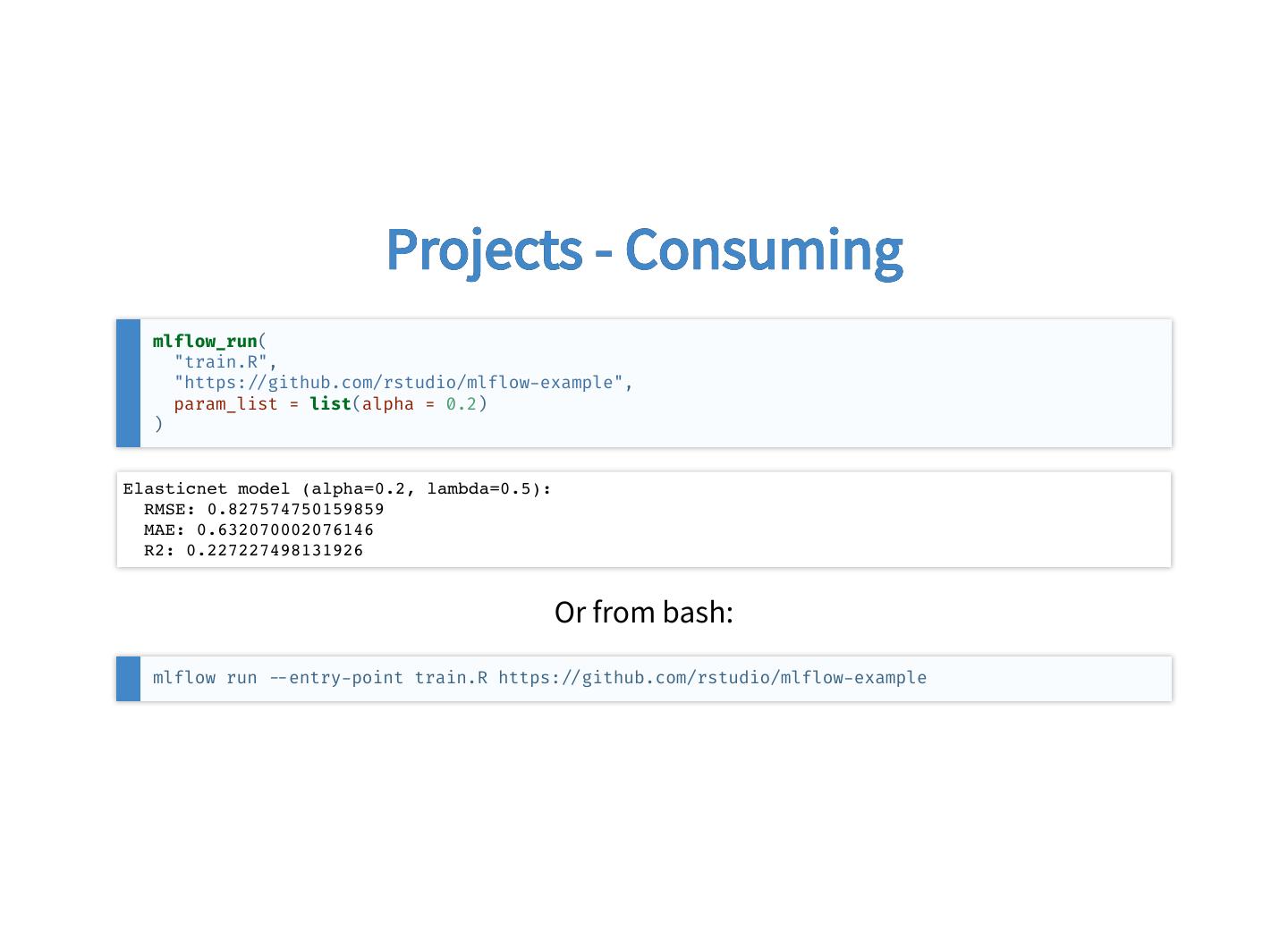
25 . Projects - Consuming mlflow_run( "train.R", "https: github.com/rstudio/mlflow example", param_list = list(alpha = 0.2) ) Elasticnet model (alpha=0.2, lambda=0.5): RMSE: 0.827574750159859 MAE: 0.632070002076146 R2: 0.227227498131926 Or from bash: mlflow run entry point train.R https: github.com/rstudio/mlflow example
26 . Models - Saving mlflow_save_model(model) Generic functions are serialized with crate: column mlflow_log_param("column", 1) model lm( Sepal.Width ~ x, data.frame(Sepal.Width = iris$Sepal.Width, x = iris[,column]) ) mlflow_save_model( crate(~ stats predict(model, .x), model) ) However, mlflow_save_model() can be extended by packages: #' @export mlflow_save_flavor.tensorflow function( ) {} mlflow_load_flavor.tensorflow function( ) {} mlflow_predict_flavor.tensorflow function( ) {}
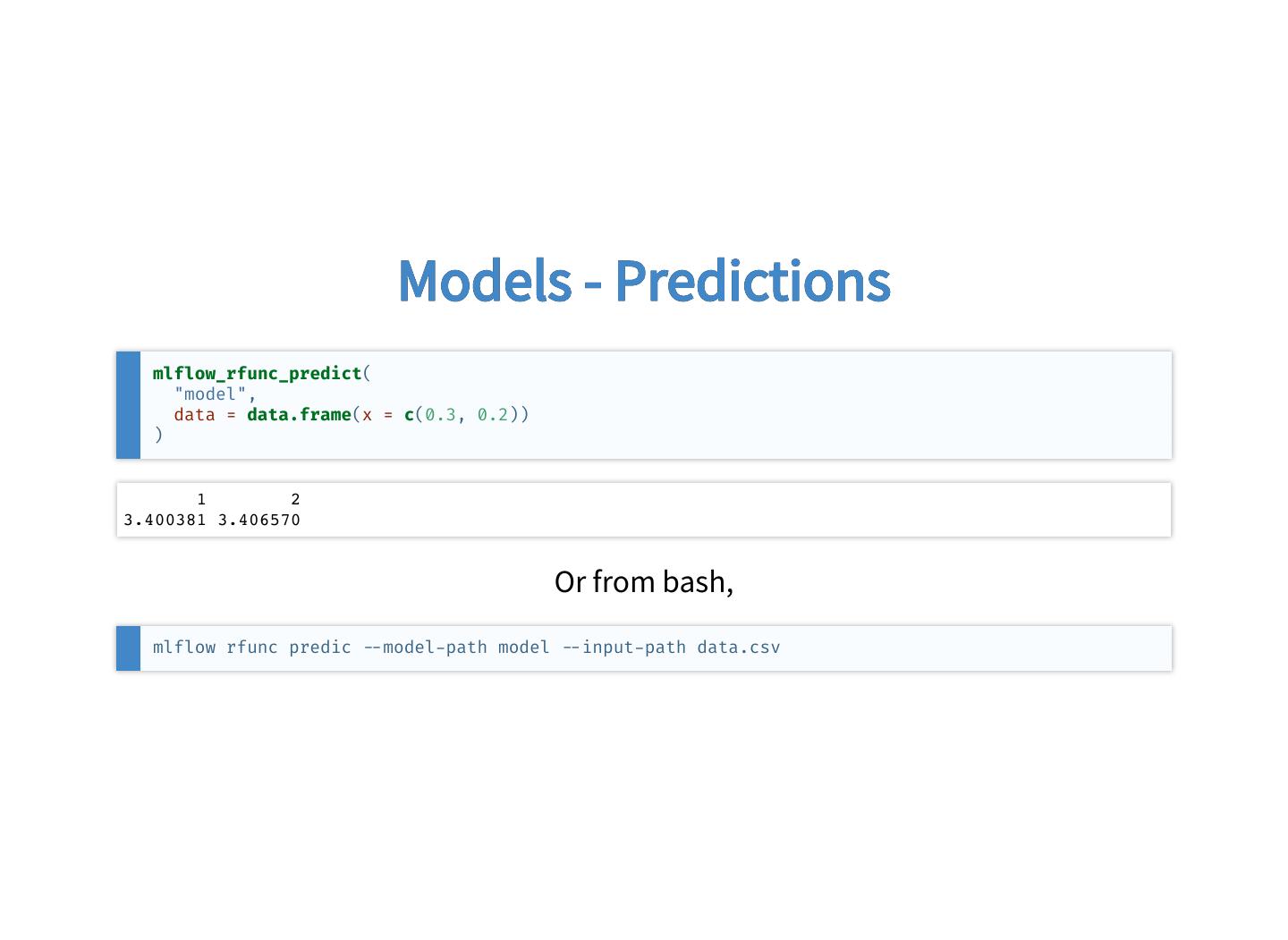
27 . Models - Predictions mlflow_rfunc_predict( "model", data = data.frame(x = c(0.3, 0.2)) ) 1 2 3.400381 3.406570 Or from bash, mlflow rfunc predic model path model input path data.csv
28 . Models - Serving mlflow_rfunc_serve("model") mlflow rfunc serve model path model curl -X POST "http: 127.0.0.1 8090/predict/" -H "accept: application/json" -H "Content-Type: application/json" d '[{"x": [0.3, 0.2]}]'
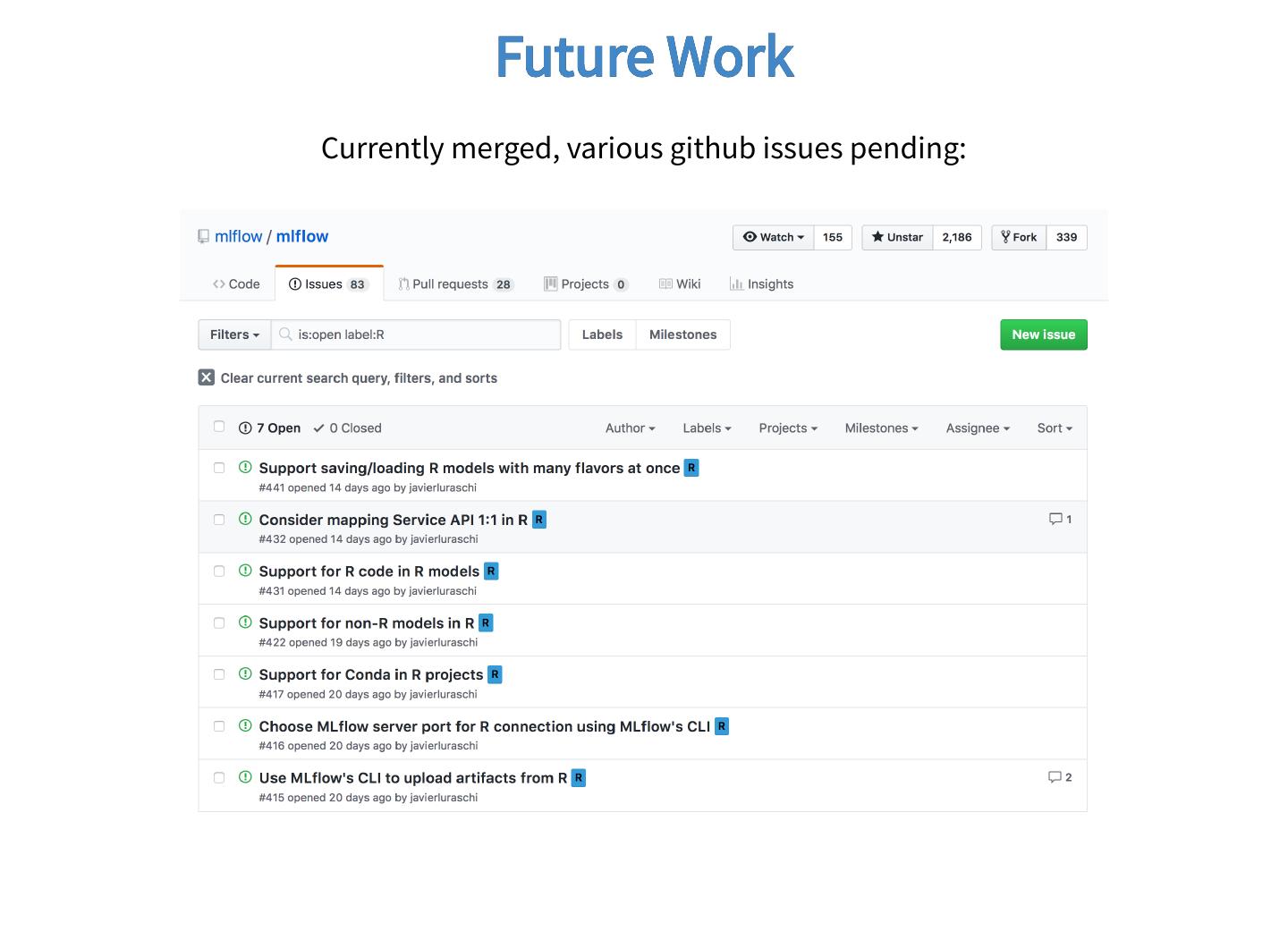
29 . Future Work Currently merged, various github issues pending: